Owner manual
Table Of Contents
- 1794-UM066A-EN-P FLEX I/O Dual Port EtherNet/IP Adapter Modules User Manual
- Important User Information
- Preface
- Table of Contents
- 1 - Overview of FLEX I/O and Your Redundant EtherNet/IP Adapter Module
- Overview
- The FLEX I/O System
- Adapter Features
- Types of Adapters
- Hardware and Software Compatibility
- What the Adapter Does
- Use of the Control and Information Protocol (CIP)
- Understanding the Producer/Consumer Model
- Specifying the Requested Packet Interval (RPI)
- Support of Rack Optimized and Direct Connections
- Chapter Summary
- 2 - Install Your FLEX I/O Adapter
- 3 - Configure the Adapter for Your EtherNet/IP Network
- 4 - Rack Optimized Discrete I/O
- 5 - Analog I/O with Direct Connection
- A - Interpret Status Indicators
- B - Specifications
- C - Configure the RSLinx Ethernet Communication Driver
- D - Adapter Web Dialogs
- Index
- Back Cover
Publication 1794-UM066A-EN-P - February 2012
16 Configure the Adapter for Your EtherNet/IP Network
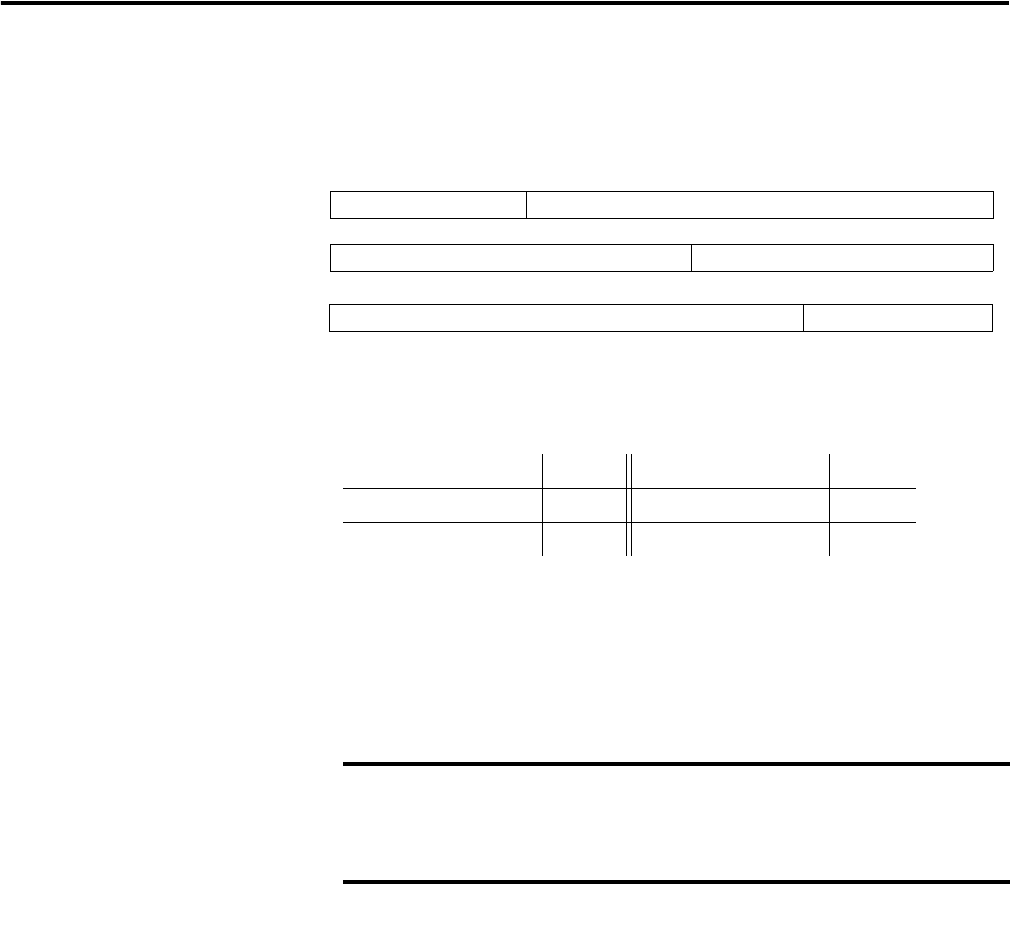
The IP address is 32 bits long and has a Net ID part and a Host ID part.
Networks are classified A, B, C, (or other). The class of the network determines
how an IP address is formatted.
You can distinguish the class of the IP address from the first integer in its
dotted-decimal IP address as follows:
Each node on the same physical network must have an IP address of the same
class and must have the same Net ID. Each node on the same network must have
a different Host ID thus giving it a unique IP address.
IP addresses are written as four decimal integers (0-255) separated by periods
where each integer gives the value of one byte of the IP address.
Gateway Address
The Gateway Address is the default address of a network. It provides a single
domain name and point of entry to the site. Gateways connect individual physical
networks into a system of networks. When a node needs to communicate with a
node on another network, a gateway transfers the data between the two
Class A
Class B
Class C
Net ID
Net ID
Net ID
Host ID
Host ID
Host ID
0
0
0
1 0
1 1 0
8
9
16
24
17
31
31
31
25
0
Range of first integer Class Range of first integer Class
0…127 A 192…223 C
128…191 B 224…255 other
EXAMPLE
For example, the 32-bit IP address:
10000000 00000001 00000000 00000001 is written as
128.1.0.1.
TIP
Contact your network administrator or the Network Information
Center for a unique fixed IP address to assign to your module.










