Installation guide
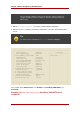
Cluster Nodes” lists the IP port numbers, their respective protocols, the components to which
the port numbers are assigned, and references to iptables rule examples. At each cluster
node, enable IP ports according to Table 2.1, “Enabled IP Ports on Red Hat Cluster Nodes”. (All
examples are in Section 2.3, “Examples of iptables Rules”.)
IP Port
Number
Protocol Component Reference to Example of
iptables Rules
5404,
5405
UDP cman (Cluster Manager) Example 2.1, “Port 5404, 5405:
cman”
11111 TCP ricci (part of Conga remote
agent)
Example 2.3, “Port 11111: ricci
(Cluster Node and Computer
Running luci)”
14567 TCP gnbd (Global Network Block
Device)
Example 2.4, “Port 14567: gnbd”
16851 TCP modclusterd (part of Conga
remote agent)
Example 2.5, “Port 16851:
modclusterd”
21064 TCP dlm (Distributed Lock Manager) Example 2.6, “Port 21064: dlm”
41966,
41967,
41968,
41969
TCP rgmanager (high-availability
service management)
Example 2.7, “Ports 41966,
41967, 41968, 41969:
rgmanager”
50006,
50008,
50009
TCP ccsd (Cluster Configuration
System daemon)
Example 2.8, “Ports 50006,
50008, 50009: ccsd (TCP)”
50007 UDP ccsd (Cluster Configuration
System daemon)
Example 2.9, “Port 50007: ccsd
(UDP)”
Table 2.1. Enabled IP Ports on Red Hat Cluster Nodes
2.2. Enabling IP Ports on Computers That Run luci
To allow client computers to communicate with a computer that runs luci (the Conga user
interface server), and to allow a computer that runs luci to communicate with ricci in the cluster
nodes, you must enable the IP ports assigned to luci and ricci. Table 2.2, “Enabled IP Ports on
a Computer That Runs luci” lists the IP port numbers, their respective protocols, the
components to which the port numbers are assigned, and references to iptables rule
examples. At each computer that runs luci, enable IP ports according to Table 2.1, “Enabled IP
Ports on Red Hat Cluster Nodes”. (All examples are in Section 2.3, “Examples of iptables
Rules”.)
Note
Chapter 2. Before Configuring a Red Hat Cluster
14