Installation guide
108 Estimating Network Performance
890 USE 100 00
3.22 Guidelines for Multiple Networks
If your application’s data rate requirements are not met between nodes
on a single network, consider the use of bridges to join smaller
networks. The grouping of nodes on each network requires
determination of which nodes must communicate at high data rates
with other nodes. Time-critical control data should be handled between
nodes on the same network. Bridging should be used for less critical
tasks like data acquisition, load-record-verify operations, and remote
programming.
Modbus Plus networks that are joined by bridges will have separate
token rotations. When a message passes through a bridge to another
network, the other network’s token rotation time will be a factor in
communication timing. In general, messages sent through bridges will
take longer to complete than messages sent between nodes on a single
network. Note also that global data is not passed through bridges.
Peer Cop and Distributed I/O data is transacted on a single network
only. It does not pass through bridges. Bridges are not applicable to
networks employing Peer Cop data transfers, nor to networks in DIO
applications.
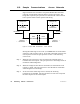
3.22.1 Bridge Communication Paths
Figure 42 shows the structure of communication paths within a bridge.
It illustrates the amount of paths that are available in each direction.