Quick Start Owner's manual
Table Of Contents
- 1756-QS001E-EN-P, Logix5000 Controllers Quick Start
- Summary of Changes
- Table of Contents
- 1 - Program and Test a Simple Project
- What You Need
- Before You Begin
- Follow These Steps
- Create a Project for the Controller
- Add Your I/O Modules
- Look at Your I/O Data
- Ladder Logic
- Enter a Function Block Diagram
- Assign Alias Tags for Your Devices
- Establish a Serial Connection to the Controller
- Download a Project to the Controller
- Select the Operating Mode of the Controller
- 2 - Organize a Project
- 3 - Program Add-On Instructions
- What You Need
- Follow These Steps
- Insert an Add-On Instruction
- Copy an Add-On Instruction Definition
- Import an Add-On Instruction Definition
- Access a Parameter That Is Not Visible
- Monitor or Change the Value of a Parameter of an Add-On Instruction
- View the Logic of an Add-On Instruction
- Edit and Monitor an Add-On Instruction
- Update an Add-On Instruction to a Newer Revision
- 4 - Program an Equipment Phase
- 5 - Program a Project Offline
- 6 - Document a Project
- 7 - Go Online to the Controller
- 8 - Program a Project Online
- 9 - Troubleshoot the Controller
- Index
- Back Cover
40 Publication 1756-QS001E-EN-P - October 2009
Chapter 2 Organize a Project
Create User-defined Data Types
User-defined data types let you organize your data to match your machine or process. This streamlines
program development and creates self-documenting code that is easier to maintain.
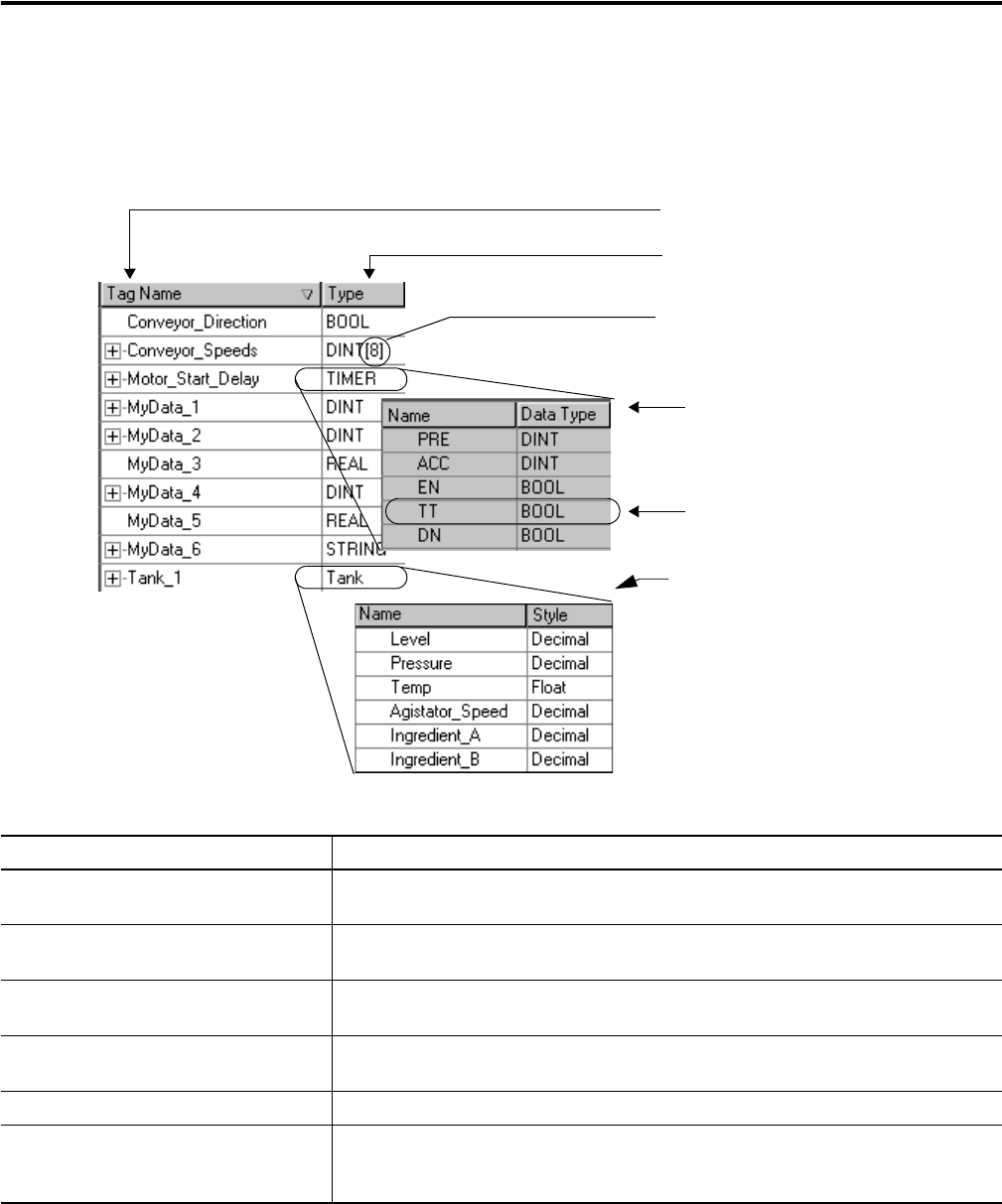
Item Description
A Tag stores data. There is no fixed data table or numeric format for data addresses. The tag
name is the address. You create the tags that you want to use.
B Data type defines the type of data that a tag stores, such as a bit, integer, floating-point
value, or string.
C Array defines a block of data (file). The entire block uses the same data type. It can have 1,
2, or 3 dimensions.
D Structure combines a group of data types into a re-usable format (template for tags). Use a
structure as the basis for multiple tags with the same data layout.
E Member describes an individual piece of data within a structure.
F User-defined data type defines your own data structure. A user-defined data type stores all
the data related to a specific aspect of your system. This keeps related data together and
easy to locate, regardless of its data type.
A
D
F
E
C
B










