Installation guide
Table Of Contents
- LVM Administrator's Guide
- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Chapter 1. The LVM Logical Volume Manager
- Chapter 2. LVM Components
- Chapter 3. LVM Administration Overview
- Chapter 4. LVM Administration with CLI Commands
- 1. Using CLI Commands
- 2. Physical Volume Administration
- 3. Volume Group Administration
- 3.1. Creating Volume Groups
- 3.2. Adding Physical Volumes to a Volume Group
- 3.3. Displaying Volume Groups
- 3.4. Scanning Disks for Volume Groups to Build the Cache File
- 3.5. Removing Physical Volumes from a Volume Group
- 3.6. Changing the Parameters of a Volume Group
- 3.7. Activating and Deactivating Volume Groups
- 3.8. Removing Volume Groups
- 3.9. Splitting a Volume Group
- 3.10. Combining Volume Groups
- 3.11. Backing Up Volume Group Metadata
- 3.12. Renaming a Volume Group
- 3.13. Moving a Volume Group to Another System
- 3.14. Recreating a Volume Group Directory
- 4. Logical Volume Administration
- 4.1. Creating Logical Volumes
- 4.2. Persistent Device Numbers
- 4.3. Resizing Logical Volumes
- 4.4. Changing the Parameters of a Logical Volume Group
- 4.5. Renaming Logical Volumes
- 4.6. Removing Logical Volumes
- 4.7. Displaying Logical Volumes
- 4.8. Growing Logical Volumes
- 4.9. Extending a Striped Volume
- 4.10. Shrinking Logical Volumes
- 5. Creating Snapshot Volumes
- 6. Controlling LVM Device Scans with Filters
- 7. Online Data Relocation
- 8. Activating Logical Volumes on Individual Nodes in a Cluster
- 9. Customized Reporting for LVM
- Chapter 5. LVM Configuration Examples
- Chapter 6. LVM Troubleshooting
- Chapter 7. LVM Administration with the LVM GUI
- Appendix A. The Device Mapper
- Appendix B. The LVM Configuration Files
- Appendix C. LVM Object Tags
- Appendix D. LVM Volume Group Metadata
- Index
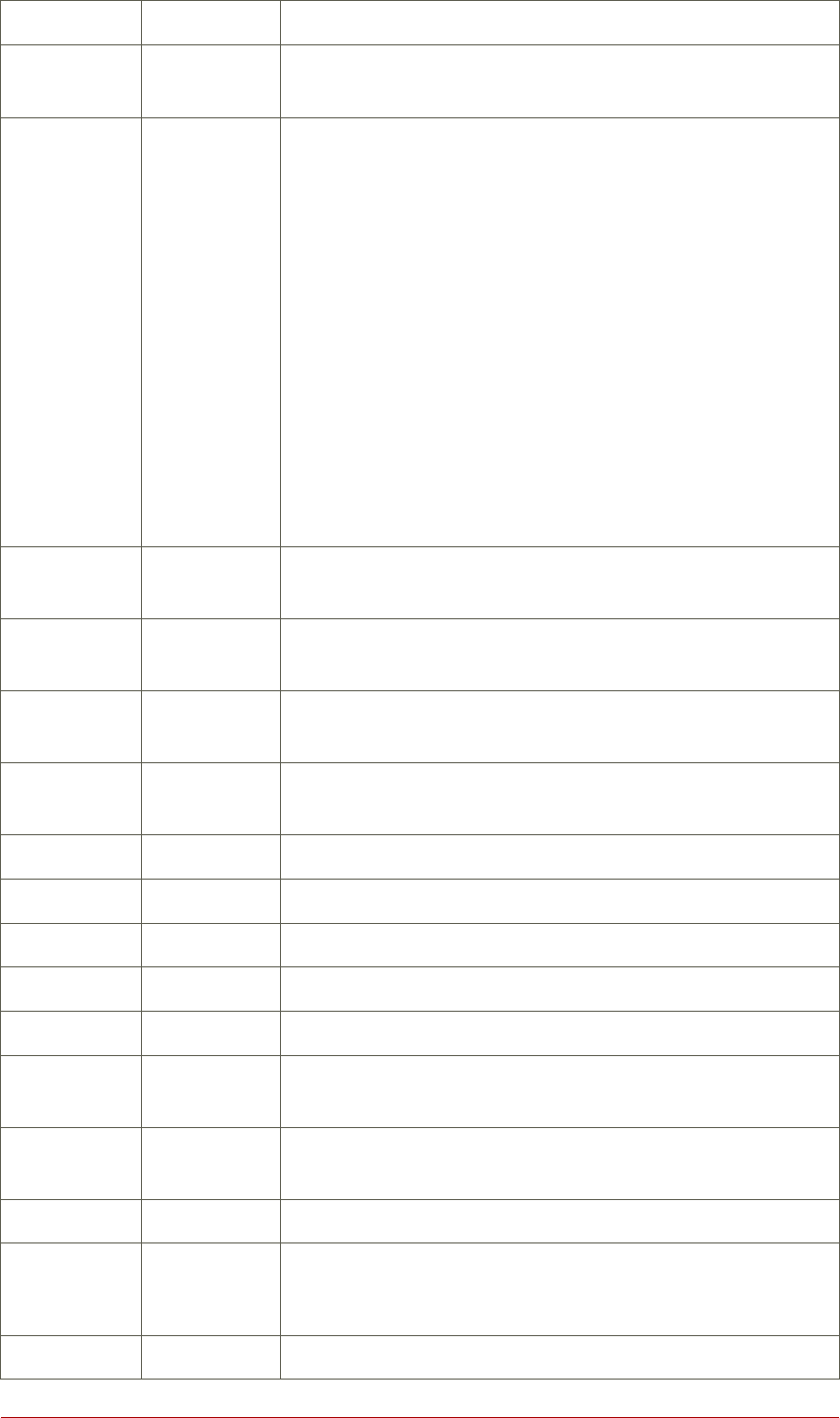
Argument Header Description
physical volumes, logical volumes, and start physical extents
and logical extents
lv_attr Attr The status of the logical volume. The logical volume attribute
bits are as follows:
Bit 1: Volume type: (m)irrored, (M)irrored without initial sync,
(o)rigin, (p)vmove, (s)napshot, invalid (S)napshot, (v)irtual
Bit2: Permissions: (w)riteable, (r)ead-only
Bit 3: Allocation policy: (c)ontiguous, (n)ormal, (a)nywhere,
(i)nherited. This is capitalized if the volume is currently locked
against allocation changes, for example while executing the
pvmove command.
Bit 4: fixed (m)inor
Bit 5 State: (a)ctive, (s)uspended, (I)nvalid snapshot, invalid
(S)uspended snapshot, mapped (d)evice present without
tables, mapped device present with (i)nactive table
Bit 6: device (o)pen
lv_kernel_maj
or
KMaj Actual major device number of the logical volume (-1 if inact-
ive)
lv_kernel_min
or
KMIN Actual minor device number of the logical volume (-1 if inact-
ive)
lv_major Maj The persistent major device number of the logical volume (-1
if not specified)
lv_minor Min The persistent minor device number of the logical volume (-1
if not specified)
lv_name LV The name of the logical volume
lv_size LSize The size of the logical volume
lv_tags LV Tags LVM tags attached to the logical volume
lv_uuid LV UUID The UUID of the logical volume.
mirror_log Log Device on which the mirror log resides
modules Modules Corresponding kernel device-mapper target necessary to use
this logical volume
move_pv Move Source physical volume of a temporary logical volume created
with the pvmove command
origin Origin The origin device of a snapshot volume
regionsize
region_size
Region The unit size of a mirrored logical volume
seg_count #Seg The number of segments in the logical volume
9.2. Object Selection
46










