Hardware manual
36
here definitions of all flags and definitions of the most functions which can be accessed
from PXMC. Now, lets try to look little bit more into details.
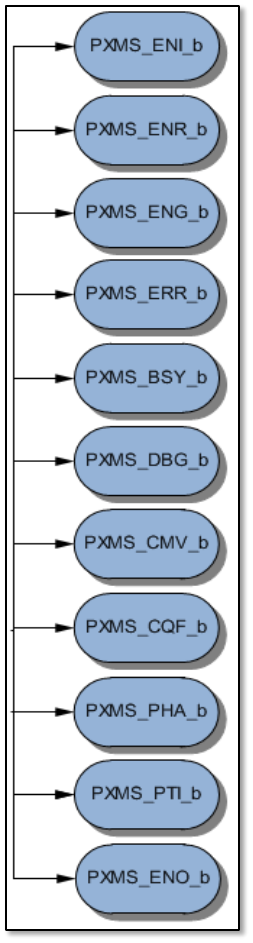
We start from flags. All of them, which are available in PXMC, are presented on the figure
nr 5.3.3-1, and in the following lines I'll try to introduce them.
The first, PXMS_ENI_b (Enable Input) enables input IRC
updates. It means that if this flag is set up, functions which
pointer is kept in pxms_do_inp will be executed.
PXMS_ENR_b (Enable Regulator) decides whether controller
and output will be switched on or not. If the flag is enabled
then functions are called which addresses are kept by
pxms_do_con and pxms_do_out.
PXMS_ENG_b (Enable Generator) is responsible for enabling
requested position generator. This flag and also two previous
are enabled according operation mode of the axis. This
mode can be like: feed forward, feedback and so one.
Whenever PXMS_ERR_b is set, it means that some error
occurred. If everything is working well this flag is disabled.
We can read error code from pxms_errno.
PXMS_BSY_b signalizes that axis/motor is busy. Because of
that calling some functions will result as error. For example it
is impossible to set new position with help of pxmc_go()
this function will be described later in this subsection.
PXMS_DBG_b enables debugging. Unfortunately the
debugging functions are not full implemented for our
(brushless) motor and it is much better to use serial line to
debug and check the code than use this flag. Unfortunately,
u
is due to relatively low speed of serial line, whereas
brushless motor can rotate several hundreds times per
second.
Fig. 5.3.3-1. Flags in PXMC.
Enabled PXMS_CMV_b flag means that motor is working in group, so its movement
should be coordinated with other motors. This flag is used by standalone library which
uses PXMC as backend.










