User manual
Table Of Contents
- NOTE: All page numbers are hyperlinks.
- Press Ctrl + - to go back.
- 870 USE 101 00 Version 3.0
- Contents
- Overview of TSX Momentum M1 Processor Adapters
- Overview of TSX Momentum Option Adapters
- Assembling TSX Momentum Components
- Assembling a CPU
- Overview
- Assembling a Processor Adapter and I/O Base
- Disassembling a Processor Adapter from an I/O Base
- Assembling a CPU with an Option Adapter
- Overview
- Assembling a Processor Adapter and an Option Adapter
- Mounting the Assembled Adapters on the I/O Base
- Disassembling a Module with an Option Adapter
- Installing Batteries in an Option Adapter
- Installation Guidelines
- Labeling the CPU
- Guidelines for Labeling the CPU
- Using the Modbus Ports
- Modbus Port 1
- Overview
- Modbus Port 1
- Cable Accessories for Modbus Port 1
- Pinouts for Modbus Port 1
- Modbus Port 2
- Overview
- Modbus Port 2
- Four-Wire Cabling Schemes for Modbus RS485 Networks
- Two-Wire Cabling Schemes for Modbus RS485 Networks
- Cable for Modbus RS485 Networks
- Connectors for Modbus RS485 Networks
- Terminating Devices for Modbus RS485 Networks
- Pinouts for Modbus RS485 Networks
- Using the Ethernet Port
- Using the I/OBus Port
- Using the Modbus Plus Ports
- Configuring an M1 CPU with Modsoft
- Configuring the Processor Adapter
- Overview
- Selecting an M1 Processor Adapter
- Specifying an M1 Processor Type
- Default Configuration Parameters
- Changing the Range of Discrete and Register References
- Changing the Size of Your Application Logic Space
- Changing the Number of Segments
- Changing the Size of the I/O Map
- Establishing Configuration Extension Memory
- Configuring Option Adapter Features
- Overview
- Reserving and Monitoring a Battery Coil
- Setting up the Time-of-Day Clock
- Setting the Time
- Reading the Time-of-Day Clock
- Modifying Communication Port Parameters
- Overview
- Accessing the Port Editor Screen
- Parameters Which Should Not Be Changed
- Changing the Mode and Data Bits
- Changing Parity
- Changing the Baud Rate
- Changing the Modbus Address
- Changing the Delay
- Changing the Protocol on Modbus Port 2
- I/O Mapping the Local I/O Points
- Accessing and Editing the I/O Map
- I/O Mapping an I/OBus Network with Modsoft
- Configuring a Modbus Plus Network in Modsoft with Peer Cop
- Getting Started
- Overview
- Accessing the Peer Cop Configuration Extension Screen
- The Default Peer Cop Screen
- Using Modbus Plus to Handle I/O
- Overview
- Devices on the Network
- Defining the Link and Accessing a Node
- Confirming the Peer Cop Summary Information
- Specifying References for Input Data
- Accessing the Remaining Devices
- Completing the I/O Device Configuration in Peer Cop
- Passing Supervisory Data over Modbus Plus
- Overview
- Devices on the Network
- Configuring a Node to Exchange Data
- Confirming the Peer Cop Summary Information
- Specifying References for Input and Output Data
- Defining the References for the Next Node
- Defining References for the Supervisory Computer
- Completing the Configuration
- Saving to Flash in Modsoft
- Configuring an M1 CPU with Concept
- Configuring the Processor Adapter
- Overview
- Selecting an M1 Processor Adapter
- Default Configuration Parameters
- Changing the Range of Discrete and Register References
- Changing the Size of the Full Logic Area
- Understanding the Number of Segments
- Changing the Size of the I/O Map
- Establishing Configuration Extension Memory for Peer Cop
- Configuring Option Adapter Features
- Overview
- Reserving and Monitoring a Battery Coil
- Setting up the Time-of-Day Clock
- Setting the Time
- Reading the Time-of-Day Clock
- Modifying Modbus Port Parameters
- Overview
- Accessing the Modbus Port Settings Dialog Box
- Changing the Baud Rate
- Changing Mode and Data Bits
- Stop Bit Should Not Be Changed
- Changing Parity
- Changing the Delay
- Changing the Modbus Address
- Changing the Protocol on Modbus Port 2
- Configuring Ethernet Address Parameters and I/O Scanning
- Overview
- Accessing the Ethernet / I/O Scanner Screen
- Ethernet Configuration Options
- Setting Ethernet Address Parameters
- Configuring I/O
- Completing the I/O Configuration
- I/O Mapping the Local I/O Points
- Accessing and Editing the I/O Map
- I/O Mapping an I/OBus Network with Concept
- Configuring a Modbus Plus Network in Concept with Peer Cop
- Getting Started
- Overview
- Accessing the Peer Cop Dialog Box
- Adjusting the Amount of Extension Memory
- Other Default Settings in the Peer Cop Dialog Box
- Using Modbus Plus to Handle I/O
- Overview
- Devices on the Network
- Changing the Peer Cop Summary Information
- Specifying References for Input Data
- Specifying References for Output Data
- Passing Supervisory Data over Modbus Plus
- Overview
- Devices on the Network
- Specifying References for Input and Output Data
- Defining the References for the Next Node
- Defining References for the Supervisory PLC
- Saving to Flash with Concept
- Ladder Logic Elements and Instructions
- Run LED Flash Patterns and Error Codes
- Index
Option Adapters
72
870 USE 101 00 V.3
Front Panel Components, Continued
MB+ ACT Flash
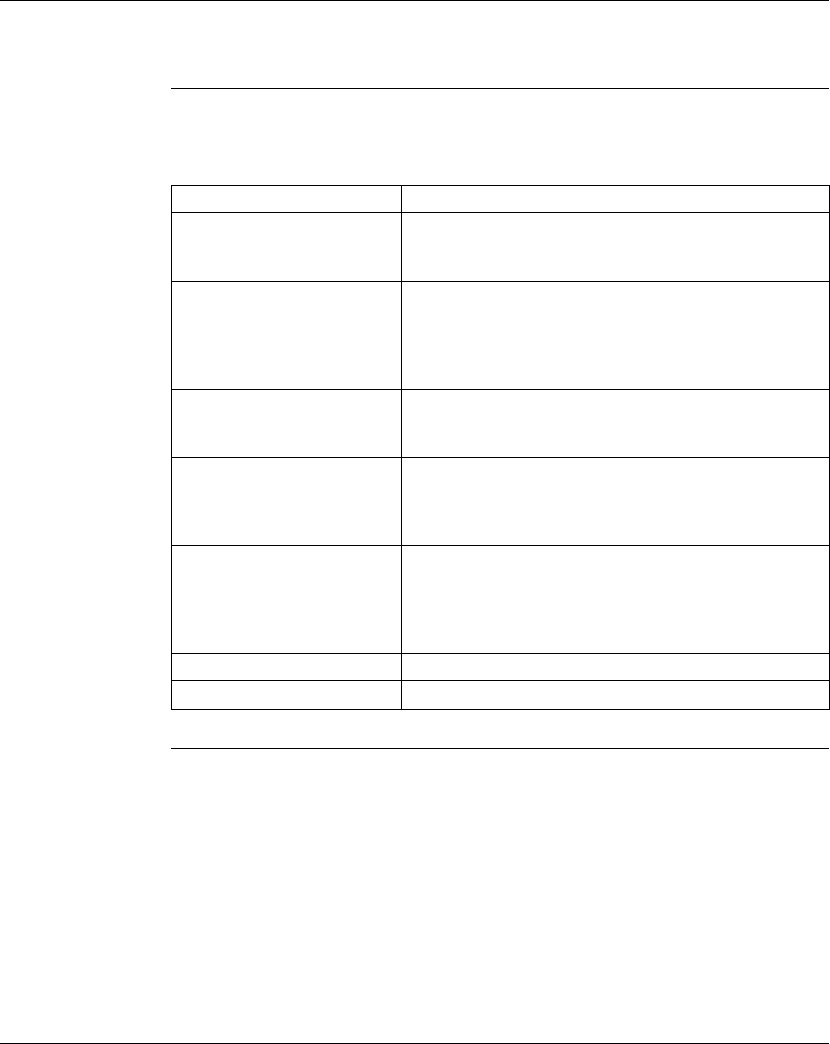
Patterns
This table provides the patterns that the MB+ ACT indicator will flash to indicate the
status of the Modbus Plus node.
Continued on next page
Pattern Meaning
6 flashes/s This is the normal operating state for the node. It is
receiving and passing the network token. All nodes on a
healthy network flash this pattern.
1 flash/s The node is offline just after power-up or after exiting the
6 flashes/s mode. In this state, the node monitors the
network and builds a table of active nodes. After being in
this state for 5s, the node attempts to go to its normal
operating state, indicated by 6 flashes/s.
2 flashes, then OFF for 2s The node detects the token being passed among the other
nodes, but never receives the token. Check the network for
an open circuit or defective termination.
3 flashes, then OFF for 1.7s The node is not detecting any tokens being passed among
the other nodes. It periodically claims the token but cannot
find another node to which to pass it. Check the network for
an open circuit or defective termination.
4 flashes, then OFF for 1.4s The node has detected a valid message from a node using
a network address identical to its own address. The node
remains in this state for as long as it continues to detect the
duplicate address. If the duplicate address is not detected
for 5s, the node changes to its 1flash/s mode.
ON Indicates an invalid node address.
OFF Possible fault with Modbus Plus Option Adapter.










