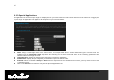
66 Public Port: Specify the public port number. Private Port: Specify the private port number. Schedule: Select a schedule to Always or Never from the drop-down list. If a schedule does not exist, you may create it in the Tools > Schedule section. Inbound Filter: Select an inbound filter from the drop-down list. If an inbound filter does not exist, you may create it from Advanced > Inbound Filter section. Click on the Add button to insert the entry into the Virtual Server list.
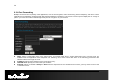
67 6.3.3.Special Applications An application rule is used to open single or multiple ports on your router when the router senses data sent to the Internet on a trigger port or port range. An application rule applies to all computers on your internal network. Name: Assign a meaningful name to the virtual server, for example Web Server. Several well-known types of virtual server are available from the Application Name drop-down list.
68 6.3.4.Port Forwarding Multiple connections are required by some applications, such as internet games, video conferencing, Internet telephony, and others. These applications have difficulties working through NAT (Network Address Translation). This section is used to open multiple ports or a range of ports in your router and redirect data through those ports to a single PC on your network. Name: Assign a meaningful name to the virtual server, for example Web Server.
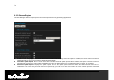
69 Inbound Filter: Select an inbound filter from the drop-down list. If an inbound filter does not exist, you may create it from Advanced > Inbound Filter section. Click on the Add button to insert the entry into the Port Forwarding list.
70 6.3.5.StreamEngine The StreamEngine feature helps improve the network performance by prioritizing applications. Enable Traffic Shaping: Place a check in the box to enable traffic shaping. When this option is enabled, the router restricts the flow of outbound traffic so as not to exceed the WAN uplink bandwidth. Automatic Uplink Speed. Place a check in this box to enable automatic uplink speed.
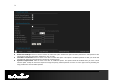
71 associated with your ISP's network. Typically, this figure will be between 87% and 91% of the stated uplink speed for xDSL connections and around 5 kbps lower for cable network connections. Manual Uplink Speed: Specify an uplink speed or select it from the drop-down list. If Automatic Uplink Speed is disabled, this options allows you to set the uplink speed manually. Uplink speed is the speed at which data can be transferred from the router to your ISP.
2 Enable StreamEngine: Place a check in this box to enable this option. Enable this option for better performance and experience with online games and other interactive applications, such as VoIP. Automatic Classification: Place a check in this box to enable this option. This option is enabled by default so that your router will automatically determine which programs should have network priority. Dynamic Fragmentation: Place a check in this box to enable this option.
73 Add StreamEngine Rule: A StreamEngine Rule identifies a specific message flow and assigns a priority to that flow. For most applications, automatic classification will be adequate, and specific StreamEngine Rules will not be required. StreamEngine supports overlaps between rules, where more than one rule can match for a specific message flow. If more than one rule is found to match the rule with the highest priority will be used.
74 6.3.6.Routing This section adds a new entry into the routing table. Name: Specify a name for the rule. Destination IP: Specify the destination IP address. Netmask: Specify the subnet mask for the IP address. Gateway: Specify the IP address of the gateway. Metric: Specify the number of routing hops. The route metric is a value from 1 to 16 that indicates the cost of using this route. A value of 1 is the lowest cost, and 15 is the highest cost.
75 6.3.7.Access Control The Access Control section allows you to control access in and out of devices on your network. Use this feature as Parental Controls to only grant access to approved sites, limit web access based on time or dates, and/or block access from applications such as peer-to-peer utilities or games. When Access Control is disabled, every device on the LAN has unrestricted access to the Internet.
76 Click on the Next button to continue. Specify a policy name and then click on the Next button to continue. Select a schedule from the drop-down list: Always or Never, or you may define a new schedule. Click on the Next button to continue.
77 Select a machine to which the policy applies. Address Type: Select the IP address or MAC address radio button. IP Address: If you selected IP address above, then specify the IP address here. MAC Address: If you need to change the MAC address of the rounter's WAN-side Ethernet interface, either type in an alternate MAC address (for example, the MAC address of the router initially connected to the ISP) or click on Clone Your PCs MAC Address.
78 Select a filtering method: Log Web Access Only: Select this radio but in order to log web access. Block All Access: Select this radio but in order to block all web access. Block Some Access: Select this radio but in order to block some web access. Click on the Save button to store the changes.
79 6.3.8.Web Filter This is a type of parental control feature used to restrict certain websites form being accessed through your network. These filters can be used for securing and restricting your network. Website/URL/Domain: Specify the web address that you would like to filter. Do not use “http://” Click on the Save button to store the changes.
80 6.3.9.MAC Address Filter This feature is used to restrict certain MAC address from accessing the Internet. These filters can be used for securing and restricting your network. Configure MAC Filtering: Select one of the options from the drop-down list. Turn MAC Filtering OFF: When "OFF" is selected, MAC addresses are not used to control network access.
81 6.3.10. Firewall The device provides a tight firewall by virtue of the way NAT works. Unless you configure the router to the contrary, the NAT does not respond to unsolicited incoming requests on any port, thereby making your LAN invisible to Internet cyber attacks. However, some network applications cannot run with a tight firewall. Those applications need to selectively open ports in the firewall to function correctly.
82 TCP / UDP NAT Endpoint Filtering options control how the router's NAT manages incoming connection requests to ports that are already being used. Select one of the radio buttons. End Point Independent Once a LAN-side application has created a connection through a specific port, the NAT will forward any incoming connection requests with the same port to the LAN-side application regardless of their origin.
83 Enable anti-spoof checking: Place a check in this box to enable anti-spoof checking. Enabling this option can provide protection from certain kinds of "spoofing" attacks. However, enble this option with care. With some modems, the WAN connection may be lost when this option is enabled. In that case, it may be necessary to change the LAN subnet to something other than 192.168.0.x (192.168.2.x, for example), to re-establish the WAN connection.
84 Application Layer Gateway (ALG) Configuration: Place a check in appropriate feature boxes to enable them. . Some protocols and applications require special handling of the IP payload to make them work with network address translation (NAT). Each ALG provides special handling for a specific protocol or application. A number of ALGs for common applications are enabled by default. PPTP: Allows multiple machines on the LAN to connect to their corporate networks using PPTP protocol.
85 6.3.11. Inbound Filter When you use the Virtual Server, Port Forwarding, or Remote Administration features to open specific ports to traffic from the Internet, you could be increasing the exposure of your LAN to cyber attacks from the Internet. In these cases, you can use Inbound Filters to limit that exposure by specifying the IP addresses of internet hosts that you trust to access your LAN through the ports that you have opened.
86 Action: Select Allow or Deny from the drop-down list. This will apply the inbound filter rule on the WAN interface. Remote IP Range: Specify the remote IP address range and then click in the check box to enable the range. Click on the Save button to store the changes. 6.3.12. WISH WISH is short for Wireless Intelligent Stream Handling, a technology developed to enhance your experience of using a wireless network by prioritizing the traffic of different applications.
87 HTTP: Place a check in this box to add HTTP as a classifier. This allows the device to recognize HTTP transfers for many common audio and video streams and prioritize them above other traffic. Such streams are frequently used by digital media players. Windows Media Center: Place a check in this box to add HTTP as a classifier.
88 6.3.13. Wi-Fi Protected Setup Wi-Fi Protected Setup is a feature that locks the wireless security settings and prevents the settings from being changed by any new external registrar using its PIN. Devices can still be added to the wireless network using Wi-Fi Protected Setup. Enable: Place a check in this box to enable this feature.
89 6.3.14. Advanced Network (UPNP, WAN Ping…) In this section you can configure the UPNP, WAN Ping, WAN port speed, multicast streams, and PPPoE pass-through settings. Enable UPnP: Place a check in this box to enable UPnP. UPnP stands for Universal Plug and Play, which is a networking architecture that provides compatibility among networking equipment, software, and peripherals. This router has optional UPnP capability, and can work with other UPnP devices and software.
90 Enable Multicast Streams: Place a check in this box to enable multicast streams. The router uses the IGMP protocol to support efficient multicasting -- transmission of identical content, such as multimedia, from a source to a number of recipients. This option must be enabled if any applications on the LAN participate in a multicast group. If you have a multimedia LAN application that is not receiving content as expected, try enabling this option.
91 6.4. Tools Click on the Tools link on the navigation drop-down menu. You will then see seven options: Time, System, Firmware, SysLog, Dynamic DNS, System Check, and Schedules. The configuration steps for each option are described below.
92 6.4.1.Time Zone Setting Click on the Time link in the navigation menu. This feature allows you to configure, update, and maintain the correct time on the device’s internal system clock as well as configure the time zone. The date and time of the device can be configured manually or by synchronizing with a time server. Note: If the device losses power for any reason, it will not be able to keep its time running, and will not display the correct time once the device has been restarted.
93 Enable Daylight Saving: Place a check in this box to enable daylight savings time. Daylight Saving Offset: Select the offset from the drop-down list. Daylight Saving Date: Select the daylight savings date from the drop-down list. Select the starting and ending times for the change to and from daylight saving time. For example, suppose for DST Start you select Month="Oct", Week="3rd", Day="Sun" and Time="2am".
94 6.4.2.1. Save To Local Hard Drive This option allows you to save the current configuration of the device into a file. Click on the Save Configuration button to begin. Save the file on your local disk by using the Save or Save to Disk button in the dialog box. 6.4.2.2. Load From Local Hard Drive This option allows you to restore a backup configuration from a file to the device. Click on the Browse button to select the file and then click on Restore Configuration from a File button.
95 Please wait while the system is rebooting. Note: Do no un-plug the device during this process as this may cause permanent damage. 6.4.2.3. Restore To Factory Default Click on the Restore all Settings to Factory Defaults button. This option restores all configuration settings back to the settings that were in effect at the time when the device was shipped from the factory. Once the dialog box appears, click on the OK button to confirm the action. Note: The current settings will be lost.
96 6.4.2.4. Reboot the device Click on the Reboot the Device button to reboot the device using its current settings. Once the dialog box appears, click on the OK button to confirm the action. Once the dialog box appears, click on the OK button to confirm the action. Note: The current settings will be lost. Click on the OK button to continue. You will then see the Rebooting page. Please wait while the system is rebooting.
97 6.4.3.Firmware Upgrade Click on the Firmware link in the navigation menu. This page allows you to upgrade the firmware of the device in order to improve the functionality and performance. This page also displays the current firmware version and its release date. Ensure that you have downloaded the appropriate firmware from the vendor’s website. Connect the device to your PC using an Ethernet cable, as the firmware cannot be upgraded using the wireless interface.
98 6.4.4.System Logs Logs display a list of events that are triggered on the Ethernet and Wireless interface. This log can be referred when an unknown error occurs on the system or when a report needs to be sent to the technical support department for debugging purposes Enable Logging to a Syslog Server: Place a check in this box to enable syslog logging. Syslog Server IP Address: Specify the IP address of the syslog server. Click on the Apply button once you have modified the settings.
99 6.4.5.Dynamic DNS The Dynamic DNS feature allows you to host a server (Web, FTP, Game Server, etc.) using a domain name that you have purchased with your dynamically assigned IP address. Most broadband Internet Service Providers assign dynamic (changing) IP addresses. When you use a Dynamic DNS service provider, your friends can enter your host name to connect to your server, no matter what your IP address is. Enable Dynamic DNS: Place a check in this box to enable the DDNS feature.
100 6.4.6.System Check Click on the System Check link in the navigation menu. This page allows you to ping a host name or IP address. Host Name or IP address: Specify the host name or IP address and then click on the Ping button.
101 6.4.7.Schedules Click on the Schedules link in the navigation menu. Schedules can be created for use with enforcing rules. For example, if you want to restrict web access to Mon-Fri from 3pm to 8pm, you could create a schedule selecting Mon, Tue, Wed, Thu, and Fri and enter a Start Time of 3pm and End Time of 8pm. Name: Specify a name for the schedule. Day(s): Select the days at which you would like the schedule to be effective.
102 6.5. Status Click on the Status link on the navigation tree menu. You will then see six options: Wireless, Logs, Statistics, WISH Sessions, Routing, and Internet Sessions. The configuration steps for each option are described below.
103 6.5.1.Wireless Status Click on the Wireless link in the navigation menu. The wireless section allows you to view the wireless clients that are connected to the device. MAC Address: The Ethernet ID (MAC address) of the wireless client. IP Address: The LAN-side IP address of the client. Mode: The transmission standard being used by the client. Values are 11a, 11b, 11g, or 11n for 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, or 802.11n respectively.
104 6.5.2.Logs Status Click on the Logs link in the navigation menu. The router automatically logs (records) events of possible interest in its internal memory. If there is not enough internal memory for all events, logs of older events are deleted, but logs of the latest events are retained. The Logs option allows you to view the router logs. You can define what types of events you want to view and the level of events to view.
105 6.5.3.Statistics Click on the Statistics link in the navigation drop-down menu. This page displays the transmitted and received packet statistics of the wired (LAN & WAN) and wireless interface. Click on the Refresh button to refresh the statistics.
106 6.5.4.WISH Session Status Click on the WISH Sessions link in the navigation drop-down menu. The WISH Sessions page displays full details of active local wireless sessions through your router when WISH has been enabled. A WISH session is a conversation between a program or application on a wirelessly connected LAN-side computer and another computer, however connected.
107 CL: Closed -- The connection is no longer active but the session is being tracked in case there are any retransmitted packets still pending. Priority: The priority given to packets sent wirelessly over this conversation by the WISH logic. The priorities are: BK: Background (least urgent). BE: Best Effort. VI: Video. VO: Voice (most urgent). Time Out: The number of seconds of idle time until the router considers the session terminated.
108 6.5.5.
109 6.5.6.Internet Session Status Click on the Internet Sessions link in the navigation drop-down menu. The Internet Sessions page displays full details of active Internet sessions through your router. An Internet session is a conversation between a program or application on a LAN-side computer and a program or application on a WAN-side computer. Local: The IP address and, where appropriate, port number of the local application.
110 300 seconds - UDP connections. 240 seconds - Reset or closed TCP connections. The connection does not close instantly so that lingering packets can pass or the connection can be re-established. 7800 seconds - Established or closing TCP connections.
111 6.5.7.Firewall This page displays the full details about firewall holes in your router -- ports that accept unsolicited messages from the WAN.
112 Appendix A – Glossary 112
8 802.11 A family of specifications for wireless local area networks (WLANs) developed by a working group of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). A Access Control List ACL. This is a database of network devices that are allowed to access resources on the network. Access Point AP. Device that allows wireless clients to connect to it and access the network ActiveX A Microsoft specification for the interaction of software components. Address Resolution Protocol ARP.
ESR9855G Wireless N Gaming Router Application layer 7th Layer of the OSI model. Provides services to applications to ensure that they can communicate properly with other applications on a network. ASCII American Standard Code for Information Interchange. This system of characters is most commonly used for text files Attenuation The loss in strength of digital and analog signals. The loss is greater when the signal is being transmitted over long distances.
ESR9855G Wireless N Gaming Router Bottleneck A time during processes when something causes the process to slowdown or stop all together Broadband A wide band of frequencies available for transmitting data Broadcast Transmitting data in all directions at once Browser A program that allows you to access resources on the web and provides them to you graphically C Cable modem A device that allows you to connect a computer up to a coaxial cable and receive Internet access from your Cable provider CardBus A new
ESR9855G Wireless N Gaming Router Data-Link layer The second layer of the OSI model.
ESR9855G Wireless N Gaming Router Domain Name System: Translates Domain Names to IP addresses Domain name A name that is associated with an IP address Download To send a request from one computer to another and have the file transmitted back to the requesting computer DSL Digital Subscriber Line.
ESR9855G Wireless N Gaming Router A computer on a network that stores data so that the other computers on the network can all access it File sharing Allowing data from computers on a network to be accessed by other computers on the network with different levels of access rights Firewall A device that protects resources of the Local Area Network from unauthorized users outside of the local network Firmware Programming that is inserted into a hardware device that tells it how to function Fragmentation Breaki
ESR9855G Wireless N Gaming Router Data cannot be transmitted and received at the same time Hashing Transforming a string of characters into a shorter string with a predefined length Hexadecimal Characters 0-9 and A-F Hop The action of data packets being transmitted from one router to another Host Computer on a network HTTP Hypertext Transfer Protocol is used to transfer files from HTTP servers (web servers) to HTTP clients (web browsers) HTTPS HTTP over SSL is used to encrypt and decrypt HTTP transmissions
ESR9855G Wireless N Gaming Router A system of worldwide networks which use TCP/IP to allow for resources to be accessed from computers around the world Internet Explorer A World Wide Web browser created and provided by Microsoft Internet Protocol The method of transferring data from one computer to another on the Internet Internet Protocol Security IPsec provides security at the packet processing layer of network communication Internet Service Provider An ISP provides access to the Internet to individuals
ESR9855G Wireless N Gaming Router Kilobits per second Kbyte Kilobyte L L2TP Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol LAN Local Area Network Latency The amount of time that it takes a packet to get from the one point to another on a network. Also referred to as delay LED Light Emitting Diode Legacy Older devices or technology Local Area Network A group of computers in a building that usually access files from a server LPR/LPD "Line Printer Requestor"/"Line Printer Daemon".
ESR9855G Wireless N Gaming Router Management Information Base is a set of objects that can be managed by using SNMP Modem A device that Modulates digital signals from a computer to an analog signal in order to transmit the signal over phone lines.
ESR9855G Wireless N Gaming Router O OFDM Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing is the modulation technique for both 802.11a and 802.
ESR9855G Wireless N Gaming Router PPTP Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol is used for creating VPN tunnels over the Internet between two networks Preamble Used to synchronize communication timing between devices on a network Q QoS Quality of Service R RADIUS Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service allows for remote users to dial into a central server and be authenticated in order to access resources on a network Reboot To restart a computer and reload it's operating software or firmware from nonvolatil
ESR9855G Wireless N Gaming Router S Server A computer on a network that provides services and resources to other computers on the network Session key An encryption and decryption key that is generated for every communication session between two computers Session layer The fifth layer of the OSI model which coordinates the connection and communication between applications on both ends Simple Mail Transfer Protocol Used for sending and receiving email Simple Network Management Protocol Governs the management
ESR9855G Wireless N Gaming Router Determines what portion of an IP address designates the Network and which part designates the Host Syslog System Logger -- a distributed logging interface for collecting in one place the logs from different sources. Originally written for UNIX, it is now available for other operating systems, including Windows. T TCP Transmission Control Protocol TCP Raw A TCP/IP protocol for transmitting streams of printer data.
ESR9855G Wireless N Gaming Router Universal Plug and Play URL Uniform Resource Locator is a unique address for files accessible on the Internet USB Universal Serial Bus UTP Unshielded Twisted Pair V Virtual Private Network VPN: A secure tunnel over the Internet to connect remote offices or users to their company's network VLAN Virtual LAN Voice over IP Sending voice information over the Internet as opposed to the PSTN VoIP Voice over IP W Wake on LAN Allows you to power up a computer though it's Network
ESR9855G Wireless N Gaming Router Wired Equivalent Privacy is security for wireless networks that is supposed to be comparable to that of a wired network Wide Area Network The larger network that your LAN is connected to, which may be the Internet itself, or a regional or corporate network Wi-Fi Wireless Fidelity Wi-Fi Protected Access An updated version of security for wireless networks that provides authentication as well as encryption Wireless ISP A company that provides a broadband Internet connection
ESR9855G Wireless N Gaming Router Appendix C – FCC Interference Statement Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation.