Instruction Sheet Smart Communications Card (Cat. No. 1403-NSC) Throughout this manual we use notes to make you aware of safety considerations: ! ATTENTION: Identifies information about practices or circumstances that can lead to personal injury or death, property damage or economic loss.
Smart Communications Card Product Description Chapter Objectives Performance Features After completing this chapter, you should be able to identify the product features and system applications. The Smart Communication Card performance features include: • PLC via R I/O • SLC 500 via R I/O with (1747-SN) Series B or later Introduction scanner module The Cat. No.
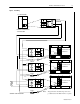
Smart Communications Card 3 Installation ! ATTENTION: Please follow appropriate ESD procedures before removal and/or installation of the Smart Communications Card. Failure to follow these procedures can result in physical damage to both the Smart Communications Card and the Master Module. 5. With the Master Module labels right side up, place the card into opening on the left side.
Smart Communications Card Wiring ! ATTENTION: Special high level isolation is required between units when the possibility of high ground potential differences exist. This may occur when separate grounds are used or when communicating to a unit connected to a power ground mat. Failure to do so can lead to personal injury or death, property damage, or economic loss. Table A.
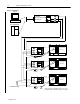
Smart Communications Card Figure 5. R I/O Wiring PLC PROCESSOR BLUE SHIELD CLEAR INTERNAL TERMINATING 150Ω RESISTOR Powermonitor II DEVICE #1 150KΩ 0.047uF Powermonitor II DEVICE #2 150KΩ 0.047uF Powermonitor II DEVICE #3 150KΩ Note: 84Ω OR 150Ω RESISTOR 0.047uF All ground wires should be kept as short as possible between the R/C and the cover plate. Publication 1403-5.
Smart Communications Card Figure 6. RS-485 Wiring IBM PC EXTERNAL RS–232C TO RS–485 RS–232C CONVERTER 150Ω RESISTOR PLC PROCESSOR Powermonitor II DEVICE #1 150KΩ 0.047uF Powermonitor II DEVICE #2 150KΩ 0.047uF Powermonitor II DEVICE #3 150KΩ 150Ω RESISTOR 0.047uF Publication 1403-5.1 Note: All ground wires should be kept as short as possible between the R/C and the cover plate.
Smart Communications Card Figure 7. RS-232C Wiring Powermonitor II Note: For CE compliance, the communication cable shield must be connected directly to the chassis ground terminal located on the communication card cover plate. The exposed shield wire should be as short as possible. IBM PC 25 PIN D–SHELL 9 PIN D–SHELL PLC PROCESSOR 1 CASE GROUND 2 3 3 2 7 5 Field Service Considerations If the Smart Communications Card requires service, please contact your nearest Allen-Bradley Sales Office.
Smart Communications Card General Operation Communications Card Set-Up Indicators All communications card options such as communications format, baud rate, address, etc., are set by configuring the Master Module. Refer to Powermonitor II Instruction Sheet, Publication 1403-5.0, Chapter 4. Figure 1. on page 2 shows the location of the LED Indicators on the communications card. Table B.
Appendix A Catalog Number Explanation Communications Cards 1403 - NSC Bulletin Number Type of Device 1403 = Power Quality and Automation Products NSC = Plug-in Communications Card for Bulletin 1403-MM Devices (RS-232C / RS-485 / Allen-Bradley R I/O Protocols) Publication 1403-5.
A–2 Catalog Number Explanation Publication 1403-5.
Appendix B Smart Communication Card Data Tables Table B.
B–2 Smart Communication Card Data Tables ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ
Smart Communication Card Data Tables B–3 ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁ
B–4 Smart Communication Card Data Tables Table B.
Smart Communication Card Data Tables B–5 ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ Á
B–6 Smart Communication Card Data Tables ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ Á
Smart Communication Card Data Tables B–7 ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ Á
B–8 Smart Communication Card Data Tables ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ Á
Smart Communication Card Data Tables B–9 ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ
B–10 Smart Communication Card Data Tables ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ
Smart Communication Card Data Tables B–11 ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ
B–12 Smart Communication Card Data Tables ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ
Smart Communication Card Data Tables B–13 ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ
B–14 Smart Communication Card Data Tables ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ
Smart Communication Card Data Tables B–15 ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ
B–16 Smart Communication Card Data Tables ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ
Smart Communication Card Data Tables Table B.16 Available Min/Max Log Parameters (Identifiers for parameter 12.
B–18 Smart Communication Card Data Tables Harmonic Distortion Tables – Read Harmonic Distortion Data Tables for Channel 2 through Channel 7 are identical to the Even and Odd Harmonic Distortion Tables for Channel 1. There are a total of 14 tables for this information. (V1, V2, V3, I1, I2, I3, I4) The table sizes indicate this is Harmonic Distortion Data. The Channel Number designates which one.
Smart Communication Card Data Tables B–19 ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ
B–20 Smart Communication Card Data Tables ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ Á ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ Á
Smart Communication Card Data Tables B–21 Harmonic Magnitude Data Tables for Channel 2 through Channel 7 are identical to the Even and Odd Harmonic Magnitude Tables for Channel 1. There are a total of 14 tables for this information.
B–22 Smart Communication Card Data Tables ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ
Smart Communication Card Data Tables B–23 ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ
B–24 Smart Communication Card Data Tables Harmonic Phase Angle Data Tables for Channel 2 through Channel 7 are identical to the Even and Odd Harmonic Phase Angle Data Tables for Channel 1. There are a total of 14 tables for this information.
Smart Communication Card Data Tables B–25 ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ
B–26 Smart Communication Card Data Tables ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ
Smart Communication Card Data Tables B–27 ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ Á
B–28 Smart Communication Card Data Tables ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ
Smart Communication Card Data Tables B–29 ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ
B–30 Smart Communication Card Data Tables ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ
Smart Communication Card Data Tables ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ
B–32 Smart Communication Card Data Tables ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁ ÁÁÁÁÁÁÁÁ
Smart Communication Card Data Tables Table B.29 Status Inputs Bitfield Definitions Description Bit Location and Value Table B.
B–34 Smart Communication Card Data Tables Publication 1403-5.
Appendix C Serial Communication Protocol Tutorial The Smart Communication Card supports the DF1 link layer protocol Table C.2 contains definitions of multiple byte codes. Table C.2 Special Symbol Meanings For additional information regarding the DF1 link layer protocol, refer to the Data Highway/Data Highway Plus/DH-485 Communication Protocol and Command Set, Allen-Bradley Publication 1770-6.5.16 (November 1991). Table C.1 contains definitions of single byte codes.
C–2 Serial Communication Protocol Tutorial Generic Packet Construction Read Polling Packet Command_Block = [ FNC_byte / Byte_size / File_number / File_type / Element_number / Sub-element_number ] [ DLE / ENQ / STN / BCC ] FNC_byte = 0xA2 Slave Message Link Packet [ DLE / STX / APP_DATA / DLE / ETX / CRC ] APP_DATA = [ DST / SRC / CMD / STS / TNS / TNS / Response_Data ] byte_size = size/ID of data table being requested in bytes (words X 2) file_number = 0x00 file_type = 0x89 Read element_number =
Serial Communication Protocol Tutorial Table C.3 Write Sequence Transmitted from Serial Network Master [ DLE / SOH / STN / DLE / STX / DST / SRC / 0x0F / 0x00 / 0x00 / 0x00 / 0xAA / data_size / 0x00 / 0x89 / 0x00 / 0x00 / 1st_dataword_lo / 1st_dataword_hi /.../ last_dataword_lo / last_dataword_hi / DLE / ETX / CRC ] C–3 Table C.
C–4 Serial Communication Protocol Tutorial CRC16 (Cyclic Redundancy Check) The 16-bit cyclic redundancy check (CRC16) is a method to check the integrity of a message packet. CRC16 provides a higher level of data security than block check character. Calculate the CRC value for master messages using the value of the STN, STX, data bytes, and the ETX (do not add in the associated DLE for STX and ETX).
Serial Communication Protocol Tutorial Table C.
C–6 Serial Communication Protocol Tutorial Table C.
Appendix D Sample Ladder Listing Ladder Program Description Appendix D contains sample ladder programs that interface to the Powermonitor II for PLC-5 R I/O, SLC-500 R I/O and SLC-500 RS-232. Because of the similarities of these three programs, only the PLC-5 R I/O example operation is discussed in detail, and the differences in operation for the SLC-500 R I/O and SLC-500 RS-232 are noted. Rung-by-rung descriptions are given for all three.
D–2 Sample Ladder Listing The SLC-500 R I/O version requires that all read and write tables be 64 words in length. This is a necessary requirement stemming from the use of the block transfer subroutines. A four word length control file needs to be initialized for each individual block transfer subroutine. The initialization values for each word are discussed in the Data Files Used section.
Sample Ladder Listing The reset word for the sequencer is N10:1. The first word in the rotation of the sequencer N10:1. The value in N10:0 must be the same as that in N10:1. This means N11:0 must equal N11:1, N12:0 must equal N12:1 and N13:0 must equal N13:1. The size of file N10 is equal to the size of the largest sequencer input file. For configuration and setpoint modes, this size will always be 2. In Run mode the size depends on the number of block transfers to be performed.
D–4 Sample Ladder Listing PLC-5 R I/O Rung 2:0 Latch configuration mode and unlatch setpoint and run modes. Clear one-shot bits. Rung 2:1 Initialize the sequencer for configuration mode. This includes loading the sequencer input file with the configuration block transfer numbers, setting the sequencer length, clearing the sequencer position and moving the reset word into the sequencer’s output file. Publication 1403-5.1 Rung 2:0 Enable configuration mode and clear one shot bits.
Sample Ladder Listing Rung 2:2 If the configuration BTW and diagnostic BTR are done, check that the diagnostic table parameters indicate a successful BTW (word 36 and 37 equal 0). If so, unlatch the configuration mode bit and latch the setpoint mode bit. Rung 2:3 Initialize the sequencer for setpoint mode. Same functionality as Rung 2:0. Rung 2:4 Move the number of setpoints into the setpoint address counter. Reset the setpoint counter. D–5 Rung 2:2 Begin setpoint mode once configuration is complete.
D–6 Sample Ladder Listing Rung 2:5 Initialize the sequencer for run mode. Same functionality as Rungs 2:0 and 2:1. Rung 2:6 This is the main block transfer sequencer. The sequencer output word, N9:0, is updated whenever the previous block transfer is done or fails. Rung 2:7 Voltage/current BTR. Rung 2:8 Real time power BTR. Publication 1403-5.1 Rung 2:5 Initialize for appropriate mode.
Sample Ladder Listing Rung 2:9 Cumulative power BTR. Rung 2:10 Device configuration BTR. Rung 2:11 Communication configuration BTR. Rung 2:12 Demand BTR. Rung 2:13 Even harmonic distortion BTR.
D–8 Sample Ladder Listing Rung 2:14 Odd harmonic distortion BTR. Rung 2:15 Even harmonic magnitude BTR. Rung 2:16 Odd harmonic magnitude BTR. Rung 2:17 Even harmonic phase BTR. Rung 2:18 Odd harmonic phase BTR. Publication 1403-5.
Sample Ladder Listing Rung 2:19 Diagnostic BTR. Rung 2:20 Relay/setpoint BTR. Rung 2:21 Command BTW. Rung 2:22 Configuration BTW. Rung 2:23 If the setpoint counter done bit is set, the last setpoint BTW has occurred and was followed by a diagnostic BTR. If the diagnostic table indicates a successful setpoint BTW, setpoint mode is done. The setpoint mode bit is unlatched, and the run mode bit is latched.
D–10 Sample Ladder Listing Rung 2:24 This rung is activated once when the sequencer output file changes to setpoint BTW. Its purpose is to determine the address of the next setpoint data and to copy the data residing at this address into the setpoint BTW data location. This is accomplished by first adding an address offset to a base address to determine the location of the next setpoint data. The data residing at the resulting address is then transferred to the setpoint BTW data location.
Sample Ladder Listing SLC-500 R I/O Rung 2:0 Latch configuration mode and unlatch setpoint and run modes. Clear one-shot bits. Rung 2:1 Initialize the sequencer for configuration mode. This includes loading the sequencer input file with the configuration block transfer numbers, setting the sequencer length, clearing the sequencer position and moving the reset word into the sequencer’s output file.
D–12 Sample Ladder Listing Rung 2:2 If the configuration BTW and diagnostic BTR are done, check that the diagnostic table parameters indicate a successful BTW (word 36 and 37 equal 0). If so, unlatch the configuration mode bit and latch the setpoint mode bit. Rung 2:3 Initialize the sequencer for setpoint mode. Same functionality as Rung 2:0. Rung 2:4 Move the number of setpoints into the setpoint address counter. Reset the setpoint counter. Publication 1403-5.
Sample Ladder Listing Rung 2:5 Initialize the sequencer for run mode. Same functionality as Rungs 2:0 and 2:1. Rung 2:6 This is the main block transfer sequencer. The sequencer output word, N9:0, is updated whenever the previous block transfer is done or fails. After each sequencer increment, the block transfer preparation subroutine is called. Rung 2:7 Voltage/current BTR. D–13 Rung 2:5 Initialize for appropriate mode.
D–14 Sample Ladder Listing Rung 2:8 Real time power BTR. Rung 2:9 Cumulative power BTR. Rung 2:10 Device configuration BTR. Rung 2:11 Communication configuration BTR. Rung 2:12 Demand BTR. Rung 2:13 Even harmonic distortion BTR. Rung 2:14 Odd harmonic distortion BTR. Rung 2:15 Even harmonic magnitude BTR. Rung 2:16 Odd harmonic magnitude BTR. Publication 1403-5.1 Rung 2:8 Perform appropriate block transfer read.
Sample Ladder Listing Rung 2:17 Even harmonic phase BTR. Rung 2:18 Odd harmonic phase BTR. Rung 2:19 Diagnostic BTR. Rung 2:20 Relay/setpoint BTR. Rung 2:21 Command BTW. Rung 2:22 Configuration BTW. Rung 2:23 If the setpoint counter done bit is set, the last setpoint BTW has occurred and was followed by a diagnostic BTR. If the diagnostic table indicates a successful setpoint BTW, setpoint mode is done. The setpoint mode bit is unlatched, and the run mode bit is latched.
D–16 Sample Ladder Listing Rung 2:24 This rung is activated once when the sequencer output file changes to setpoint BTW. Its purpose is to determine the address of the next setpoint data and to copy the data residing at this address into the setpoint BTW data location. This is accomplished by first adding an address offset to a base address to determine the location of the next setpoint data. The data residing at the resulting address is then transferred to the setpoint BTW data location.
Sample Ladder Listing BTR and BTW Subroutines D–17 2. The file M0.1 is used for the BTW while file M0.2 is used for the BTR routine. The SLC-500 R I/O BTR and BTW subroutines mimic the read and write block transfer examples listed in the back of the Publication 1747–6.6, R I/O Scanner User Manual. The following rung descriptions and notes pertain to modifications or additions to these examples. 1. The BTR and BTW subroutines use different files and bits than those given in the R I/O Scanner Manual.
D–18 Sample Ladder Listing Rung 3:2 When a BTR successfully completes, buffer the BT data and unlatch the BT enable bit. As shown, 63 words are copied to the BTR destination file, beginning at word 1, in order to match the Powermonitor II data table layout. Also, unlatch the BTR pending bit and latch the bit that continues checking the BTR status until the SN module turns off the done bit. Rung 3:3 If a BTR error occurs, unlatch the enable bit and buffer the BT error code.
Sample Ladder Listing Rung 3:4 When a new BTR is initiated, latch the enable bit, as long as a BTR is not in progress. Also, latch the BTR pending bit, so the BTR status file will be BTR by the ladder program. Because this rung marks the beginning of the BTR, both the done and error bits for the block transfer control word are unlatched along with the block transfer initiate bit. Rung 3:5 Move the virtual control words to the M0 file for the SN module whenever a transition of the BTR enable bit occurs.
D–20 Sample Ladder Listing BTW ( File 4 ) Rung 4:0 Copy the BTW status area to a file which will be used throughout the program, only when a BTW is pending. This avoids accessing the M1 file multiple times during each scan. Each time an instruction containing an M1 file bit, word or file is scanned by the processor, an immediate data transfer to the module occurs and therefore will impact the processor scan time. Rung 4:1 Unlatch the bit that continues to check the BTW status.
Sample Ladder Listing Rung 4:3 If a BTW errors, unlatch the enable bit, the BTW pending bit and buffer the BTW error code. Also, latch the bit that continues checking the BTW status until the SN module turns off the error bit and latch the control word error bit. Rung 4:4 When a new BTW is initiated, copy the data to the M0 file data area and latch the virtual BTW enable bit provided that a BTW is not in progress.
D–22 Sample Ladder Listing Rung 4:5 Move the virtual control words to the M0 file for the SN module whenever a transition of the BTW enable bit occurs. Rung 4:6 If all the conditions of this rung are true, the BTW cycle is complete. Latch the control word done bit if the error word at N15:4 is clear, or the control word error bit if it is not. Rung 4:7 Return from subroutine. Rung 4:8 End of file. Publication 1403-5.
Sample Ladder Listing D–23 BT Preparation ( File 5 ) Rung 5:0 In preparation for execution of a block transfer, this rung clears the 8 words of file N15, moves the BT data table location into word N15:7, latches the BT initiate bit and unlatches the BT enable bit. Rung 5:1 Return from subroutine. Rung 5:2 End of file.
D–24 Sample Ladder Listing SLC–500 RS-232 Rung 2:0 Latch configuration mode and unlatch setpoint and run modes. Clear one-shot bits. Rung 2:1 Initialize the sequencer for configuration mode. This includes loading the sequencer input file with the configuration block transfer numbers, setting the sequencer length, clearing the sequencer position and moving the reset word into the sequencer’s output file. Publication 1403-5.1 Rung 2:0 Enable configuration mode and clear one shot bits.
Sample Ladder Listing Rung 2:2 If the configuration BTW and diagnostic BTR are done, check that the diagnostic table parameters indicate a successful BTW (word 36 and 37 equal 0). If so, unlatch the configuration mode bit and latch the setpoint mode bit. Rung 2:3 Initialize the sequencer for setpoint mode. Same functionality as Rung 2:0. Rung 2:4 Move the number of setpoints into the setpoint address counter. Reset the setpoint counter. D–25 Rung 2:2 Begin setpoint mode once configuration is complete.
D–26 Sample Ladder Listing Rung 2:5 Initialize the sequencer for run mode. Same functionality as rungs 2:0 and 2:1. Rung 2:6 This is the main block transfer sequencer. The sequencer output word, N9:0, is updated whenever the previous block transfer is done or fails. Rung 2:7 Voltage/current BTR. Publication 1403-5.1 Rung 2:5 Initialize for appropriate mode.
Sample Ladder Listing Rung 2:8 Real time power BTR. Rung 2:9 Cumulative power BTR. Rung 2:10 Device configuration BTR. Rung 2:11 Communication configuration BTR. Rung 2:12 Demand BTR. Rung 2:13 Even harmonic distortion BTR.
D–28 Sample Ladder Listing Rung 2:14 Odd harmonic distortion BTR. Rung 2:15 Even harmonic magnitude BTR. Rung 2:16 Odd harmonic magnitude BTR. Rung 2:17 Even harmonic phase BTR. Rung 2:18 Odd harmonic phase BTR. Rung 2:19 Diagnostic BTR. Publication 1403-5.
Sample Ladder Listing Rung 2:20 Relay/setpoint BTR. Rung 2:21 Command BTW. Rung 2:22 Configuration BTW. Rung 2:23 If the setpoint counter done bit is set, the last setpoint BTW has occurred and was followed by a diagnostic BTR. If the diagnostic table indicates a successful setpoint BTW, setpoint mode is done. The setpoint mode bit is unlatched, and the run mode bit is latched.
D–30 Sample Ladder Listing Rung 2:24 This rung is activated once when the sequencer output file changes to setpoint BTW. Its purpose is to determine the address of the next setpoint data and to copy the data residing at this address into the setpoint BTW data location. This is accomplished by first adding an address offset to a base address to determine the location of the next setpoint data. The data residing at the resulting address is then transferred to the setpoint BTW data location.
Appendix E Technical Specifications Product Approvals UL 508 Component Recognized File E96956 and CSA C22.2 approval for Industrial Control Equipment. Compliance to European Union Directives If this product has the CE mark it is approved for installation within the European Union and EEA regions. It has been designed and tested to meet the following directives. Screw Torque and Wire Size Position Ratings Mounting Screw Tightening Torque 0.9 to 1.1 Nm (8 to 10 lb-in.) Communications Connector 0.
E–2 Technical Specifications Publication 1403-5.
Allen-Bradley, a Rockwell Automation Business, has been helping its customers improve productivity and quality for more than 90 years. We design, manufacture and support a broad range of automation products worldwide. They include logic processors, power and motion control devices, operator interfaces, sensors and a variety of software. Rockwell is one of the world’s leading technology companies. Worldwide representation.