Manual
Table Of Contents
- Ordering Information
- Features
- Description
- Architectural Overview
- General Purpose Register File
- ALU - Arithmetic Logic Unit
- ISP Flash Program Memory
- SRAM Data Memory
- Program and Data Addressing Modes
- Register Direct, Single Register Rd
- Register Direct, Two Registers Rd and Rr
- I/O Direct
- Data Direct
- Data Indirect with Displacement
- Data Indirect
- Data Indirect With Pre-Decrement
- Data Indirect With Post-Increment
- Constant Addressing Using the LPM and ELPM Instructions
- Direct Program Address, JMP and CALL
- Indirect Program Addressing, IJMP and ICALL
- Relative Program Addressing, RJMP and RCALL
- EEPROM Data Memory
- Memory Access Times and Instruction Execution Timing
- I/O Memory
- Reset and Interrupt Handling
- Reset Sources
- Power-On Reset
- External Reset
- Watchdog Reset
- MCU Status Register - MCUSR
- Interrupt Handling
- External Interrupt Mask Register - EIMSK
- External Interrupt Flag Register - EIFR
- External Interrupt Control Register - EICR
- Timer/Counter Interrupt Mask Register - TIMSK
- Timer/Counter Interrupt Flag Register - TIFR
- Interrupt Response Time
- Sleep Modes
- Timer/Counters
- Timer/Counter Prescalers
- 8-bit Timer/Counters T/C0 and T/C2
- Timer/Counter0 Control Register - TCCR0
- Timer/Counter2 Control Register - TCCR2
- Timer/Counter0 - TCNT0
- Timer/Counter2 - TCNT2
- Timer/Counter0 Output Compare Register - OCR0
- Timer/Counter2 Output Compare Register - OCR2
- Timer/Counter 0 and 2 in PWM mode
- Asynchronous Status Register - ASSR
- Asynchronous Operation of Timer/Counter0
- 16-bit Timer/Counter1
- Timer/Counter1 Control Register A - TCCR1A
- Timer/Counter1 Control Register B - TCCR1B
- Timer/Counter1 - TCNT1H and TCNT1L
- Timer/Counter1 Output Compare Register - OCR1AH and OCR1AL
- Timer/Counter1 Output Compare Register - OCR1BH and OCR1BL
- Timer/Counter1 Input Capture Register - ICR1H and ICR1L
- Timer/Counter1 in PWM mode
- Watchdog Timer
- EEPROM Read/Write Access
- Serial Peripheral Interface - SPI
- UART
- Analog Comparator
- Analog to Digital Converter
- Interface to external SRAM
- I/O-Ports
- Memory Programming
- Electrical Characteristics
- Typical characteristics
- Register Summary
- Instruction Set Summary (Continued)
ATmega603/103
7
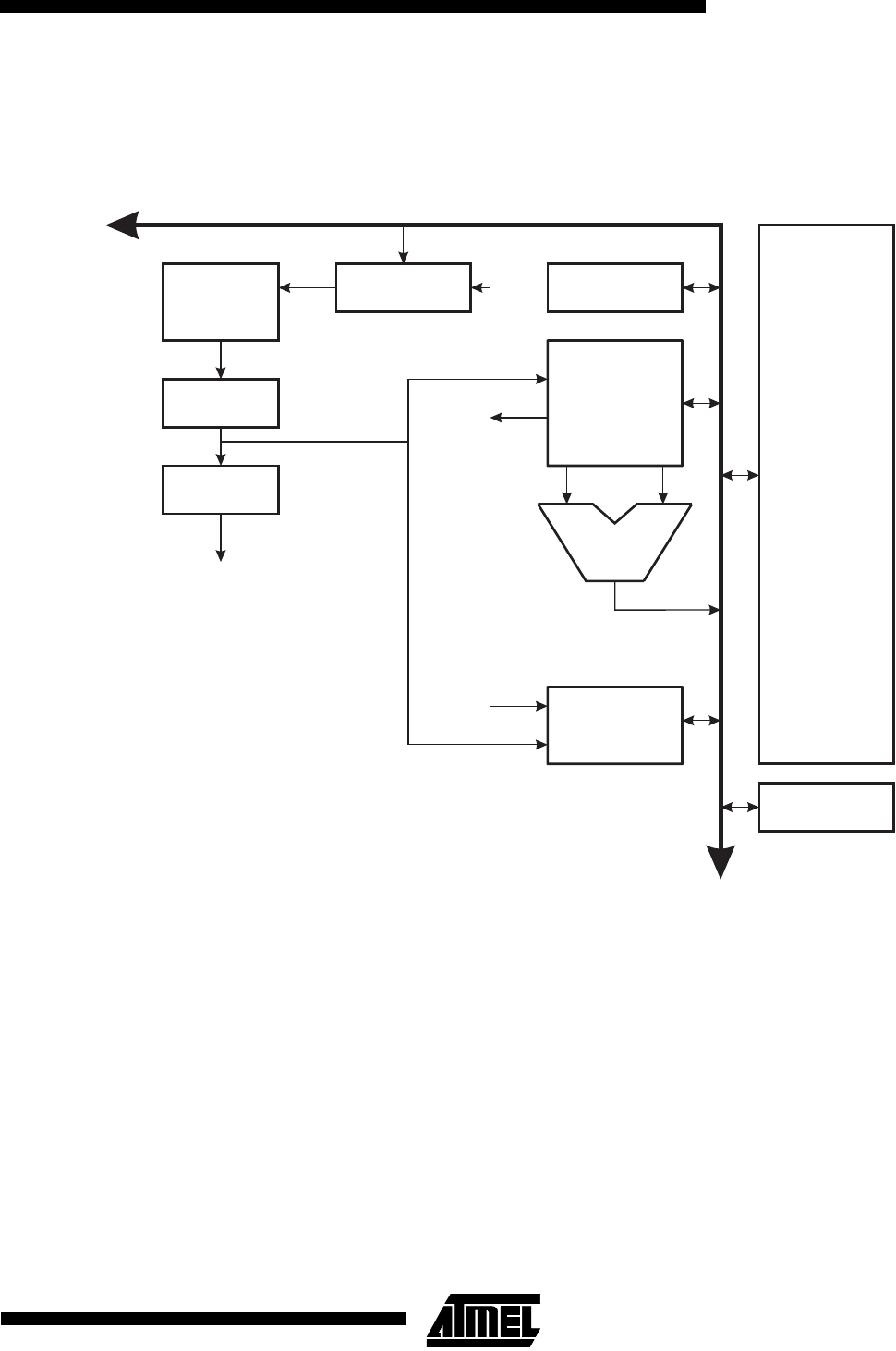
Architectural Overview
Figure 4. The ATmega603/103 AVR RISC Architecture
The AVR uses a Harvard architecture concept - with separate memories and buses for program and data. The program
memory is accesses with a single level pipeline. While one instruction is being executed, the next instruction is pre-fetched
from the program memory. This concept enables instructions to be executed in every clock cycle. The program memory is
in-system programmable Flash memory. With a few exceptions, AVR instructions have a single 16-bit word format,
meaning that every program memory address contains a single 16-bit instruction.
During interrupts and subroutine calls, the return address program counter (PC) is stored on the stack. The stack is
effectively allocated in the general data SRAM, and consequently the stack size is only limited by the total SRAM size and
the usage of the SRAM. All user programs must initialize the SP in the reset routine (before subroutines or interrupts are
executed). The 16-bit stack pointer SP is read/write accessible in the I/O space.
The 4000 bytes data SRAM can be easily accessed through the five different addressing modes supported in the AVR
architecture.
32K/64K x 16
Program
Memory
Instruction
Register
Instruction
Decoder
Program
Counter
Control Lines
32 x 8
General
Purpose
Registers
ALU
Status
and Test
2K/4K x 8
EEPROM
Peripherals
Data Bus 8-bit
AVR ATmega603/103 Architecture
4K x 8
Data
SRAM
DirectAddressing
IndirectAddressing










