Installation guide
Introducing the Modbus Plus Network
890 USE 100 00
27
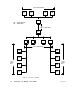
1.10.2 A Peer Cop Example
Figure 14 shows a network with three nodes that are handling Peer
Cop data transfers. Other nodes are also present elsewhere on the
network.
GLOBAL OUT:
NODE
5
NODE
7
NODE
2
GLOBAL IN FROM 2:
4001740048 (32)
GLOBAL IN FROM 18:
30010 (1)
1009710129 (2)
4020040202 (3)
SPECIFIC OUT TO 5:
SPECIFIC OUT TO 7:
SPECIFIC IN FROM 2:
SPECIFIC IN FROM 10:
SPECIFIC IN FROM 2:
1001710048 (2)
1001710048 (2)
1001710048 (2)
4010040131 (32)
1020110216 (2)
TOKEN PASS (TO NODE 3)
TOKEN
MONITOR
TOKEN
MONITOR
Figure 14 Peer Cop Example
Node 2 currently holds the token and passes it to the next addressed
node (node 3). Nodes 5 and 7 monitor the pass and extract data as they
have been configured to do.
Node 2 transmits two words of Specific Output for node 5 from its
references 10017 ... 10048 (32 bits of discrete reference data, a total of
two 16-bit words). It also transmits these same references as Specific
Output for node 7. In the token frame, node 2 transmits 32 words of
Global Output from its references 40017 ... 40048.
Node 5 has been configured to receive Global Input from node 2. It
places one word into its reference 30010, and two words (32 discretes)
into references 10097 ... 10129. Node 5 indexes into the 32 words of
data and maps its 3 words into these references. Node 5 has also been
configured to receive Specific Input from node 2, and places it into
references 10017 ... 10048. Note that the application uses identical
references for this data in nodes 2 and 5. The references could have
been different if required.