Hardware manual
35
5.3.2. General work of PXMC.
Before we go into descriptions of several files, which belong to PXMC library, we need to
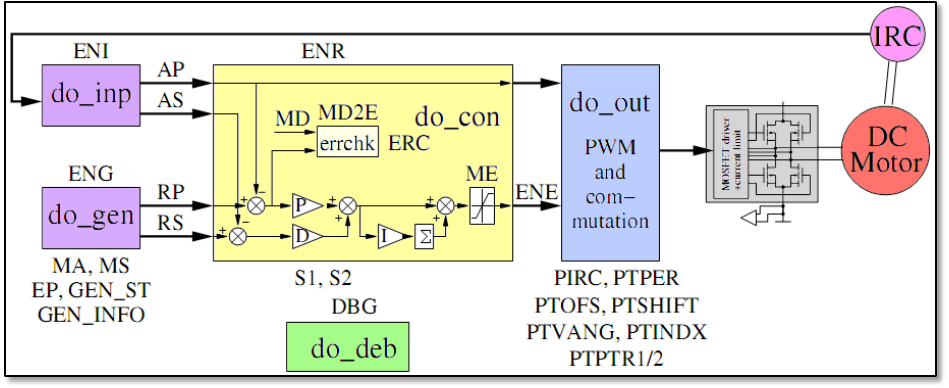
get some information how PXMC is working in general. On the figure 5.3.2-1 we can see
the internal structure of PXMC and the most important variables and flags.
Fig. 5.3.2-1. Internal structure of PXMC.
IRC. This component makes the measurements of the DC motor, which
later could be used by do_inp. Now, if the flag ENI (enable input) is enabled, do_inp
calculate the actual position (AP) and actual speed (AS). These two values are later used
by the controller (do_con). At the same time, if the flag ENG (enable generator) is
enabled, functions do_gen calculates request position (RP) and request speed (RS). As
before, also these two variables are used by the controller. Now, if flag ENR (enable
regulator) is enabled, the AP, AS, RP and RS and using P, D and I
constants calculates power (ENE). From last sentence we see that in this case the
controller is a PID type controller. When we have calculated power, we use function
do_out to combine it with proper values taken form a phase table(s) and send it to the
motor in a PWM form. Thanks that, the motor rotates little bit, IRC makes the
measurements and the whole situation repeats.
5.3.3. PXMC.H
Let start with the heart of PXMC library, namely pxmc.h. The most important thing
about this file is that we need to include it in all projects/programs in which we want to
use PXMC library. The importance of pxmc.h is that it defines pxmc_state_t structure,
which stores all needed information about motor(s) connected to our board. We also find










