User Manual
Table Of Contents
- 1771-6.5.88, Plastic Molding Module Reference Manual
- Summary of Changes
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- 1 - Abbreviated Command and Status Blocks
- Chapter Contents
- CLC - Clamp and Eject ERC Values Block
- CPC - Clamp Close Profile Block
- DYC - Dynamic Command Block
- EAC - Ejector Advance Configuration Block
- EPC - Ejector Profile Block
- ERC - Ejector Retract Configuration Block
- FCC - First Clamp Close Configuration Block
- FOC - First Clamp Open Configuration Block
- HDC - Hold Configuration Block
- HPC - Pack/Hold Profile Block
- INC - Injection Configuration Block
- IPC - Injection Profile Block
- JGC - Jog Configuration Block
- LPC - Clamp Low Pressure Close Configuration Block
- MCC - Module Configuration Command Block
- OPC - Clamp Open Profile Block
- OSC - Clamp Open Slow Configuration Block
- PKC - Pack Configuration Block
- PLC - Plastication Configuration Block
- PPC - Plastication Profile Block
- PRC - Pre-decompression Configuration Block
- PSC - Post- decompression Configuration Block
- PTC - Process Trace Configuration Block
- RLC - Inject ERC Values Block
- SCC - Second Clamp Close Configuration Block
- SOC - Second Clamp Open Configuration Block
- TCC - Third Clamp Close Configuration Block
- TOC - Third Clamp Open Configuration Block
- CLS - Clamp and Eject ERC Values Status Block
- CPS - Clamp Close Profiles Status Block
- EPS - Ejector Profile Status Block
- HPS - Pack/Hold Profile Status Block
- IPS - Injection Profile Status Block
- OPS - Clamp Open Profiles Status Block
- PPS - Plastication Profile Status Block
- PTS - Process Trace Status Block
- RLS - Inject ERC Values Status Block
- SYS - System Status Block
- 2 - Command Word/Bit Descriptions
- Alphabetical List of Command Blocks and Block ID Codes
- List of Data Words
- Engineering Units
- Data Blocks Require I/O Configuration
- Data Blocks for System Control
- Data Blocks for Controlling Ram (Screw) Position
- Data Blocks for Controlling Clamp Position
- Data Blocks for Controlling Ejector Position
- Sensors Required
- CLC CLC - Clamp and Eject ERC Values Block
- CPC - Clamp Close Profile Block
- DYC DYC - Dynamic Command Block
- EAC - Ejector Advance Configuration Block
- EPC - Ejector Profile Block
- ERC - Ejector Retract Configuration Block
- FCC - First Clamp Close Configuration Block
- FOC - First Clamp Open Configuration Block
- HDC - Hold Configuration Block
- HPC - Pack/Hold Profile Block
- INC - Injection Configuration Block
- IPC - Injection Profile Block
- JGC - Jog Configuration Block
- LPC - Clamp Low Pressure Close Configuration Block
- MCC - Module Configuration Command Block
- OPC - Clamp Open Profile Block
- OSC - Clamp Open Slow Configuration Block
- PKC - Pack Configuration Block
- PLC Plastication Configuration Command Block (PLC)
- PPC - Plastication Profile Block
- PRC - Pre-decompression Configuration Block
- PSC - Post-decompression Configuration Block
- PTC - Process Trace Configuration Block
- RLC - Inject ERC Values Block
- SCC - Second Clamp Close Configuration Block
- SOC - Second Clamp Open Configuration Block
- TCC - Third Clamp Close Configuration Block
- TOC - Third Clamp Open Configuration Block
- 3 - Word/Bit Descriptions
- List of Status Blocks and Block ID Codes
- List of Data Words
- Data Blocks Require I/O Configuration
- Engineering Units
- Status Block for Reporting System Status
- Status Blocks for Reporting Ram (Screw) Position
- Status Blocks for Reporting Clamp Position
- Status Blocks for Reporting Ejector Position
- CLS - Clamp and Eject ERC Values Status Block
- CPS - Clamp Close Profiles Status Block
- EPS - Ejector Profile Status Block
- HPS - Pack/Hold Profile Status Block
- IPS ú Injection Profile Status Block
- OPS - Clamp Open Profiles Status Block
- PPS - Plastication Profile Status Block
- PTS - Process Trace Status Block
- RLS - Inject ERC Values Status Block
- SYS - System Status Block
- 4 - Programming Error Codes
- 5 - Module Specifications
- 6 - Calibration Instructions
- A - Single transfer for Reporting Ejector Status
- Back cover
4–2 Programming Error Codes
Publication
1771-6.5.88 – July 1997
You read error codes on your programming terminal by examining
system status words in the PLC data table:
• SYS61 = ID of the block that contains the error
• SYS62 = error code
You can interpret most error codes by memorizing 9 basic types and
knowing how the codes are organized.
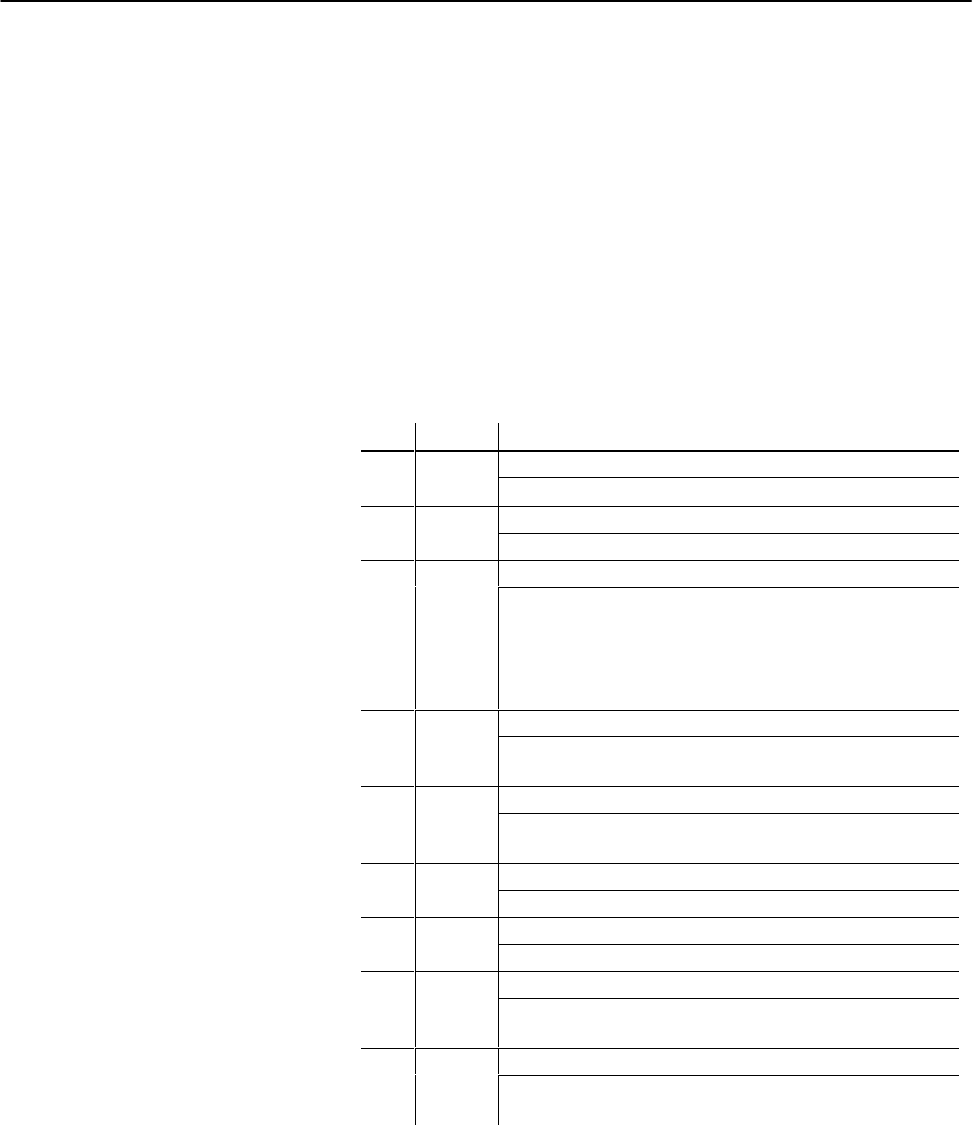
The 4-digit code, xxyy, has two parts:
• xx = type description
• yy = word in the command block that contains the error
Here we list the type descriptions, each with an example error code.
Type Example Description
02
0222
Outside fixed limits
02 0222
MCC22 is out of range. Valid range is 00000
≤
MCC22
≤
00099.
03
Cannot be equal
03
0311
MCC11 is equal to MCC12. They must not be equal.
Outside range established by another entry
04
0427
MCC27 is out of range.
If MCC28 is non-zero, MCC27 must be within
MCC23
≤
MCC27
≤
MCC28.
If MCC28 is zero, MCC27 must be within
MCC23
≤
MCC27
≤
MCC24.
Bit selection error
05
0502
You configured the module for 4/4 I/O by MCC02-B03=1.
Therefore, MCC02-B04=1 and MCC02-B05=1 is illegal.
Block-related configuration error
06 0609
Your CPC10 must be zero because of invalid FCC.
(SYS15-B02 = 0)
07
0712
Required non-zero entry
07 0712
IPC12 cannot be zero when IPC14 > 00000.
08
0816
Entry must be zero
08 0816
IPC16 must be 00000 when IPC12 = 00000.
Entry combination error (group is outside fixed limits)
09 0960
Your entry combination is illegal:
IPC60 = IPC61 = IPC62 = IPC63 = 00000.
Error in entry order
10
1015
IPC is not in decreasing positional order.
If non-zero, IPC15 must be less than IPC11.
How to Read Error Codes










