Quadra User's Guide
Table Of Contents
- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Installation and Setup
- Operations
- In This Chapter
- Introduction to Operations
- Setting Output Format
- Testing Outputs
- Selecting an Input Source
- Enabling and Disabling Outputs
- Understanding Auto Sync
- Cropping an Image
- Zooming an Image
- Panning an Image
- Sizing the Output Image
- Using Position
- Adjusting Brightness and Contrast
- Adjusting Hue and Saturation
- Adjusting Sharpness
- Creating a Background
- Creating a 2x2 Monitor Wall
- Command Line Interface
- Image Concepts
- Communications Setup
- Connector Types
- Firmware Upgrades and Troubleshooting
- Technical Specifications
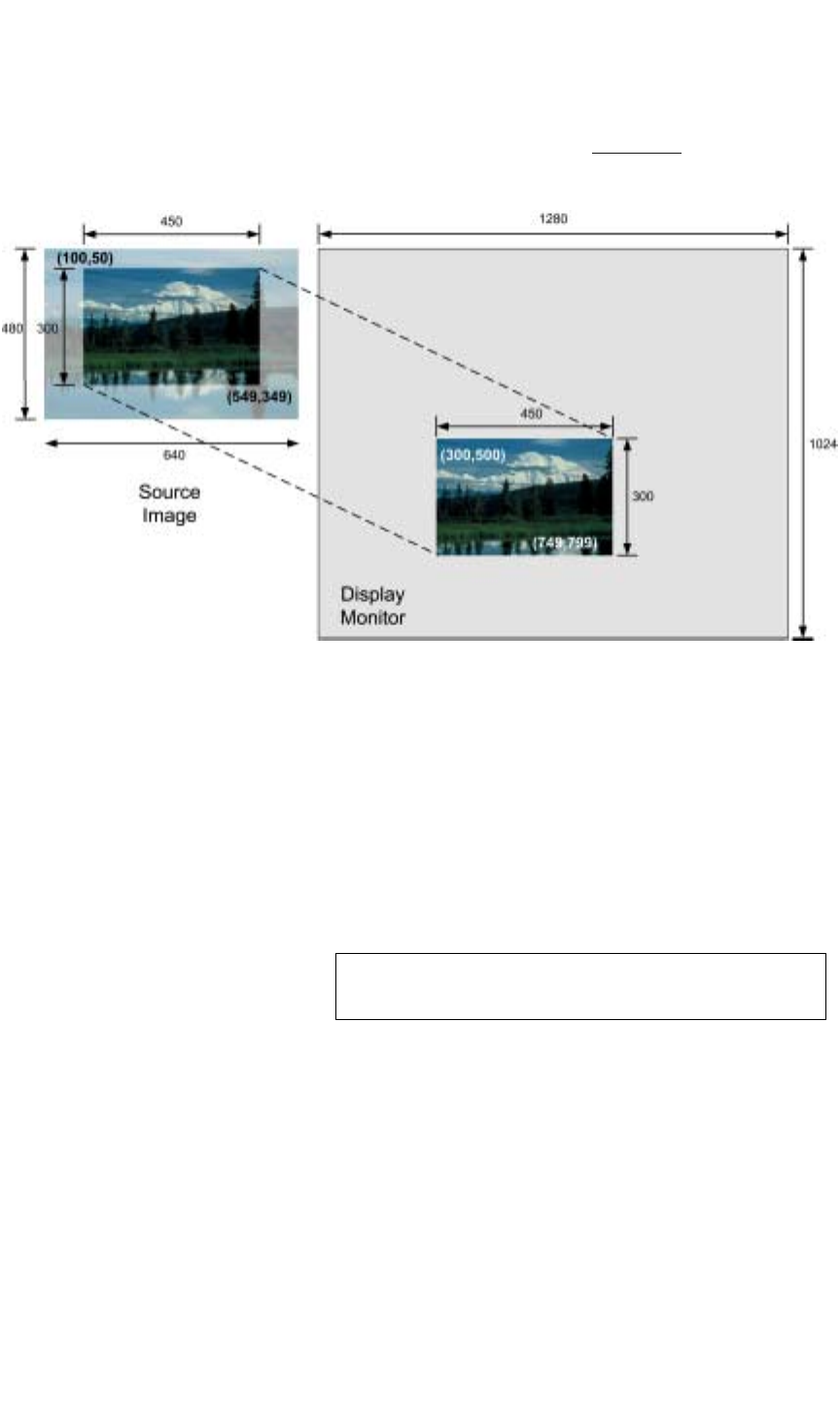
IMAGE CONCEPTS
Aspect Ratio
350-7951 Quadra User’s Guide 87
. . . . .
In the next example, the “cropped” image from Figure A-2 is mapped to a new
destination space on the display device.
Figure A-4.
Cropped Source mapped to Destination
In this case, the WDR value would be defined as:
300 500 450 300
Using WDR, you can take a portion of the source image and (without resizing
it) can place it anywhere on the display device. By changing the destination
size parameters (450,300 in the above example), to 1280 x 1024, we could
expand this cropped image to fill the display device. In this case, the WDR
value would be defined as:
0 0 1280 1024
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ASPECT RATIO
As you learned in the previous sections, the source rectangle parameter selects
any desired rectangular portion of an input image. This image can then be
displayed (mapped) in a destination rectangle — in an identical or different
configuration of size and position. Please note:
• The destination rectangle can be set to any shape and any size on the
output monitor — up to the full size of the output display screen.
Note This action is effectively zooming into a section of the
source image.










