User Manual Owner's manual
Table Of Contents
- Important User Information
- Preface
- Table of Contents
- About the Interface
- Overview
- Important Interface Considerations
- About the Interface
- Interface Features
- What the Interface Does
- Hardware/Software Compatibility
- Use of the Common Industrial Protocol (CIP)
- Understand the Producer/ Consumer Model
- Specify the Requested Packet Interval (RPI)
- Support of Data Connections
- Chapter Summary
- Install a Guardmaster EtherNet/IP Network Interface
- Configure the Interface for Your EtherNet/ IP Network
- Automation Controller Communications
- Troubleshoot the Interface
- EtherNet/IP Network Interface Specifications
- Interface Web Dialogs
- Configure the RSLinx Ethernet Communication Driver
- Tag Definitions
22 Rockwell Automation Publication 440R-UM009B-EN-P - February 2014
Chapter 3 Configure the Interface for Your EtherNet/IP Network
Subnet Mask
The subnet mask is used for splitting IP networks into a series of subgroups, or
subnets. The mask is a binary pattern that is matched up with the IP address to
turn part of the Host ID address field into a field for subnets
.
Two bits of the Class B host ID are used to extend the network ID. Each unique
combination of bits in the part of the Host ID where subnet mask bits are 1
specifies a different physical network.
The new configuration is:
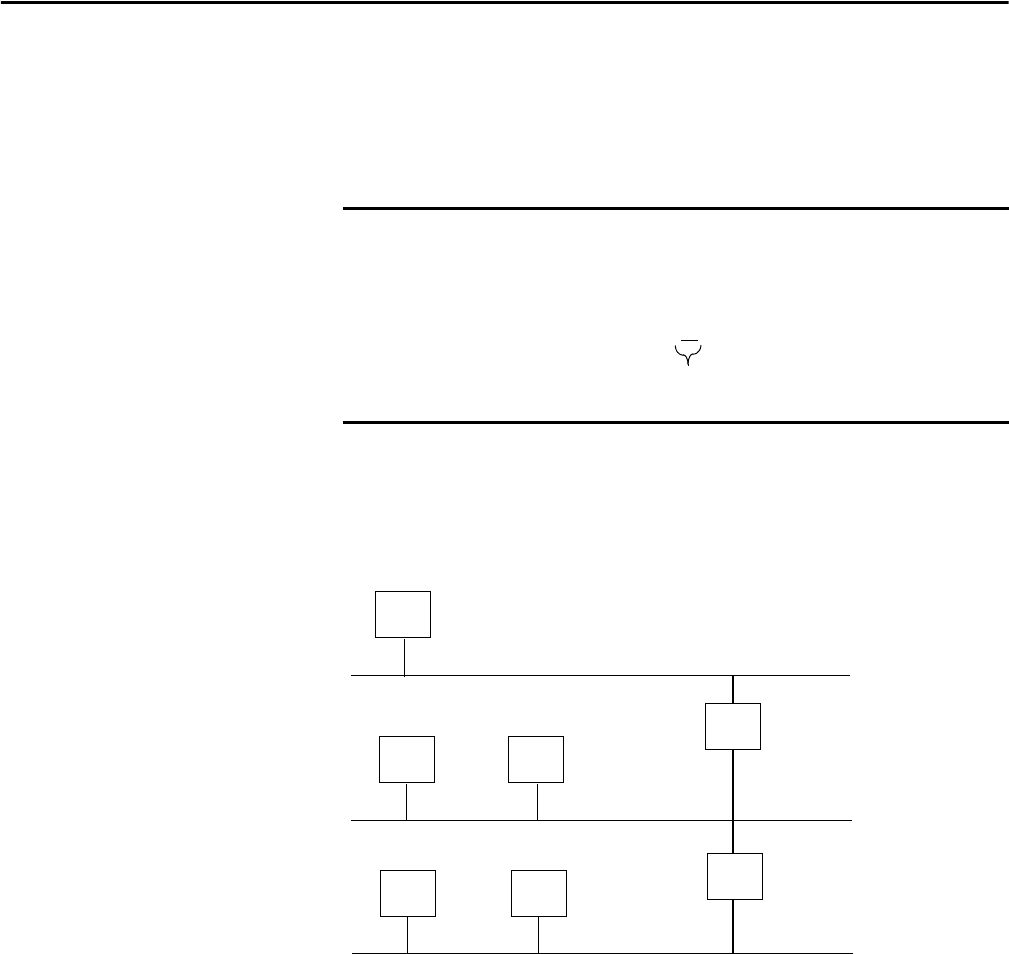
A second network with Hosts D and E was added. Gateway G2 connects
Network 2.1 with Network 2.2.
Hosts D and E will use Gateway G2 to communicate with hosts not on
Network 2.2.
Hosts B and C will use Gateway G to communicate with hosts not on
Network 2.1.
When B is communicating with D, G (the configured Gateway for B) will route
the data from B to D through G2.
EXAMPLE
Take Network 2 (a Class B network) in the previous
example and add another physical network. Selecting the
following subnet mask would add two additional
network ID bits, allowing for four physical networks:
11111111 11111111 11
000000 00000000 = 255.255.192.0
These two bits of the Host ID are used to extend the
netdwork ID.
Network 1
Network 2.1
Network 2.2
A
BC
DE
128.1.0.2
128.1.0.1
128.2.64.3
128.2.128.2
128.2.64.1 128.2.64.2
128.2.128.3
128.2.128.1
G2
G










