User's Manual
27
Date Code 20170317 Instruction Manual SEL-FT50/SEL-FR12 Fault Transmitter and Receiver System
Appendix B: Two Branch Application
Appendix B: Two Branch Application
Two Branch
Application
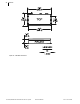
This application has two three-phase branches, A and B, as shown in
Figure 22. Branch B has a fuse and uses a fuse-blowing scheme, while
Branch A does not. When a fault occurs on Branch A, the recloser operates to
clear the fault. In traditional protection schemes, those without the
SEL-FT50/SEL-FR12 system, the time-inverse overcurrent curves of the
SEL-651R recloser control are set above the fuse-clearing curve, resulting in
longer tripping times for faults on Branch A. Use the SEL-FT50/SEL-FR12
system to improve this protection scheme.
Figure 22 SEL-FT50/SEL-FR12 System Protection Scheme
Insert a set of three SEL-FT50 Fault Transmitters on each branch, one per
phase. The SEL-FR12 connects to the SEL-651R with an SEL-C272 serial
cable. In this example, the load current of Branch A is 200 A, and the load
current of Branch B is 100 A. The 51 element pickup of the SEL-651R is set
above 200 percent of the load current. In this example, the fuse size is 140 T,
the SEL-651R 51 element pickup is 550 A, and the settings from Table 11
apply.
This settings example uses Network ID = 3, and the fault current pickup
threshold is set above the load current and below the pickup.
The Network ID of the SEL-FR12 matches the Network ID of the SEL-FT50
Fault Transmitters. Table 12 assumes that the distances of the SEL-FT50 Fault
Transmitters are farther than 300 m (1000 ft).
See Table 13 for the settings of
the SEL-651R and Table 14 for the SEL-651R transmit M
IRRORED BITS
settings.
R
SEL-FR12
SEL-651R-2
SEL-FT50
SEL-FT50
1
2
3
4
5
6
A
B
Table 11 Settings for the SEL-FT50 Fault Transmitters
SEL-FT50 Branch
Unit ID
Control (DIP)
Switch Positions
Network ID
Control (DIP)
Switch Positions
Pickup
Threshold
Control (DIP)
Switch Positions
1 A 1—(0000) 3—(0010) 400 A—(011)
2 A 2—(0001) 3—(0010) 400 A—(011)
3 A 3—(0010) 3—(0010) 400 A—(011)
4 B 4—(0011) 3—(0010) 200 A—(010)
5 B 5—(0100) 3—(0010) 200 A—(010)
6 B 6—(0101) 3—(0010) 200 A—(010)