Installation guide
Introducing the Modbus Plus Network
890 USE 100 00
7
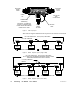
1.3 Overview of the Logical Network
Network nodes are identified by addresses assigned by the user. Each
node’s address is independent of its physical site location. Addresses
are within the range of 1 to 64 decimal, and do not have to be
sequential. Duplicate addresses are not allowed.
Network nodes function as peer members of a logical ring, gaining
access to the network upon receipt of a token frame. The token is a
grouping of bits that is passed in a rotating address sequence from one
node to another. Each network maintains its own token rotation
sequence independently of the other networks. Where multiple
networks are joined by bridges, the token is not passed through the
bridge device.
While holding the token, a node initiates message transactions with
other nodes. Each message contains routing fields that define its
source and destination, including its routing path through bridges to a
node on a remote network.
When passing the token, a node can write into a global database that is
broadcast to all nodes on the network. Global data is transmitted as a
field within the token frame. Other nodes monitor the token pass and
can extract the global data if they have been programmed to do so. Use
of the global database allows rapid updating of alarms, setpoints, and
other data. Each network maintains its own global database, as the
token is not passed through a bridge to another network.