Technical data
7
94
Manual – Gear Units and Gearmotors
Thermal characteristics (→ GM, → MM)
Project Planning for AC Motors
MOVIMOT
®
drives For MOVIMOT
®
drives, the factors f
T
und f
H
are given in the following diagrams:
Duty types The following duty types are defined in IEC 60034-1 (EN 60034-1):
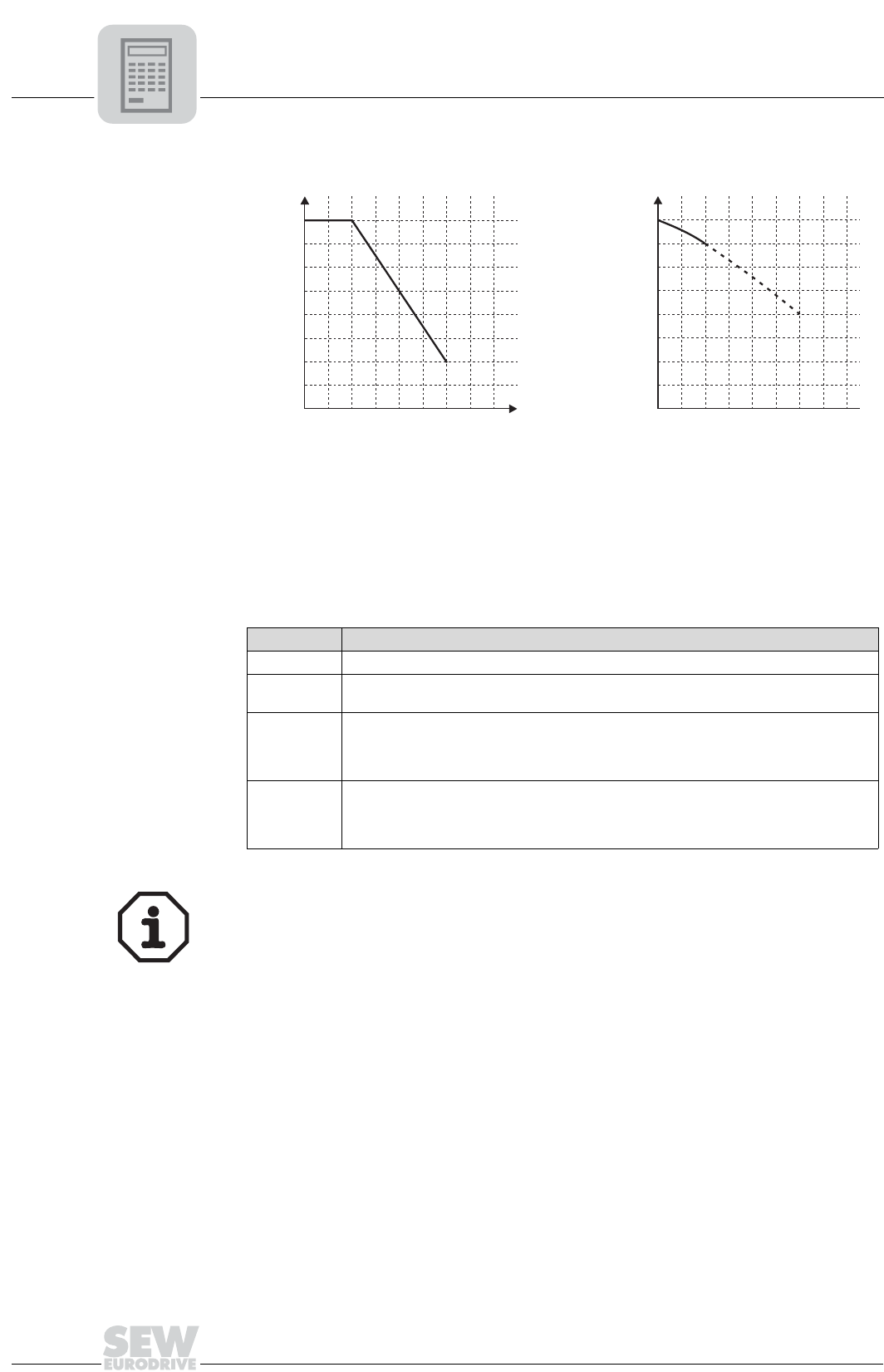
04051BUS
Figure 40: Power reduction dependent on ambient temperature and altitude
[1] Ambient temperature
[2] Altitude above sea level (Altitudes of more than 6600 ft subject to limitations. Observe the
installation notes in the "MOVIMOT
®
MM03C"MM03C-MM3XC operating instructions.
86
[1] [2]
104 122 140 ˚F
3300 6600 9900 13200 ft
0.4
0.6
0.9
1.0
f
T
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
f
H
0.8
0.7
0.5
0.3
Duty type Explanation
S1 Continuous duty: Operation at a constant load; the motor reaches thermal equilibrium.
S2
Short-time duty: Operation at constant load for a given time followed by a time at rest.
The motor returns to ambient temperature during the rest period.
S3
Intermittent periodic duty: The starting current does not significantly affect the tempera-
ture rise. Characterized by a sequence of identical duty cycles, each including a time of
operation at constant load and a time at rest. Described by the "cyclic duration factor
(cdf)" in %.
S4...S10
Intermittent periodic duty: The starting current affecting the temperature rise. Charac-
terized by a sequence of identical duty cycles, each including a time of operation at
constant load and a time at rest. Described by the "cyclic duration factor (cdf)" in % and
the number of cycles per hour.
For inverter operation, S1 continuous duty is usually assumed. For a great number of
cycles per hour, it may be necessary to assume S9 intermittent periodic duty.










