User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Cover
- Notice
- General Precautions in the Handling of Microprocessing Unit and Microcontroller Unit Products
- How to Use This Manual
- Contents
- Features
- 1. Overview
- 2. CPU
- 2.1 Features
- 2.2 Register Set of the CPU
- 2.2.1 General-Purpose Registers (R0 to R15)
- 2.2.2 Control Registers
- 2.2.2.1 Interrupt Stack Pointer (ISP)/User Stack Pointer (USP)
- 2.2.2.2 Exception Table Register (EXTB)
- 2.2.2.3 Interrupt Table Register (INTB)
- 2.2.2.4 Program Counter (PC)
- 2.2.2.5 Processor Status Word (PSW)
- 2.2.2.6 Backup PC (BPC)
- 2.2.2.7 Backup PSW (BPSW)
- 2.2.2.8 Fast Interrupt Vector Register (FINTV)
- 2.2.2.9 Floating-Point Status Word (FPSW)
- 2.2.3 Accumulator
- 2.3 Processor Mode
- 2.4 Data Types
- 2.5 Endian
- 2.6 Vector Table
- 2.7 Operation of Instructions
- 2.8 Number of Cycles
- 3. Operating Modes
- 4. Address Space
- 5. I/O Registers
- 6. Resets
- 7. Option-Setting Memory (OFSM)
- 8. Voltage Detection Circuit (LVDAb)
- 9. Clock Generation Circuit
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Register Descriptions
- 9.2.1 System Clock Control Register (SCKCR)
- 9.2.2 System Clock Control Register 3 (SCKCR3)
- 9.2.3 PLL Control Register (PLLCR)
- 9.2.4 PLL Control Register 2 (PLLCR2)
- 9.2.5 USB-dedicated PLL Control Register (UPLLCR)
- 9.2.6 USB-dedicated PLL Control Register 2 (UPLLCR2)
- 9.2.7 Main Clock Oscillator Control Register (MOSCCR)
- 9.2.8 Sub-Clock Oscillator Control Register (SOSCCR)
- 9.2.9 Low-Speed On-Chip Oscillator Control Register (LOCOCR)
- 9.2.10 IWDT-Dedicated On-Chip Oscillator Control Register (ILOCOCR)
- 9.2.11 High-Speed On-Chip Oscillator Control Register (HOCOCR)
- 9.2.12 High-Speed On-Chip Oscillator Control Register 2 (HOCOCR2)
- 9.2.13 Oscillation Stabilization Flag Register (OSCOVFSR)
- 9.2.14 Oscillation Stop Detection Control Register (OSTDCR)
- 9.2.15 Oscillation Stop Detection Status Register (OSTDSR)
- 9.2.16 Main Clock Oscillator Wait Control Register (MOSCWTCR)
- 9.2.17 CLKOUT Output Control Register (CKOCR)
- 9.2.18 Main Clock Oscillator Forced Oscillation Control Register (MOFCR)
- 9.2.19 Memory Wait Cycle Setting Register (MEMWAIT)
- 9.2.20 Low-Speed On-Chip Oscillator Trimming Register (LOCOTRR)
- 9.2.21 IWDT-Dedicated On-Chip Oscillator Trimming Register (ILOCOTRR)
- 9.2.22 High-Speed On-Chip Oscillator Trimming Register n (HOCOTRRn) (n = 0, 3)
- 9.3 Main Clock Oscillator
- 9.4 Sub-Clock Oscillator
- 9.5 Dedicated Clock Oscillator for Bluetooth
- 9.6 Oscillation Stop Detection Function
- 9.7 PLL Circuit
- 9.8 Internal Clock
- 9.9 Usage Notes
- 10. Clock Frequency Accuracy Measurement Circuit (CAC)
- 10.1 Overview
- 10.2 Register Descriptions
- 10.2.1 CAC Control Register 0 (CACR0)
- 10.2.2 CAC Control Register 1 (CACR1)
- 10.2.3 CAC Control Register 2 (CACR2)
- 10.2.4 CAC Interrupt Request Enable Register (CAICR)
- 10.2.5 CAC Status Register (CASTR)
- 10.2.6 CAC Upper-Limit Value Setting Register (CAULVR)
- 10.2.7 CAC Lower-Limit Value Setting Register (CALLVR)
- 10.2.8 CAC Counter Buffer Register (CACNTBR)
- 10.3 Operation
- 10.4 Interrupt Requests
- 10.5 Usage Notes
- 11. Low Power Consumption
- 11.1 Overview
- 11.2 Register Descriptions
- 11.2.1 Standby Control Register (SBYCR)
- 11.2.2 Module Stop Control Register A (MSTPCRA)
- 11.2.3 Module Stop Control Register B (MSTPCRB)
- 11.2.4 Module Stop Control Register C (MSTPCRC)
- 11.2.5 Module Stop Control Register D (MSTPCRD)
- 11.2.6 Operating Power Control Register (OPCCR)
- 11.2.7 Sub Operating Power Control Register (SOPCCR)
- 11.2.8 Sleep Mode Return Clock Source Switching Register (RSTCKCR)
- 11.3 Reducing Power Consumption by Switching Clock Signals
- 11.4 Module Stop Function
- 11.5 Function for Lower Operating Power Consumption
- 11.6 Low Power Consumption Modes
- 11.7 Usage Notes
- 12. Battery Backup Function
- 13. Register Write Protection Function
- 14. Exception Handling
- 15. Interrupt Controller (ICUb)
- 15.1 Overview
- 15.2 Register Descriptions
- 15.2.1 Interrupt Request Register n (IRn) (n = interrupt vector number)
- 15.2.2 Interrupt Request Enable Register m (IERm) (m = 02h to 1Fh)
- 15.2.3 Interrupt Source Priority Register n (IPRn) (n = interrupt vector number)
- 15.2.4 Fast Interrupt Set Register (FIR)
- 15.2.5 Software Interrupt Generation Register (SWINTR)
- 15.2.6 DTC Transfer Request Enable Register n (DTCERn) (n = interrupt vector number)
- 15.2.7 DMAC Trigger Select Register m (DMRSRm) (m = DMAC channel number)
- 15.2.8 IRQ Control Register i (IRQCRi) (i = 0, 1, and 4 to 7)
- 15.2.9 IRQ Pin Digital Filter Enable Register 0 (IRQFLTE0)
- 15.2.10 IRQ Pin Digital Filter Setting Register 0 (IRQFLTC0)
- 15.2.11 Non-Maskable Interrupt Status Register (NMISR)
- 15.2.12 Non-Maskable Interrupt Enable Register (NMIER)
- 15.2.13 Non-Maskable Interrupt Status Clear Register (NMICLR)
- 15.2.14 NMI Pin Interrupt Control Register (NMICR)
- 15.2.15 NMI Pin Digital Filter Enable Register (NMIFLTE)
- 15.2.16 NMI Pin Digital Filter Setting Register (NMIFLTC)
- 15.3 Vector Table
- 15.4 Interrupt Operation
- 15.5 Non-maskable Interrupt Operation
- 15.6 Return from Power-Down States
- 15.7 Usage Note
- 16. Buses
- 17. Memory-Protection Unit (MPU)
- 17.1 Overview
- 17.2 Register Descriptions
- 17.2.1 Region-n Start Page Number Register (RSPAGEn) (n = 0 to 7)
- 17.2.2 Region-n End Page Number Register (REPAGEn) (n = 0 to 7)
- 17.2.3 Memory-Protection Enable Register (MPEN)
- 17.2.4 Background Access Control Register (MPBAC)
- 17.2.5 Memory-Protection Error Status-Clearing Register (MPECLR)
- 17.2.6 Memory-Protection Error Status Register (MPESTS)
- 17.2.7 Data Memory-Protection Error Address Register (MPDEA)
- 17.2.8 Region Search Address Register (MPSA)
- 17.2.9 Region Search Operation Register (MPOPS)
- 17.2.10 Region Invalidation Operation Register (MPOPI)
- 17.2.11 Instruction-Hit Region Register (MHITI)
- 17.2.12 Data-Hit Region Register (MHITD)
- 17.3 Functions
- 17.4 Procedures for Using Memory Protection
- 18. DMA Controller (DMACA)
- 18.1 Overview
- 18.2 Register Descriptions
- 18.2.1 DMA Source Address Register (DMSAR)
- 18.2.2 DMA Destination Address Register (DMDAR)
- 18.2.3 DMA Transfer Count Register (DMCRA)
- 18.2.4 DMA Block Transfer Count Register (DMCRB)
- 18.2.5 DMA Transfer Mode Register (DMTMD)
- 18.2.6 DMA Interrupt Setting Register (DMINT)
- 18.2.7 DMA Address Mode Register (DMAMD)
- 18.2.8 DMA Offset Register (DMOFR)
- 18.2.9 DMA Transfer Enable Register (DMCNT)
- 18.2.10 DMA Software Start Register (DMREQ)
- 18.2.11 DMA Status Register (DMSTS)
- 18.2.12 DMA Activation Source Flag Control Register (DMCSL)
- 18.2.13 DMA Module Activation Register (DMAST)
- 18.3 Operation
- 18.4 Ending DMA Transfer
- 18.5 Interrupts
- 18.6 Event Link Function
- 18.7 Low Power Consumption Function
- 18.8 Usage Notes
- 18.8.1 DMA Transfer to Peripheral Modules
- 18.8.2 Access to the Registers during DMA Transfer
- 18.8.3 DMA Transfer to Reserved Areas
- 18.8.4 Interrupt Request by the DMA Activation Source Flag Control Register (DMCSL) at the End of each Transfer
- 18.8.5 Setting of DMAC Activation Source Select Register of the Interrupt Controller (ICU.DMRSRm)
- 18.8.6 Suspending or Restarting DMA Activation
- 19. Data Transfer Controller (DTCa)
- 19.1 Overview
- 19.2 Register Descriptions
- 19.2.1 DTC Mode Register A (MRA)
- 19.2.2 DTC Mode Register B (MRB)
- 19.2.3 DTC Transfer Source Register (SAR)
- 19.2.4 DTC Transfer Destination Register (DAR)
- 19.2.5 DTC Transfer Count Register A (CRA)
- 19.2.6 DTC Transfer Count Register B (CRB)
- 19.2.7 DTC Control Register (DTCCR)
- 19.2.8 DTC Vector Base Register (DTCVBR)
- 19.2.9 DTC Address Mode Register (DTCADMOD)
- 19.2.10 DTC Module Start Register (DTCST)
- 19.2.11 DTC Status Register (DTCSTS)
- 19.3 Request Sources
- 19.4 Operation
R01UH0823EJ0110 Rev.1.10 Page 209 of 1852
Nov 30, 2020
RX23W Group 9. Clock Generation Circuit
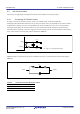
Figure 9.13 Flow of Recovery from Detection of Oscillator Stop
9.6.2 Oscillation Stop Detection Interrupts
The main clock oscillator stop is notified to port output enable 23 (POE) if the oscillation-stop detection flag
(OSTDSR.OSTDF) becomes 1 while the oscillation-stop detection interrupt enable bit (OSTDCR.OSTDIE) is 1
(oscillation stop detection interrupt enabled). On accepting the notification of the oscillation stop, the POE sets the
OSTST high-impedance flag in input level control/status register 3 (ICSR3.OSTSTF) to 1. After the oscillation stop is
detected, wait for at lease 10 cycles of PCLK before writing to this ICSR3.OSTSTF flag. When the OSTDSR.OSTDF
flag requires clearing, do so setting the oscillation stop detection interrupt enable bit (OSTDCR.OSTDIE) to 0. Wait for
at least two cycles of PCLKB clock before again setting the OSTDCR.OSTDIE bit to 1. According to the number of
cycles for access to read a given I/O register, wait time longer than two cycles of PCLKB may have to be secured.
The oscillation stop detection interrupt is a non-maskable interrupt. Since non-maskable interrupts are disabled in the
initial state after a reset release, enable the non-maskable interrupts by the software before using oscillation stop
detection interrupts. For details, refer to section 15, Interrupt Controller (ICUb).
When the PLL detects an oscillation stop and is running at its own oscillation frequency, this indicates the occurrence of
some system failure. An emergency measure should be taken to handle the failure.
Start
Switch to SCKCR3.CKSEL[2:0] = 000b
(LOCO)
Setting OSTDCR.OSTDIE = 0
Setting OSTDSR.OSTDF = 0
OSTDSR.OSTDF = 0
Switch to SCKCR3.CKSEL[2:0] = 010b
(main clock oscillator)
End
Yes
Reading OSTDSR.OSTDF = 1
Try again?
Yes
No
No
Note: On return from the oscillation-stopped state, the factor responsible for stopping the main clock oscillation
circuit must be removed on the user system to allow the return of oscillation.