User guide
Table Of Contents
- Features
- Pin Configurations
- Overview
- AVR CPU Core
- AVR ATmega162 Memories
- System Clock and Clock Options
- Power Management and Sleep Modes
- System Control and Reset
- Interrupts
- I/O-Ports
- Introduction
- Ports as General Digital I/O
- Alternate Port Functions
- Register Description for I/O-Ports
- Port A Data Register – PORTA
- Port A Data Direction Register – DDRA
- Port A Input Pins Address – PINA
- Port B Data Register – PORTB
- Port B Data Direction Register – DDRB
- Port B Input Pins Address – PINB
- Port C Data Register – PORTC
- Port C Data Direction Register – DDRC
- Port C Input Pins Address – PINC
- Port D Data Register – PORTD
- Port D Data Direction Register – DDRD
- Port D Input Pins Address – PIND
- Port E Data Register – PORTE
- Port E Data Direction Register – DDRE
- Port E Input Pins Address – PINE
- External Interrupts
- 8-bit Timer/Counter0 with PWM
- Timer/Counter0, Timer/Counter1, and Timer/Counter3 Prescalers
- 16-bit Timer/Counter (Timer/Counter1 and Timer/Counter3)
- Restriction in ATmega161 Compatibility Mode
- Overview
- Accessing 16-bit Registers
- Timer/Counter Clock Sources
- Counter Unit
- Input Capture Unit
- Output Compare Units
- Compare Match Output Unit
- Modes of Operation
- Timer/Counter Timing Diagrams
- 16-bit Timer/Counter Register Description
- Timer/Counter1 Control Register A – TCCR1A
- Timer/Counter3 Control Register A – TCCR3A
- Timer/Counter1 Control Register B – TCCR1B
- Timer/Counter3 Control Register B – TCCR3B
- Timer/Counter1 – TCNT1H and TCNT1L
- Timer/Counter3 – TCNT3H and TCNT3L
- Output Compare Register 1 A – OCR1AH and OCR1AL
- Output Compare Register 1 B – OCR1BH and OCR1BL
- Output Compare Register 3 A – OCR3AH and OCR3AL
- Output Compare Register 3 B – OCR3BH and OCR3BL
- Input Capture Register 1 – ICR1H and ICR1L
- Input Capture Register 3 – ICR3H and ICR3L
- Timer/Counter Interrupt Mask Register – TIMSK(1)
- Extended Timer/Counter Interrupt Mask Register – ETIMSK(1)
- Timer/Counter Interrupt Flag Register – TIFR(1)
- Extended Timer/Counter Interrupt Flag Register – ETIFR(1)
- 8-bit Timer/Counter2 with PWM and Asynchronous operation
- Serial Peripheral Interface – SPI
- USART
- Analog Comparator
- JTAG Interface and On-chip Debug System
- IEEE 1149.1 (JTAG) Boundary-scan
- Boot Loader Support – Read-While-Write Self-programming
- Features
- Application and Boot Loader Flash Sections
- Read-While-Write and No Read-While-Write Flash Sections
- Boot Loader Lock Bits
- Entering the Boot Loader Program
- Addressing the Flash During Self- programming
- Self-programming the Flash
- Performing Page Erase by SPM
- Filling the Temporary Buffer (Page Loading)
- Performing a Page Write
- Using the SPM Interrupt
- Consideration while Updating BLS
- Prevent Reading the RWW Section During Self- programming
- Setting the Boot Loader Lock Bits by SPM
- EEPROM Write Prevents Writing to SPMCR
- Reading the Fuse and Lock Bits from Software
- Preventing Flash Corruption
- Programming Time for Flash When Using SPM
- Simple Assembly Code Example for a Boot Loader
- ATmega162 Boot Loader Parameters
- Memory Programming
- Program And Data Memory Lock Bits
- Fuse Bits
- Signature Bytes
- Calibration Byte
- Parallel Programming Parameters, Pin Mapping, and Commands
- Parallel Programming
- Enter Programming Mode
- Considerations for Efficient Programming
- Chip Erase
- Programming the Flash
- Programming the EEPROM
- Reading the Flash
- Reading the EEPROM
- Programming the Fuse Low Bits
- Programming the Fuse High Bits
- Programming the Extended Fuse Bits
- Programming the Lock Bits
- Reading the Fuse and Lock Bits
- Reading the Signature Bytes
- Reading the Calibration Byte
- Parallel Programming Characteristics
- Serial Downloading
- SPI Serial Programming Pin Mapping
- Programming via the JTAG Interface
- Programming Specific JTAG Instructions
- AVR_RESET (0xC)
- PROG_ENABLE (0x4)
- PROG_COMMANDS (0x5)
- PROG_PAGELOAD (0x6)
- PROG_PAGEREAD (0x7)
- Data Registers
- Reset Register
- Programming Enable Register
- Programming Command Register
- Virtual Flash Page Load Register
- Virtual Flash Page Read Register
- Programming Algorithm
- Entering Programming Mode
- Leaving Programming Mode
- Performing Chip Erase
- Programming the Flash
- Reading the Flash
- Programming the EEPROM
- Reading the EEPROM
- Programming the Fuses
- Programming the Lock Bits
- Reading the Fuses and Lock Bits
- Reading the Signature Bytes
- Reading the Calibration Byte
- Electrical Characteristics
- ATmega162 Typical Characteristics
- Active Supply Current
- Idle Supply Current
- Power-down Supply Current
- Power-save Supply Current
- Standby Supply Current
- Pin Pull-up
- Pin Driver Strength
- Pin Thresholds and Hysteresis
- BOD Thresholds and Analog Comparator Offset
- Internal Oscillator Speed
- Current Consumption of Peripheral Units
- Current Consumption in Reset and Reset Pulsewidth
- Register Summary
- Instruction Set Summary
- Ordering Information
- Packaging Information
- Erratas
- Datasheet Change Log for ATmega162
- Table of Contents
25
ATmega162/V
2513E–AVR–09/03
The control bits for the External Memory Interface are located in three registers, the
MCU Control Register – MCUCR, the Extended MCU Control Register – EMCUCR, and
the Special Function IO Register – SFIOR.
When the XMEM interface is enabled, it will override the settings in the Data Direction
registers corresponding to the ports dedicated to the interface. For details about this port
override, see the alternate functions in section “I/O-Ports” on page 62. The XMEM inter-
face will autodetect whether an access is internal or external. If the access is external,
the XMEM interface will output address, data, and the control signals on the ports
according to Figure 13 (this figure shows the wave forms without wait-states). When
ALE goes from high to low, there is a valid address on AD7:0. ALE is low during a data
transfer. When the XMEM interface is enabled, also an internal access will cause activ-
ity on address-, data- and ALE ports, but the RD
and WR strobes will not toggle during
internal access. When the External Memory Interface is disabled, the normal pin and
data direction settings are used. Note that when the XMEM interface is disabled, the
address space above the internal SRAM boundary is not mapped into the internal
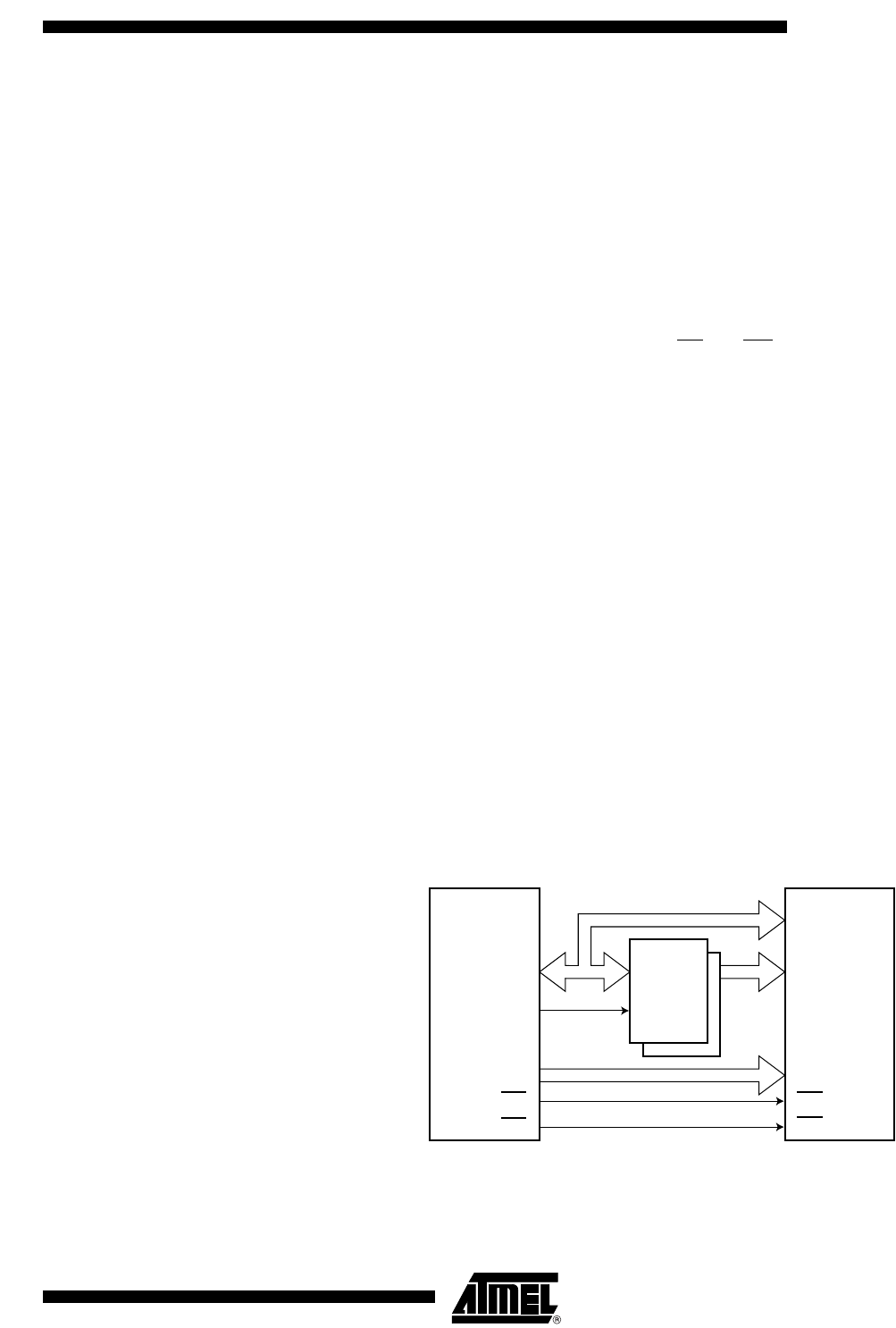
SRAM. Figure 12 illustrates how to connect an external SRAM to the AVR using an octal
latch (typically “74x573” or equivalent) which is transparent when G is high.
Address Latch Requirements Due to the high-speed operation of the XRAM interface, the address latch must be
selected with care for system frequencies above 8 MHz @ 4V and 4 MHz @ 2.7V.
When operating at conditions above these frequencies, the typical old style 74HC series
latch becomes inadequate. The external memory interface is designed in compliance to
the 74AHC series latch. However, most latches can be used as long they comply with
the main timing parameters. The main parameters for the address latch are:
• D to Q propagation delay (t
pd
).
• Data setup time before G low (t
su
).
• Data (address) hold time after G low (
th
).
The external memory interface is designed to guaranty minimum address hold time after
G is asserted low of t
h
= 5 ns (refer to t
LAXX_LD
/t
LLAXX_ST
in Table 115 to Table 122 on
page 271). The D to Q propagation delay (t
pd
) must be taken into consideration when
calculating the access time requirement of the external component. The data setup time
before G low (t
su
) must not exceed address valid to ALE low (t
AVLLC
) minus PCB wiring
delay (dependent on the capacitive load).
Figure 12. External SRAM Connected to the AVR
D[7:0]
A[7:0]
A[15:8]
RD
WR
SRAM
DQ
G
AD7:0
ALE
A15:8
RD
WR
AVR










