User`s manual
Table Of Contents
- Cover
- Keep safety first in your circuit designs!
- Notes regarding these materials
- IMPORTANT INFORMATION
- SAFETY PAGE
- Introduction
- About This Manual
- Contents
- Emulator Debugger Part
- Section 1 Overview
- Section 2 Preparation before Use
- Section 3 E6000 Emulator Functions
- Section 4 Preparation before Use
- Section 5 Debugging
- 5.1 Setting the Environment for Emulation
- 5.2 Downloading a Program
- 5.3 Viewing the Current Status
- 5.4 Reading and Displaying the Emulator Information Regularly
- 5.5 Displaying Memory Contents in Realtime
- 5.6 Viewing the Variables
- 5.7 Using the Event Points
- 5.7.1 Software Breakpoints
- 5.7.2 Event Points
- 5.7.3 Event Detection System
- 5.7.4 Signals to Indicate Bus States and Areas
- 5.7.5 Opening the [Event] Window
- 5.7.6 Setting Software Breakpoints
- 5.7.7 Setting Event Points
- 5.7.8 Setting Trigger Points
- 5.7.9 Editing Event Points
- 5.7.10 Modifying Event Points
- 5.7.11 Enabling an Event Point
- 5.7.12 Disabling an Event Point
- 5.7.13 Deleting an Event Point
- 5.7.14 Deleting All Event Points
- 5.7.15 Viewing the Source Line for an Event Point
- 5.8 Viewing the Trace Information
- 5.8.1 Opening the [Trace] Window
- 5.8.2 Acquiring Trace Information
- 5.8.3 Specifying Trace Acquisition Conditions
- 5.8.4 Searching for a Trace Record
- 5.8.5 Clearing the Trace Information
- 5.8.6 Saving the Trace Information in a File
- 5.8.7 Viewing the [Editor] Window
- 5.8.8 Trimming the Source
- 5.8.9 Acquiring a Snapshot of the Trace Information
- 5.8.10 Temporarily Stopping Trace Acquisition
- 5.8.11 Restarting Trace Acquisition
- 5.8.12 Extracting Records from the Acquired Information
- 5.8.13 Calculating the Difference in Time Stamping
- 5.8.14 Analyzing Statistical Information
- 5.8.15 Extracting Function Calls from the Acquired Trace Information
- 5.9 Analyzing Performance
- Section 6 Tutorial
- 6.1 Introduction
- 6.2 Running the High-performance Embedded Workshop
- 6.3 Downloading the Tutorial Program
- 6.4 Setting a Software Breakpoint
- 6.5 Setting Registers
- 6.6 Executing the Program
- 6.7 Reviewing Breakpoints
- 6.8 Referring to Symbols
- 6.9 Viewing Memory
- 6.10 Watching Variables
- 6.11 Displaying Local Variables
- 6.12 Stepping Through a Program
- 6.13 Forced Breaking of Program Executions
- 6.14 Resetting the MCU
- 6.15 Break Function
- 6.16 Trace Functions
- 6.17 Stack Trace Function
- 6.18 Performance Measurement Function
- 6.19 Monitor Function
- 6.20 What Next?
- Section 7 Hardware Specifications Specific to This Product
- 7.1 H8/3800 E6000 Emulator Specifications
- 7.2 User System Interface of H8/3800 E6000 Emulator
- 7.3 Differences between MCU and H8/3800 E6000 Emulator
- 7.4 Handling Evaluation Chip Board (HS3800EBK61H)
- 7.5 Host PC Interface (only for HS38000EPI61H + HS3800EBK61H)
- 7.6 H8/388R E6000 Emulator Specifications
- 7.7 User System Interface of H8/388R E6000 Emulator
- 7.8 Differences between MCU and H8/388R E6000 Emulator
- 7.9 Handling Evaluation Chip Board (HS388REBK61H)
- 7.10 Host PC Interface (only for HS38000EPI61H + HS388REBK61H)
- Section 8 Software Specifications Specific to This Product
- 8.1 Software Specifications of the H8/3800 E6000 Emulator
- 8.1.1 Target Hardware
- 8.1.2 Selectable Platform
- 8.1.3 [Configuration Properties] Dialog Box ([General] Page)
- 8.1.4 Memory Mapping Function
- 8.1.5 [Status] Window
- 8.1.6 Extended Monitor Function
- 8.1.7 Signals to Indicate Bus States and Areas
- 8.1.8 Monitoring Function
- 8.1.9 Trigger Points
- 8.1.10 Trace Information
- 8.1.11 Searching for a Trace Record
- 8.1.12 Trace Filtering Function
- 8.2 Note on Usage of the H8/3800 E6000 Emulator
- 8.3 Software Specifications of the H8/388R E6000 Emulator
- 8.3.1 Target Hardware
- 8.3.2 Selectable Platforms
- 8.3.3 [Configuration Properties] Dialog Box ([General] Page)
- 8.3.4 Memory Mapping Function
- 8.3.5 [Status] Window
- 8.3.6 Extended Monitor Function
- 8.3.7 Signals to Indicate Bus States and Areas
- 8.3.8 Monitoring Function
- 8.3.9 Trigger Points
- 8.3.10 Trace Information
- 8.3.11 Searching for a Trace Record
- 8.3.12 Trace Filtering Function
- 8.4 Note on Usage of the H8/388R E6000 Emulator
- 8.5 Performance Analysis Function
- 8.1 Software Specifications of the H8/3800 E6000 Emulator
- Appendix A I/O File Format
- Appendix B Menus
- Appendix C Command Lines
- Appendix D Diagnostic Test Procedure
- Colophon
74
5.8 Viewing the Trace Information
The emulator acquires the results of each instruction execution into the trace buffer as trace information and
displays it in the [Trace] window. The conditions for the trace information acquisition can be specified in the
[Trace Acquisition] dialog box.
Since trace information in bus-cycles is acquired by the hardware circuit and stored in the trace buffer, the
realtime operation is retained. The [Trace] window displays the content of the trace buffer, which records up to
32,768 bus cycles from the last program run and is always updated.
5.8.1 Opening the [Trace] Window
To open the [Trace] window, choose [View -> Code -> Trace] or click the [Trace] toolbar button (
).
5.8.2 Acquiring Trace Information
When the emulator does not set the acquisition condition of the trace information, all bus cycles are acquired by
default without any condition (free trace mode).
In the free trace mode, trace acquisition is started with the execution of the user program and stopped by halting
the user program. The acquired trace information is displayed in the [Trace] window.
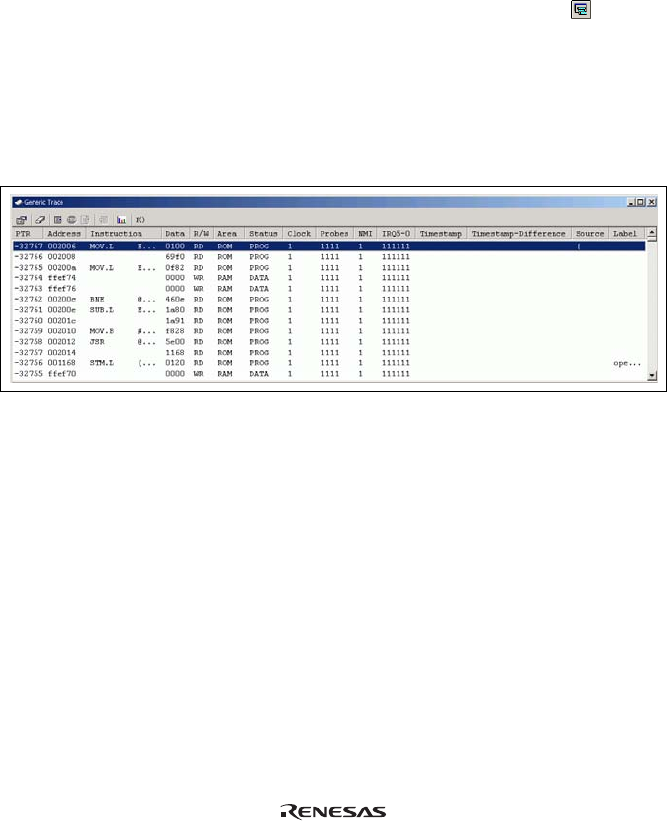
Figure 5.29 [Trace] Window
This window displays the following trace information items:
[PTR]: Cycle number in the trace buffer. When the most recent record is record 0, earlier
record numbers go backwards (-1, -2, ...). If a delay count has been set, the cycle
number where the trace stop condition has been satisfied is record 0. For the cycle
(during delay) executed until the trace has stopped, earlier record numbers go forward
(+1, +2, ...) the most recent record.
[Address]: Address (6-digit hexadecimal)
[Instruction]: Disassembled code of the executed instruction
[Data]: Data bus value, displayed as 2-digit or 4-digit hexadecimal
[R/W]: Whether access was read (RD) or write (WR)
[Area]: Memory area being accessed; ROM, RAM, 8- or 16-bit I/O, 8- or 16-bit EXT
(external), or DTC RAM (not available when a time stamp is acquired)










