Installation guide
Table Of Contents
- LVM Administrator's Guide
- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Chapter 1. The LVM Logical Volume Manager
- Chapter 2. LVM Components
- Chapter 3. LVM Administration Overview
- Chapter 4. LVM Administration with CLI Commands
- 1. Using CLI Commands
- 2. Physical Volume Administration
- 3. Volume Group Administration
- 3.1. Creating Volume Groups
- 3.2. Adding Physical Volumes to a Volume Group
- 3.3. Displaying Volume Groups
- 3.4. Scanning Disks for Volume Groups to Build the Cache File
- 3.5. Removing Physical Volumes from a Volume Group
- 3.6. Changing the Parameters of a Volume Group
- 3.7. Activating and Deactivating Volume Groups
- 3.8. Removing Volume Groups
- 3.9. Splitting a Volume Group
- 3.10. Combining Volume Groups
- 3.11. Backing Up Volume Group Metadata
- 3.12. Renaming a Volume Group
- 3.13. Moving a Volume Group to Another System
- 3.14. Recreating a Volume Group Directory
- 4. Logical Volume Administration
- 4.1. Creating Logical Volumes
- 4.2. Persistent Device Numbers
- 4.3. Resizing Logical Volumes
- 4.4. Changing the Parameters of a Logical Volume Group
- 4.5. Renaming Logical Volumes
- 4.6. Removing Logical Volumes
- 4.7. Displaying Logical Volumes
- 4.8. Growing Logical Volumes
- 4.9. Extending a Striped Volume
- 4.10. Shrinking Logical Volumes
- 5. Creating Snapshot Volumes
- 6. Controlling LVM Device Scans with Filters
- 7. Online Data Relocation
- 8. Activating Logical Volumes on Individual Nodes in a Cluster
- 9. Customized Reporting for LVM
- Chapter 5. LVM Configuration Examples
- Chapter 6. LVM Troubleshooting
- Chapter 7. LVM Administration with the LVM GUI
- Appendix A. The Device Mapper
- Appendix B. The LVM Configuration Files
- Appendix C. LVM Object Tags
- Appendix D. LVM Volume Group Metadata
- Index
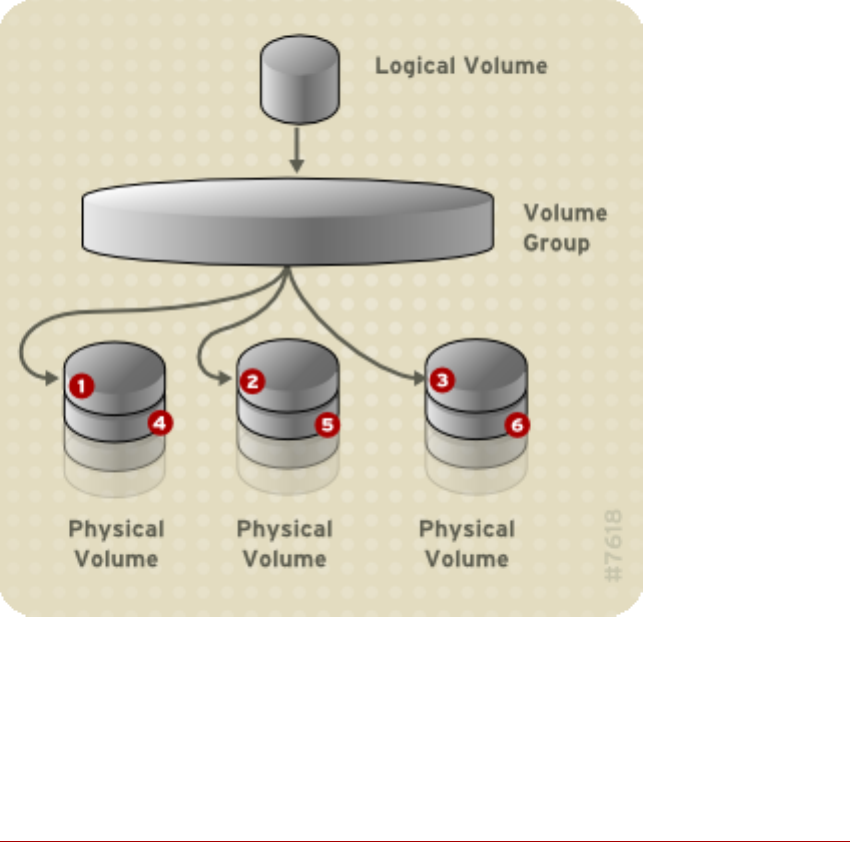
3.2. Striped Logical Volumes
When you write data to an LVM logical volume, the file system lays the data out across the un-
derlying physical volumes. You can control the way the data is written to the physical volumes
by creating a striped logical volume. For large sequential reads and writes, this can improve the
efficiency of the data I/O.
Striping enhances performance by writing data to a predetermined number of physical volumes
in round-round fashion. With striping, I/O can be done in parallel. In some situations, this can
result in near-linear performance gain for each additional physical volume in the stripe.
The following illustration shows data being striped across three physical volumes. In this figure:
• the first stripe of data is written to PV1
• the second stripe of data is written to PV2
• the third stripe of data is written to PV3
• the fourth stripe of data is written to PV1
In a striped logical volume, the size of the stripe cannnot exceed the size of an extent.
Figure 2.5. Striping Data Across Three PVs
Striped logical volumes can be extended by concatenating another set of devices onto the end
of the first set. In order extend a striped logical volume, however, there must be enough free
3.2. Striped Logical Volumes
11










