User manual
Calculating Program Timing
Chapter 9
9-11
File Instructions
The instruction timing for file instructions depends on the data type,
number of files acted on per scan, number of elements acted on per scan,
and whether the instruction converts data between integer and floating
point formats.
Table 9.O shows PLC-5/10, -5/12, -5/15, and -5/25 processors. When you
use these tables, keep these guidelines in mind:
for integer to floating point conversion, add:
8
µs for each element address
10
µs for each file address (# prefix)
for floating point to integer conversion add:
33
µs for each element address
44
µs for each file address (# prefix)
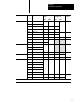
Table 9.O
Timing
and Memory Requirements for File Instructions
Category Code Title
Time
(
µs)
Integer
True
Time (µs)
Floating point
True
Time (µs)
Integer or
Floating Point
False
Words of
Memory
1
File Arithmetic and Logic FAL add
98 + W[36.7 + N] 98 + W[95.1 + N] 54 712
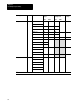
subtract
multiply 98 + W[42.5 + N] 98 + W[101.2 + N]
divide 98 + W[51.1 + N] 98 + W[180.3 + N]
square root 98 + W[84.7 + N] 98 + W[220.5 + N]
54 610
negate 98 + W[29.2 + N] 98 + W[37.2 + N]
clear 98 + W[18.4 + N] 98 + W[24.0 + N] 54 58
move 98 + W[27.3 + N] 98 + W[36.2 + N]
54 610
convert to BCD 98 + W[54.3 + N]
convert from BCD 98 + W[45.4 + N]
AND 98 + W[37.2 + N]
54 712
OR 98 + W[37.2 + N]
XOR 98 + W[37.2 + N]
NOT 98 + W[28.2 + N]
54 610
File Search and Compare FSC all comparisons 93 + W[32.7 +N] 93 + W[43.3 +N]
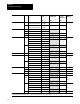
W =
number of elements acted on per scan
N =
2 x (number of integer file addresses) + 8 x (number of floatingpoint file addresses) + 6 x (number of timer
, counter
, or control
file addresses) + ( number of conversions between integer and floating point formats)
1
Use
the smaller number if all addresses are below word 4096; use the larger number if all addresses are above 4096.