Installation Guide Manual
Rockwell Automation Publication CNET-IN001C-EN-P - October 2011 29
Topology and Signal Considerations Chapter 2
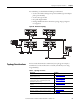
For redundancy, you should do the following on each channel:
• Use the same number and types of repeater assemblies (repeater adapters
plus repeater modules)
• Use the same type of cable
• Keep cable lengths similar
• If using redundant media in a linear bus topology, ring topologies are
not supported.
Figure 10 - Redundant Topology
Topology Considerations
For best results, determine the constraints of your topology. For example, a
maximum of 99 nodes are allowed on a network (98 nodes if you are using
ring redundancy).
31420-M
Table 4 - Topology constraints
Constraint Example
Only one path is allowed between nodes (non-ring
repeater modules only)
See Figure 7 on page 23.
In series topology, maximum of 20 repeaters in a series
In ring topology, up to 20 1786-RPFRL/B or 1786-
RPFRXL/B modules per ring
See Figure 5 on page 21
See Figure 8 on page 24
Constraint of each coax segment (taps and trunk-cable
sections)
See Figure 11 on page 30.
Constraint of each fiber segment application See page 31.
Power loss budget of each fiber segment See Table 5 on page 33
.
Maximum propagation delay through the network See page 39
.