User`s guide
RIGOL
© 2008 RIGOL Technologies, Inc.
User’s Guide for DS1000E, DS1000D Series
2-14
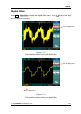
Using the FFT
The FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) process converts a time-domain signal into its
frequency components mathematically. FFT waveforms are useful in the following
applications:
Measuring harmonic content and distortion in systems
Characterizing noise in DC power supplies
Analyzing vibration
Figure 2- 17 Table 2- 6 The FFT menu
Menu
Settings
Comments
Operate
A+B
A-B
A x B
FFT
Add source A to source B
Subtract source B from source A
Multiply source B by source A
Fast Fourier Transform
Source
CH1
CH2
Define CH1 or CH2 as FFT source
Window
Rectangle
Hanning
Hamming
Blackman
Select window for FFT
Display
Split
Full screen
Display FFT waveform on half screen
Display FFT waveform on full screen
Scale
Vrms
dBVrms
Set “Vrms ” as vertical unit
Set “dBVrms ” as vertical unit
Key points for FFT
1. Signals that have a DC component or offset can cause incorrect FFT waveform
component magnitude values. To minimize the DC component, choose AC
Coupling on the source signal.
2. To reduce random noise and aliases components in repetitive or single-shot
events, set the oscilloscope acquisition mode to average.
3. To display FFT waveforms with a large dynamic range, use the dBVrms scale.
The dBVrms scale displays component magnitudes using a log scale.