User Manual Owner's manual
Table Of Contents
- 1772-6.5.8, Mini-PLC-2/02, -2/16, -2/17 Processor, User Manual
- Important User Information
- Summary of Changes
- Table of Contents
- 1 - Using This Manual
- 2 - Fundamentals of a Programmable Controller
- 3 - Hardware Features
- 4 - Installing Your Programmable Controller
- 5 - Starting Your Processor
- 6 - Maintaining and Troubleshooting Your Processor
- 7 - Memory Organization
- 8 - Scan Theory
- 9 - Relay-Like Instructions
- 10 - Program Control Instructions
- 11 - Timers and Counters
- 12 - Data Manipulation and Compare Instructions
- 13 - Three-Digit Math Instructions
- 14 - EAF Math Instructions
- 15 - EAF Log, Trig, and FIFO Instructions
- 16 - EAF Process Control Instructions
- 17 - Jump Instructions and Subroutines
- 18 - Block Transfer
- 19 - Data Transfer Instructions
- 20 - Bit Shift Registers
- 21 - Sequencers
- 22 - Selectable Timer Interrupts
- 23 - Report Generation
- 24 - Program Editing
- 25 - Programming Techniques
- 26 - Program Troubleshooting
- A - Specifications
- B - Processor Comparison Chart
- C - Number Systems
- D - Glossary
- E - Quick Reference
- Index
- Back Cover
Jump Instructions and
Subroutine Programming
Chapter 17
17-5
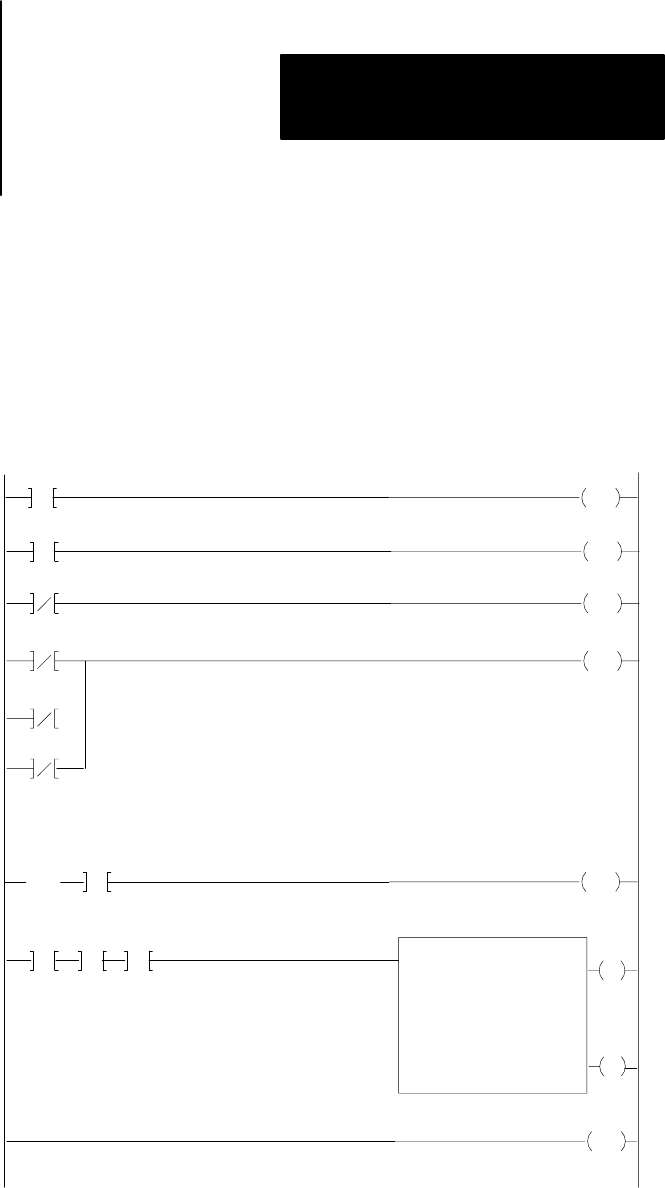
You can program a maximum of 8 subroutines in the subroutine area.
Each subroutine begins with a Label instruction and ends with a return
instruction. The Return should be an unconditional rung. The subroutine
area serves as the end of the main program and defines the beginning of
the subroutine area (Figure 17.2).
Figure 17.2
Subroutine
Programming Example
JSR
01
112
00
10
013
112
02
U
012
114
06
116
02
116
02
116
13
012
11
01
LBL
114
06
116
11
12 13
EN
FILE TO FILE MOVE
COUNTER ADDR:
POSITION:
FILE LENGTH:
FILE A:
200
001
007
400- 406
FILE R: 500- 506
RATE PER SCAN: 007
RET
OFF 11
116 116
DN
200
17
200
15
SUBROUTINE AREA
U
200
OFF 17
You can establish a subroutine area by performing the following steps.
1. Move the cursor down to the end of the main program.
2. Press [Shift] [SBR]