User's Manual
1.3.2.6.1 RMS CCA Detailed Theory
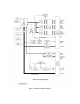
Battery-backed DC power 1_+48V and 2_+48V enter via connector P2-25 and P2-26, diode-OR’D by
diodes CR13 and CR14, and fused by F2. This voltage is further regulated to +5V by DC-DC converter
U39, diode CR15, and inductor L3. Over-voltage protection for the +5V is provided by SCR Q5, zener
diodes CR19 and CR20, capacitor C115, and resistor R65. The +5V supply is further regulated by linear
regulator U40 to create DVCC (+3.3V). The +5V is measurable at TP14 while DVCC is available at TP7.
The DVCC and +5V supplies power the U8 microcontroller and its peripherals. The U8 microcontroller
acts as a DC-DC converter to create +1.2V (measurable at TP3) for powering its core (VDDINT) by pulse-
width-modulating U8-4/5 and using transistor Q1, diode CR2, and inductor L1. Diode CR1 insures proper
power supply sequencing during power-up/down.
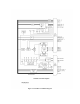
The U8 microcontroller utilizes 512Kx16 of flash ROM (U1 and U2) for non-volatile program storage as
well as 32Kx8 non-volatile RAM (U3) for variable storage. Oscillator Y2 provides the system clock for U8
as well as UARTs U16, U22, and U28 after buffering by U17. The system clock can be measured at test
point TP1.
Data buffers U33/U34 and address buffers U35/U36 are decoded by AND gates U47:B, U47:C, and U47:D
to activate the buffers only during a valid asynchronous memory select cycle. Resistor networks RN5
through RN9 act as pull-ups on these buffered bus lines. Only the bus lines between U8 and the 16Mx16
SDRAM (U4) are not buffered in some form. The U4 SDRAM is used for program and variable storage
and has very fast access/refresh times.
The U8 microcontroller has direct control of the CPU_OK LED (CR5) by utilizing output PF8 (U8-36) and
transistor Q2. The ~TEST signal, from the LCU via connector P2-B8, also can light the CR5 LED when
active. Zener diode CR17 limits the maximum voltage while resistor R11 limits the maximum current of
the CR5 LED.
Buffer U37 is used to buffer address lines A17, A18, and A19, control signals ~AOE and ~AWE, as well as
the serial peripheral interface (SPI). The SCK, MISO, and MOSI SPI signals (U8-53, U8-54, and U8-55)
along with ~SPI_CS0 (U8-49) are used in conjunction with the SPI Boot header J4 for in-factory
programming of flash ROM. Latch U7 and inverter U10 combine to create the SPI chip select signals
~SPI_CS1 through ~SPI_CS8 for communications to off-board serial SPI devices through connector P2-A8
through P2-A16.
Real-time clock (RTC) U15 is clocked by oscillator U9 and battery-backed up by battery B1 if header JP1
is strapped between JP1-2 and JP1-3. The 512 Hertz heartbeat of RTC U15 can be measured at test point
TP13. Oscillator U9 is a highly accurate temperature-compensated crystal oscillator (TCXO) whose
accuracy eliminates the need for a potentiometer or adjustable capacitor.
Emulator header J3 is used for in-factory testing and development only.
The ~MRESET signal from the LCU enters via connector P2-B16 and is filtered by inductor FL1 and
capacitor C39 to create reset signal ~EXT_RES. Signal ~EXT_RES is bi-directional in that either the LCU
or the RMS can cause the signal to be active and reset the entire DME system.
When the LCU pulls ~MRESET (and subsequently ~EXT_RES) low, voltage supervisor / watchdog input
U6-1 is low; causing output U6-7 to go low which resets the U8 microcontroller and on-board latch U7
immediately. UARTs U16, U22, and U28 as well as USB host U38 will also be immediately reset by the
RESET output of inverter U17:A. Latch U29 will be reset after being delayed by inverters U45:A, U45:B,
resistor R13, capacitor C114, and diode CR16.
The RMS can initiate a system reset by activating ARM_SYS_RES (U29-9) and stopping the periodic
strobing of voltage supervisor / watchdog input U6-6. A reset from U6-7 will occur approximately one
second after the last watchdog strobe; causing inverter U17:A, transistors Q4/Q3 and ~EXT_RES to