Installation guide
Estimating Network Performance
890 USE 100 00
93
Addresses below the drop-out
This general formula is used to calculate the NDOL for each node with
an address lower than that of the lowest drop-out node. This time is
abbreviated NDOL
(L)
, where
(L)
is the address of any remaining node.
NDOL
(L)
= 80 + 4(lowest node address) + (qty of nodes remaining 1)
+ 5(quantity of nodes dropped 1)
Addresses above the drop-out
This general formula is used to calculate the NDOL for each node with
an address higher than that of the lowest drop-out node. This time is
abbreviated NDOL
(H)
, where
(H)
is the address of any remaining node.
NDOL
(H)
= NDOL
(L)
+ (one token rotation time)
The resulting times for both NDOL
(L)
and NDOL
(H)
are in ms.
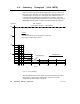
Figure 39 summarizes the use of the two NDOL formulas.
MODBUS PLUS NETWORK
CPU
2 3 7 9 10 12
CPU CPU CPU CPU CPU
NDOL
(L)
= 80 + 4(lowest node address) + (qty of nodes remaining 1) + 5(qty of nodes dropped 1)
NDOL
(H)
= NDOL
(L)
+ (one token rotation time)
NODE
DROPS OUT
NDOL
(L)
NDOL
(H)
Figure 39 Predicting Node Dropout Latency Time