Hardware manual
43
First one, *ptr is used to store information about speed and power sent to the output.
The*buff is used mainly to store a profile of speed generator. The *end pointer shows the
end of the buffer. Please see PXMC_DEB.C subsection to get little bit more information
about debugging.
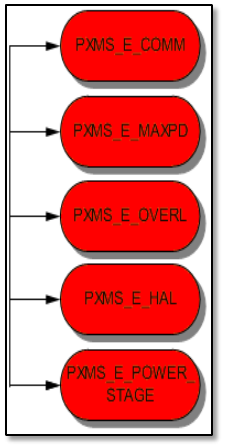
Other very important thinks are error flags. We know from the table in point 5.3.3 that
pxms_state structure has field called pxms_errno, which keeps last error code. All error
flags are presented on the picture nr 5.3.3-5 and below is short description of them (the
value given after the name of a flag represents the hexadecimal code of the error):
PXMS_E_COMM - 0x105 signalizes that the new index
position for phase table(s) is greater than the length of the
phase table(s).
PXMS_E_MAXPD 0x106 signalizes that the difference of
position is over limit. It means that absolute value of differenc
between pxms_ap and pxms_rp is greater than pxms_md.
PXMS_E_OVERL 0x107 signalizes that overload of
energy/power occurred. In other words, if the controller
function calculates new pxms_ene and it turns out to be
greater than pxms_me then this error occurs.
PXMS_E_HAL 0x108 signalizes that there was some
problem with reading of hall sensors.
Fig. 5.3.3-5. Error flags.
PXMS_E_POWER_STAGE 0x109 signalizes a power stage fault signal
At the end of the description of pxmc.h file, I want to give one very important note.
Namely, in every application which uses PXMC, we need to define one global variable
called: pxmc_main_list with a pxmc_state_list_t type. This structure consists from a list of
pxms_state structures (which describe motors) and the number of elements in this list.
The pxmc_main_list is in other words a total list of all motors which we want to use and
control in our program. It is mainly called from functions which provide some special
services and tasks for all motors. The small example how to create such list is present
here:










