Manual
Programming
Chapter 3
32
Qualifier: Use:
TO to
specify the destination of the data transfer
. Y
ou must use T
O when using
either command and it must be followed an address (which must include a
data table address and can include a remote node address). You can
abbreviate as T
.
FROM
to specify where you want to transfer data from. You can use FROM with either com
mand, but if omitted, you must replace it with an integer constant. FROM is always
followed by an address (which must include a data table address and can include a
remote node address). You can abbreviate as F.
NOSTATUS only
with a TMOVE command designed to transfer data to some remote
node. Use when error reporting is not necessary and you want to eliminate
the time spent receiving information about the success or failure of the
command (see the TMOVE Command section for usage). You can
abbreviate as N.
You can specify an integer constant in a MOVE or TMOVE command in
place of the FROM qualifier and its associated address. The correct
format for an integer constant is:
#digit
Where digit is either the integer 0 or 1. You can use integer constants only
when moving bits.
You enter the commands and qualifiers in a command line to create a
PLC–3 message instruction. The following is an example of a typical
command line containing a command and qualifiers:
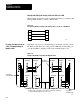
MOVE FROM 1:50$B222:2 TO $B111:1, 1000
Figure 3.1 shows an example message instruction display of the data from
the command above.
Figure 3.1
Example
of a Message Instruction Display
MSG
MESSAGE TYPE 1
CTL=FB010:0000= XXX
CH:E2.9.1
MOVE FROM 1:50$B222:2
TO $B111:1,1000
( EN )
STAT
( DN )
STAT
( ER )
STAT
12
15
13
I0:10
02
11013-I