Hardware manual
17
3.5. General work of brushless motor.
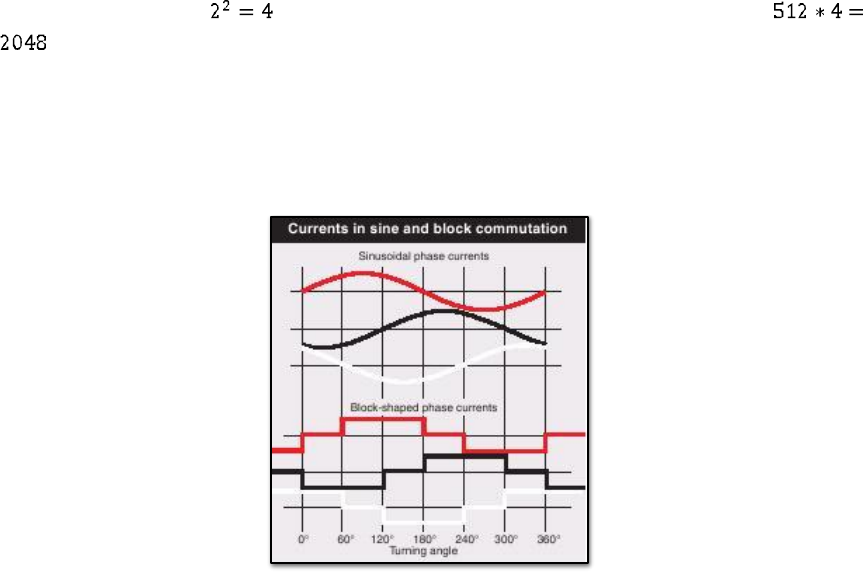
As we know from the previous sections, to make the brushless motor rotating we need to put on
the three windings currents with shifted phases. In the easiest case, when we have 3-phases
motor the shift in the phases is equal to 120
o
. To fulfill this requirement, in most cases we will
need to use some microcontroller to control the motor. This approach provides to a first
problem. Namely, the use of a microcontroller forces us to work not with continuous signals but
with their discrete versions. What does it mean for us? The answer is very easy. We need to
make some discretization of sinusoidal currents waves. After doing this as the result we will get
a discrete phase tables with several values which correspond to real current levels. Of course at
this point, there occurs question. How many levels should have these phase tables and how
many values should they store? The answers to these questions are quite easy and depend on
the specification of the microcontroller, the motor and the library which we use to control the
motor. If it goes about the number of a phase table levels for PXMC, it should be equal to 0x7fff.
This limitation is due to 16bits (in C/C++ it is short) which are used for keeping phase table
values because the last bit is used for sign then there stay 15bits which can give maximum
value equal to 0x7fff. If it goes about the length of phase table, we can calculate it by taking
from documentation of the motor two values: number of channels and the count per turn. After
that we just multiply them. For example, during my work with PXMC I had a motor which had 2
channels and count per turn equal to 512. Two channels give us total number of possible
combination equal to: . The length of phase table in this case was equal to:
elements.
The short example of it is shown on the picture 3.5-1. To
make it more readable, the size of phase table was limited only to 6 levels and the number of
levers to 3.
Fig. 3.5-1. Example of discretization.










