User Manual Owner's manual
Table Of Contents
- 1772-6.5.8, Mini-PLC-2/02, -2/16, -2/17 Processor, User Manual
- Important User Information
- Summary of Changes
- Table of Contents
- 1 - Using This Manual
- 2 - Fundamentals of a Programmable Controller
- 3 - Hardware Features
- 4 - Installing Your Programmable Controller
- 5 - Starting Your Processor
- 6 - Maintaining and Troubleshooting Your Processor
- 7 - Memory Organization
- 8 - Scan Theory
- 9 - Relay-Like Instructions
- 10 - Program Control Instructions
- 11 - Timers and Counters
- 12 - Data Manipulation and Compare Instructions
- 13 - Three-Digit Math Instructions
- 14 - EAF Math Instructions
- 15 - EAF Log, Trig, and FIFO Instructions
- 16 - EAF Process Control Instructions
- 17 - Jump Instructions and Subroutines
- 18 - Block Transfer
- 19 - Data Transfer Instructions
- 20 - Bit Shift Registers
- 21 - Sequencers
- 22 - Selectable Timer Interrupts
- 23 - Report Generation
- 24 - Program Editing
- 25 - Programming Techniques
- 26 - Program Troubleshooting
- A - Specifications
- B - Processor Comparison Chart
- C - Number Systems
- D - Glossary
- E - Quick Reference
- Index
- Back Cover
Appendix
C
C-1
Number Systems
This appendix describes the four numbering systems the processor uses:
decimal
octal
binary
hexadecimal
These numbering systems differ by their number sets and place values.
Timers, counters and math operations word values use the decimal
numbering system. This is a numbering system made up of ten digits: the
numbers 0 through 9 (Table C.A). All decimal numbers are composed of
these digits. The value of a decimal number depends on the digits used
and the place value of each digit.
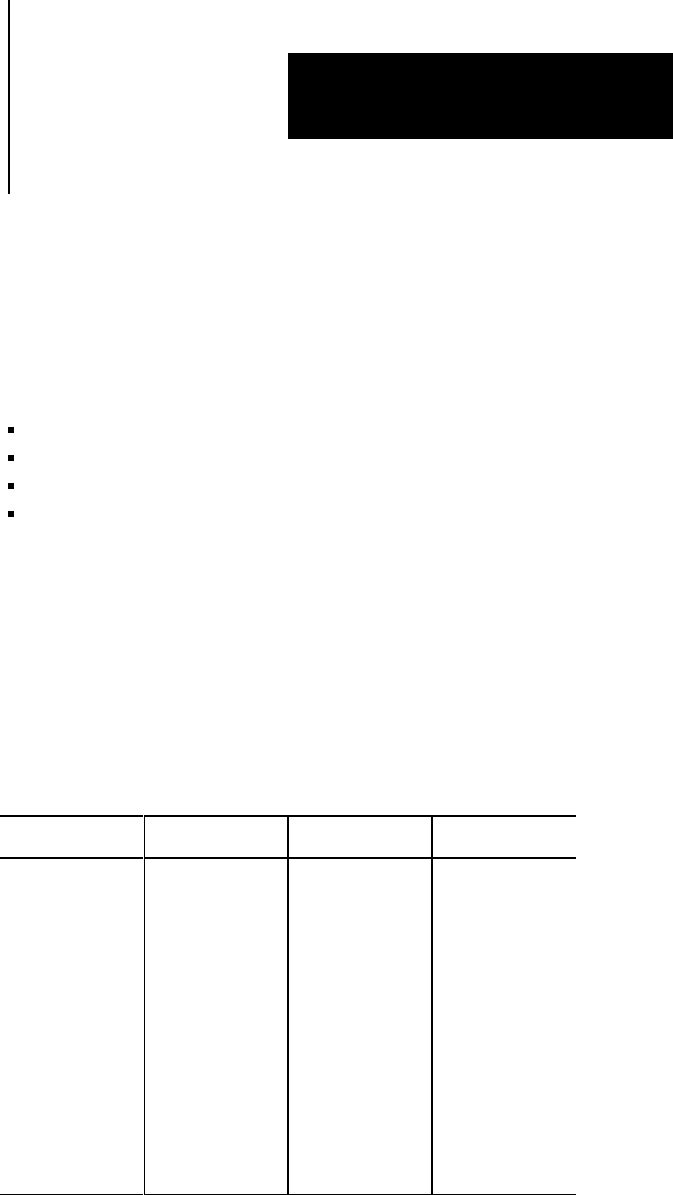
Table C.A
Numbering System Conversion Chart
Hexadecimal Binary Decimal Octal
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
0000
0001
0010
0011
0100
0101
0110
0111
1000
1001
1010
1011
1100
1101
1110
1111
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
000
001
002
003
004
005
006
007
010
011
012
013
014
015
016
017
Each place value in a decimal number represents a power of ten starting
with ten raised to the zero power (10
0
=1) (Figure C.1). You can compute
the decimal value of a number by multiplying each digit by its
corresponding place value and adding these numbers together.
Objectives
Decimal Numbering System