Hardware manual
45
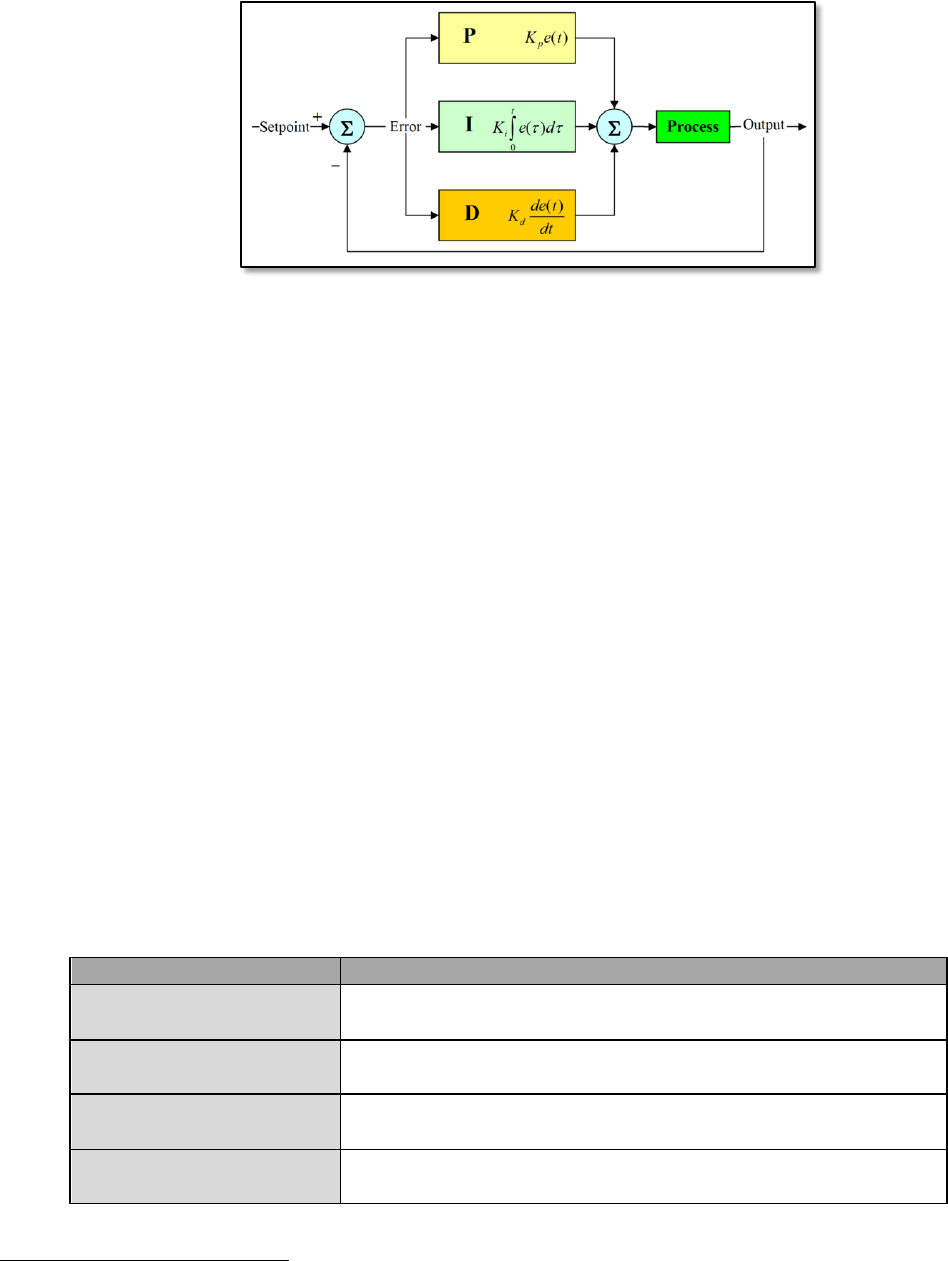
Fig. 5.3.5-1. General structure of PID controller.
PID used by PXMC can be seen on figure 5.3.2-1.
The efficiency and performance of PID controller depend on three constants: proportional
(pxms_p), integration (pxms_i) and derivative (pxms_d). Because of that it is very
important to set these variables properly. To do this without use of identification and
advanced mathematics, we can use so called Ziegler-Nichols Method of PID tuning
2
. This
c
) and the oscillation period (O
p
constant equal to: 0.6 K
c
p
P*O
p
/8.
5.3.6. PXMC_DEB.C
This file implements some basic functions for debugging of a controller. The use of below
functions allows making a tuning/identification of the controller. To have access to all
functions listed below, during compilation we need to define PXMC_WITH_DBG_HIST.
One important thing we need to keep in mind. These functions are not for debugging of
the PXMC library!
Name of pole
Short description
pxmc_dbg_histfree
It frees memory previously allocated for pxmc_dbg_hist_t
structure.
pxmc_dbg_histalloc
In opposite to above, this function allocates memory for
pxmc_dbg_hist_t structure, which stores debugging information.
pxmc_dbg_ene_as
This function stores in pxmc_dbg_hist_t structure the speed and
the power sent to the output.
pxmc_dbg_gnr_gi*
It is responsible for storing the speed generator profile in
pxmc_dbg_hist_t structure.
2
Hägglund PID Controllers: Theory, Design, and Tuning, 2nd Edition.










