Installation guide
Release Notes
14
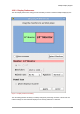
Figure 6. Decrypting Data
However, if the passphrase is misplaced, the encryption key cannot be used, and data on the
encrypted storage device cannot be accessed.
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 provides the ability to save encryption keys and create backup
passphrases. This feature allows for the recovery of an encrypted volume (including the root device)
even when the original passphrase is misplaced.
8.4. sVirt
libvirt is a C language application programming interface (API) for managing and interacting with the
virtualization capabilities of Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6. In this release, libvirt features the new sVirt
component. sVirt integrates with SELinux, providing security mechanisms to prevent unauthorized
access of guests and hosts in a virtualized environment.
8.5. Enterprise Security Client
The Enterprise Security Client (ESC) is a simple GUI that allows Red Hat Enterprise Linux to manage
smart cards and tokens. New smart cards can be formatted and enrolled, meaning that new keys are
generated and certificates requested for the smart card automatically. The smart card lifecycle can be
managed, as well, so that lost smart cards can have their certificates revoked and expired certificates
can be renewed. The ESC works in conjunction with a larger public-key infrastructure management
product, either Red Hat Certificate System or Dogtag PKI.
9. Networking
9.1. Multiqueue Networking
Every data packet transferred over a network device represents processing which must be completed
by a CPU. The low-level network implementation in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 allows network device
drivers to divide network packet processing across multiple queues. Dividing these processes allows a
system to better utilize the multiple processors and CPU cores present on modern systems.
9.2. Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6)
The next-generation Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) specification is designed as the successor to
Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4). IPv6 specifies a wide range of improvements over IPv4, including:
expanded addressing capabilities, flow labeling and simplified header formats.
9.2.1. Optimistic Duplicate Address Detection
Duplicate Address Detection (DAD) is a feature of the Neighbor Discovery Protocol portion of IPv6.
Specifically, DAD is tasked with checking if an IPv6 address is already being used. Red Hat Enterprise
Linux features Optimistic Duplicate Address Detection, a speed optimization of DAD.