Users Manual
Table Of Contents
- 34. IrDA Interface
- 35. I2C-bus Interface (RIICa)
- 35.1 Overview
- 35.2 Register Descriptions
- 35.2.1 I2C-bus Control Register 1 (ICCR1)
- 35.2.2 I2C-bus Control Register 2 (ICCR2)
- 35.2.3 I2C-bus Mode Register 1 (ICMR1)
- 35.2.4 I2C-bus Mode Register 2 (ICMR2)
- 35.2.5 I2C-bus Mode Register 3 (ICMR3)
- 35.2.6 I2C-bus Function Enable Register (ICFER)
- 35.2.7 I2C-bus Status Enable Register (ICSER)
- 35.2.8 I2C-bus Interrupt Enable Register (ICIER)
- 35.2.9 I2C-bus Status Register 1 (ICSR1)
- 35.2.10 I2C-bus Status Register 2 (ICSR2)
- 35.2.11 Slave Address Register Ly (SARLy) (y = 0 to 2)
- 35.2.12 Slave Address Register Uy (SARUy) (y = 0 to 2)
- 35.2.13 I2C-bus Bit Rate Low-Level Register (ICBRL)
- 35.2.14 I2C-bus Bit Rate High-Level Register (ICBRH)
- 35.2.15 I2C-bus Transmit Data Register (ICDRT)
- 35.2.16 I2C-bus Receive Data Register (ICDRR)
- 35.2.17 I2C-bus Shift Register (ICDRS)
- 35.3 Operation
- 35.4 SCL Synchronization Circuit
- 35.5 SDA Output Delay Function
- 35.6 Digital Noise Filters
- 35.7 Address Match Detection
- 35.8 Automatic Low-Hold Function for SCL
- 35.9 Arbitration-Lost Detection Functions
- 35.10 Start Condition/Restart Condition/Stop Condition Generating Function
- 35.11 Bus Hanging
- 35.12 SMBus Operation
- 35.13 Interrupt Sources
- 35.14 Initialization of Registers and Functions When a Reset is Applied or a Condition is Detected
- 35.15 Event Link Function (Output)
- 35.16 Usage Notes
- 36. CAN Module (RSCAN)
R01UH0823EJ0110 Rev.1.10 Page 1052 of 1852
Nov 30, 2020
RX23W Group 33. Serial Communications Interface (SCIg, SCIh)
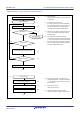
Figure 33.28 Example Flowchart of Serial Transmission in Clock Synchronous Mode
No
End
Yes
Initialization
Start transmission
Write transmit data to the TDR register
No
Yes
No
Yes
Set the SCR.TIE, TE, and TEIE bits to 0
TXI interrupt
All transmit data written?
TEI interrupt
[ 1 ]
[ 2 ]
[ 3 ]
Set the SCR.TIE bit to 0, and
set the SCR.TEIE bit to 1
[ 1 ] SCI initialization:
Set data transmission.
[ 2 ] Writing transmit data write to the TDR register by a TXI
interrupt request:
When transmit data is transferred from the TDR register
to the TSR register, a transmit data empty interrupt
(TXI) request is generated.
Transmit data is written to the TDR register once from
the handling routine for TXI requests.
[ 3 ] Serial transmission continuation procedure:
To continue serial transmission, write transmit data to
the TDR register upon accepting a transmit data empty
interrupt (TXI) request. Transmit data can also be
written to the TDR register by activating the DMAC or
DTC by the TXI interrupt request.
When TEI interrupt requests are in use, set the
SCR.TIE bit to 0 and the SCR.TEIE bit to 1 after the last
of the data to be transmitted are written to the TDR
register.
Note: When the external clock is in use (the value of the SCR.CKE[1:0] bits is 10b or 11b), the rising edge on the SCK pin for
the last bit sets the SSR.TEND flag to 1. Setting the SCR.TE bit to 0 immediately after this may lead to insufficient
received-data hold time on the receiver side.