Users Manual
Table Of Contents
- 37. Serial Sound Interface (SSI)
- 38. Serial Peripheral Interface (RSPIa)
- 38.1 Overview
- 38.2 Register Descriptions
- 38.2.1 RSPI Control Register (SPCR)
- 38.2.2 RSPI Slave Select Polarity Register (SSLP)
- 38.2.3 RSPI Pin Control Register (SPPCR)
- 38.2.4 RSPI Status Register (SPSR)
- 38.2.5 RSPI Data Register (SPDR)
- 38.2.6 RSPI Sequence Control Register (SPSCR)
- 38.2.7 RSPI Sequence Status Register (SPSSR)
- 38.2.8 RSPI Bit Rate Register (SPBR)
- 38.2.9 RSPI Data Control Register (SPDCR)
- 38.2.10 RSPI Clock Delay Register (SPCKD)
- 38.2.11 RSPI Slave Select Negation Delay Register (SSLND)
- 38.2.12 RSPI Next-Access Delay Register (SPND)
- 38.2.13 RSPI Control Register 2 (SPCR2)
- 38.2.14 RSPI Command Register m (SPCMDm) (m = 0 to 7)
- 38.3 Operation
- 38.3.1 Overview of RSPI Operations
- 38.3.2 Controlling RSPI Pins
- 38.3.3 RSPI System Configuration Examples
- 38.3.3.1 Single Master/Single Slave (with This MCU Acting as Master)
- 38.3.3.2 Single Master/Single Slave (with This MCU Acting as Slave)
- 38.3.3.3 Single Master/Multi-Slave (with This MCU Acting as Master)
- 38.3.3.4 Single Master/Multi-Slave (with This MCU Acting as Slave)
- 38.3.3.5 Multi-Master/Multi-Slave (with This MCU Acting as Master)
- 38.3.3.6 Master (Clock Synchronous Operation)/Slave (Clock Synchronous Operation) (with This MCU Acting as Master)
- 38.3.3.7 Master (Clock Synchronous Operation)/Slave (Clock Synchronous Operation) (with This MCU Acting as Slave)
- 38.3.4 Data Format
- 38.3.5 Transfer Format
- 38.3.6 Communications Operating Mode
- 38.3.7 Transmit Buffer Empty/Receive Buffer Full Interrupts
- 38.3.8 Error Detection
- 38.3.9 Initializing RSPI
- 38.3.10 SPI Operation
- 38.3.11 Clock Synchronous Operation
- 38.3.12 Loopback Mode
- 38.3.13 Self-Diagnosis of Parity Bit Function
- 38.3.14 Interrupt Sources
- 38.4 Link Operation by Event Linking
- 38.5 Usage Notes
- 39. CRC Calculator (CRC)
- 40. SD Host Interface (SDHIa)
- 40.1 Overview
- 40.2 Register Details
- 40.2.1 Command Register (SDCMD)
- 40.2.2 Argument Register (SDARG)
- 40.2.3 Data Stop Register (SDSTOP)
- 40.2.4 Block Count Register (SDBLKCNT)
- 40.2.5 Response Register 10 (SDRSP10), Response Register 32 (SDRSP32), Response Register 54 (SDRSP54), Response Register 76 (SDRSP76)
- 40.2.6 SD Status Register 1 (SDSTS1)
- 40.2.7 SD Status Register 2 (SDSTS2)
- 40.2.8 SD Interrupt Mask Register 1 (SDIMSK1)
- 40.2.9 SD Interrupt Mask Register 2 (SDIMSK2)
- 40.2.10 SDHI Clock Control Register (SDCLKCR)
- 40.2.11 Transfer Data Size Register (SDSIZE)
- 40.2.12 Card Access Option Register (SDOPT)
- 40.2.13 SD Error Status Register 1 (SDERSTS1)
- 40.2.14 SD Error Status Register 2 (SDERSTS2)
- 40.2.15 SD Buffer Register (SDBUFR)
- 40.2.16 SDIO Mode Control Register (SDIOMD)
- 40.2.17 SDIO Status Register (SDIOSTS)
- 40.2.18 SDIO Interrupt Mask Register (SDIOIMSK)
- 40.2.19 DMA Transfer Enable Register (SDDMAEN)
- 40.2.20 SDHI Software Reset Register (SDRST)
- 40.2.21 Swap Control Register (SDSWAP)
- 40.3 SDHI Operation
- 40.3.1 Data Block Format of the SD Card
- 40.3.2 SD Buffer and the SDBUFR Register
- 40.3.3 SD Card Detection
- 40.3.4 SD Card Write Protection
- 40.3.5 Communication Errors and Timeouts
- 40.3.6 Examples of Issuing a Command
- 40.3.6.1 Command Absent of Response Reception and Data Transfer
- 40.3.6.2 Command Absent of Data Transfer
- 40.3.6.3 Single Block Read Command (CMD17)
- 40.3.6.4 Single Block Write Command (CMD24)
- 40.3.6.5 Multi-Block Read Command (CMD18)
- 40.3.6.6 Multi-Block Write Command (CMD25)
- 40.3.6.7 IO_RW_DIRECT Command (CMD52)
- 40.3.6.8 IO_RW_EXTENDED Command (CMD53 (Multi-Block Read))
- 40.3.6.9 IO_RW_EXTENDED (CMD53 Multi-Block Write)
- 40.3.6.10 DMA Transfer
- 40.4 Interrupts
- 40.5 Notes on Using the SDHI
- 40.5.1 Illegal Read Access During a Multi-Block Read and How To Avoid It
- 40.5.2 SDBUFR Register Illegal Write Error
- 40.5.3 Automatic Control of the SDHI Clock Output
- 40.5.4 Restrictions on Setting the C52PUB Bit During a Multi-Block Write Sequence
- 40.5.5 Note on Setting the SDCLKCR Register
- 40.5.6 Writing to the SDSTOP Register During a Multi-Block Read Sequence
- 40.5.7 Controlling Module Operation
- 41. Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
- 42. Trusted Secure IP (TSIP-Lite)
- 43. Capacitive Touch Sensing Unit (CTSU)
- 43.1 Overview
- 43.2 Register Descriptions
- 43.2.1 CTSU Control Register 0 (CTSUCR0)
- 43.2.2 CTSU Control Register 1 (CTSUCR1)
- 43.2.3 CTSU Synchronous Noise Reduction Setting Register (CTSUSDPRS)
- 43.2.4 CTSU Sensor Stabilization Wait Control Register (CTSUSST)
- 43.2.5 CTSU Measurement Channel Register 0 (CTSUMCH0)
- 43.2.6 CTSU Measurement Channel Register 1 (CTSUMCH1)
- 43.2.7 CTSU Channel Enable Control Register 0 (CTSUCHAC0)
- 43.2.8 CTSU Channel Enable Control Register 1 (CTSUCHAC1)
- 43.2.9 CTSU Channel Enable Control Register 2 (CTSUCHAC2)
- 43.2.10 CTSU Channel Enable Control Register 3 (CTSUCHAC3)
- 43.2.11 CTSU Channel Enable Control Register 4 (CTSUCHAC4)
- 43.2.12 CTSU Channel Transmit/Receive Control Register 0 (CTSUCHTRC0)
- 43.2.13 CTSU Channel Transmit/Receive Control Register 1 (CTSUCHTRC1)
- 43.2.14 CTSU Channel Transmit/Receive Control Register 2 (CTSUCHTRC2)
- 43.2.15 CTSU Channel Transmit/Receive Control Register 3 (CTSUCHTRC3)
- 43.2.16 CTSU Channel Transmit/Receive Control Register 4 (CTSUCHTRC4)
- 43.2.17 CTSU High-Pass Noise Reduction Control Register (CTSUDCLKC)
- 43.2.18 CTSU Status Register (CTSUST)
- 43.2.19 CTSU High-Pass Noise Reduction Spectrum Diffusion Control Register (CTSUSSC)
- 43.2.20 CTSU Sensor Offset Register 0 (CTSUSO0)
- 43.2.21 CTSU Sensor Offset Register 1 (CTSUSO1)
- 43.2.22 CTSU Sensor Counter (CTSUSC)
- 43.2.23 CTSU Reference Counter (CTSURC)
- 43.2.24 CTSU Error Status Register (CTSUERRS)
- 43.3 Operation
- 43.4 Usage Notes
- 44. 12-Bit A/D Converter (S12ADE)
- 44.1 Overview
- 44.2 Register Descriptions
- 44.2.1 A/D Data Registers y (ADDRy) (y = 0 to 7, 16 to 20, 27), A/D Data Duplication Register (ADDBLDR), A/D Temperature Sensor Data Register (ADTSDR), A/D Internal Reference Voltage Data Register (ADOCDR)
- 44.2.2 A/D Self-Diagnosis Data Register (ADRD)
- 44.2.3 A/D Control Register (ADCSR)
- 44.2.4 A/D Channel Select Register A0 (ADANSA0)
- 44.2.5 A/D Channel Select Register A1 (ADANSA1)
- 44.2.6 A/D Channel Select Register B0 (ADANSB0)
- 44.2.7 A/D Channel Select Register B1 (ADANSB1)
- 44.2.8 A/D-Converted Value Addition/Average Function Select Register 0 (ADADS0)
- 44.2.9 A/D-Converted Value Addition/Average Function Select Register 1 (ADADS1)
- 44.2.10 A/D-Converted Value Addition/Average Count Select Register (ADADC)
- 44.2.11 A/D Control Extended Register (ADCER)
- 44.2.12 A/D Conversion Start Trigger Select Register (ADSTRGR)
- 44.2.13 A/D Conversion Extended Input Control Register (ADEXICR)
- 44.2.14 A/D Sampling State Register n (ADSSTRn) (n = 0 to 7, L, T, O)
- 44.2.15 A/D Disconnection Detection Control Register (ADDISCR)
- 44.2.16 A/D Event Link Control Register (ADELCCR)
- 44.2.17 A/D Group Scan Priority Control Register (ADGSPCR)
- 44.2.18 A/D Compare Function Control Register (ADCMPCR)
- 44.2.19 A/D Compare Function Window A Channel Select Register 0 (ADCMPANSR0)
- 44.2.20 A/D Compare Function Window A Channel Select Register 1 (ADCMPANSR1)
- 44.2.21 A/D Compare Function Window A Extended Input Select Register (ADCMPANSER)
- 44.2.22 A/D Compare Function Window A Comparison Condition Setting Register 0 (ADCMPLR0)
- 44.2.23 A/D Compare Function Window A Comparison Condition Setting Register 1 (ADCMPLR1)
- 44.2.24 A/D Compare Function Window A Extended Input Comparison Condition Setting Register (ADCMPLER)
- 44.2.25 A/D Compare Function Window A Lower-Side Level Setting Register (ADCMPDR0)
- 44.2.26 A/D Compare Function Window A Upper-Side Level Setting Register (ADCMPDR1)
- 44.2.27 A/D Compare Function Window A Channel Status Register 0 (ADCMPSR0)
- 44.2.28 A/D Compare Function Window A Channel Status Register 1 (ADCMPSR1)
- 44.2.29 A/D Compare Function Window A Extended Input Channel Status Register (ADCMPSER)
- 44.2.30 A/D High-Potential/Low-Potential Reference Voltage Control Register (ADHVREFCNT)
- 44.2.31 A/D Compare Function Window A/B Status Monitor Register (ADWINMON)
- 44.2.32 A/D Compare Function Window B Channel Select Register (ADCMPBNSR)
- 44.2.33 A/D Compare Function Window B Lower-Side Level Setting Register (ADWINLLB)
- 44.2.34 A/D Compare Function Window B Upper-Side Level Setting Register (ADWINULB)
- 44.2.35 A/D Compare Function Window B Channel Status Register (ADCMPBSR)
- 44.2.36 A/D Data Storage Buffer Register n (ADBUFn) (n = 0 to 15)
R01UH0823EJ0110 Rev.1.10 Page 1492 of 1852
Nov 30, 2020
RX23W Group 42. Trusted Secure IP (TSIP-Lite)
42. Trusted Secure IP (TSIP-Lite)
This MCU incorporates a Trusted Secure IP Lite (TSIP-Lite) module to provide security functions. The module consists
of an access management circuit, encryption engine, and random number generator. In combination with the TSIP-Lite
library, the TSIP-Lite can prevent eavesdropping (confidentiality), falsification of information (integrity), and
impersonation (authenticity).
Key information to be used in encrypting and decrypting data is only stored within the TSIP-Lite, and any external
access can be shut out to obtain a system with strong security.
42.1 Overview
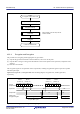
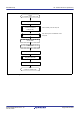
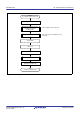
Table 42.1 summarizes the specifications of the TSIP-Lite. Figure 42.1 shows a block diagram of the TSIP-Lite.
Note 1. This does not include the overhead for calling functions of the TSIP-Lite library.
Table 42.1 Specifications of TSIP-Lite
Item Description
Access control Access management circuit
• In case of irregular access to the TSIP-Lite due to a falsified program or runaway execution of a program,
this circuit blocks all subsequent access and stops the output of data from the TSIP-Lite.
Encryption engine AES: Compliant with NIST FIPS PUB 197 algorithm
• Key sizes: 128 or 256 bits
• Block sizes: 128 bits
• Block cipher mode of operation
ECB, CBC, CTR: Compliant with NIST SP 800-38A
CMAC: Compliant with NIST SP 800-38B
CCM: Compliant with NIST SP 800-38C
GCM: Compliant with NIST SP 800-38D
XTS: Compliant with NIST SP 800-38E
GCTR
• Number of cycles for execution*
1
ECB, CBC, CTR, CMAC, GCTR, XTS:
44 cycles of PCLKB for 128-bit keys, 61 cycles of PCLKB for 256-bit keys
CCM:
88 cycles of PCLKB for 128-bit keys
AES-GCM
• AES-GCM is realized by combining AES-GCTR and GHASH.
Key management
• Keys are only valid within the TSIP-Lite.
• Only key generation information is output from the TSIP-Lite.
• Keys can be regenerated by the input of key generation information to the TSIP-Lite.
Endian
• Big or little
Generation of random
numbers
32-bit true random number generator
• The TSIP-Lite library can assemble 32-bit true random numbers to generate 128- or 256-bit true random
numbers.
• The generated 128-bit and 256-bit true random numbers are used as keys in encrypting and decrypting
data.
Protection against illicit
key copying
• An ID unique to the MCU (unique ID) is accessible from the access management circuit through the
dedicated bus.
• Combining the unique ID with the key generation information prevents the illicit copying of the key to
another MCU.
Supervisor mode
• The supervisor mode signal is connected to the access management circuit and is used to limit control of
the TSIP-Lite module to supervisor mode only.
Interrupt sources Three
These can be used as triggers for data transfer by the DMAC or DTC.
Low power
consumption
Setting of the module stop state is possible.