User Manual Owner's manual
Table Of Contents
- 1772-6.5.8, Mini-PLC-2/02, -2/16, -2/17 Processor, User Manual
- Important User Information
- Summary of Changes
- Table of Contents
- 1 - Using This Manual
- 2 - Fundamentals of a Programmable Controller
- 3 - Hardware Features
- 4 - Installing Your Programmable Controller
- 5 - Starting Your Processor
- 6 - Maintaining and Troubleshooting Your Processor
- 7 - Memory Organization
- 8 - Scan Theory
- 9 - Relay-Like Instructions
- 10 - Program Control Instructions
- 11 - Timers and Counters
- 12 - Data Manipulation and Compare Instructions
- 13 - Three-Digit Math Instructions
- 14 - EAF Math Instructions
- 15 - EAF Log, Trig, and FIFO Instructions
- 16 - EAF Process Control Instructions
- 17 - Jump Instructions and Subroutines
- 18 - Block Transfer
- 19 - Data Transfer Instructions
- 20 - Bit Shift Registers
- 21 - Sequencers
- 22 - Selectable Timer Interrupts
- 23 - Report Generation
- 24 - Program Editing
- 25 - Programming Techniques
- 26 - Program Troubleshooting
- A - Specifications
- B - Processor Comparison Chart
- C - Number Systems
- D - Glossary
- E - Quick Reference
- Index
- Back Cover
Starting Your Processor
Chapter 5
5-12
Assigning I/O Rack Numbers
When you select 1-slot addressing, each slot is an I/O group. You still
assign one I/O rack number to eight I/O groups; therefore, in a 16-slot I/O
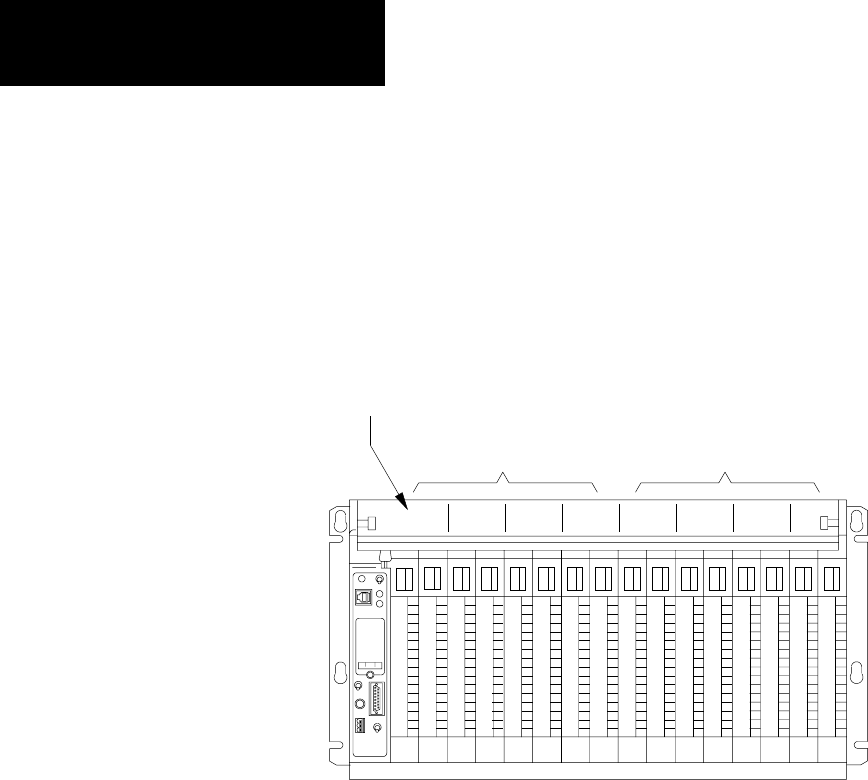
chassis you now have two I/O racks (Figure 5.9).
Figure 5.9
Assigning
I/O Rack Numbers with 1Slot Addressing
01 23 45 67 01 23 45 67
13077
I/O group number
1771A4B I/O chassis using 1slot addressing.
assigned
I/O rack number 1
assigned
I/O rack number 2
In Figure 5.3, we showed how the 5-digit input or output instruction is
associated with a particular I/O module terminal. With two I/O racks you
use the instruction address to identify which rack you are
communicating with.
Figure 5.10 illustrates addressing two modules, each in the same I/O group
number but in different assigned racks of a single I/O chassis.