Installation guide
To administer a cluster or storage, an administrator adds (or registers) a cluster or a computer to a
lu ci server. When a cluster or a computer is registered with lu ci, the FQDN hostname or IP address
of each computer is stored in a lu ci database.
You can populate the database of one lu ci instance from another lu ciinstance. That capability
provides a means of replicating a lu ci server instance and provides an efficient upgrade and testing
path. When you install an instance of lu ci, its database is empty. However, you can import part or all
of a lu ci database from an existing lu ci server when deploying a new lu ci server.
Each lu ci instance has one user at initial installation — admin. Only the admin user may add
systems to a lu ci server. Also, the admin user can create additional user accounts and determine
which users are allowed to access clusters and computers registered in the lu ci database. It is
possible to import users as a batch operation in a new lu ci server, just as it is possible to import
clusters and computers.
When a computer is added to a lu ci server to be administered, authentication is done once. No
authentication is necessary from then on (unless the certificate used is revoked by a CA). After that,
you can remotely configure and manage clusters and storage through the lu ci user interface. lu ci
and ricci communicate with each other via XML.
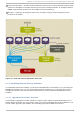
The following figures show sample displays of the three major lu ci tabs: h o meb ase, clu st er, and
st o rag e.
For more information about C o n g a, refer to Chapter 3, Configuring Red Hat Cluster With Conga,
Chapter 4, Managing Red Hat Cluster With Conga, and the online help available with the lu ci server.
Fig u re 1.3. lu ci h o meb ase T ab
Red Hat Ent erprise Linux 5 Clust er Administ rat ion
12