User guide
Table Of Contents
- Features
- 1. Description
- 2. Pin Configurations and Pinouts
- 3. Block Diagram
- 4. Memory Array
- 5. Device Operation
- 6. Read Commands
- 7. Program and Erase Commands
- 8. Sector Protection
- 9. Hardware Controlled Protection
- 10. Security Features
- 11. Additional Commands
- 12. Deep Power-down
- 13. “Power of 2” Binary Page Size Option
- 14. Manufacturer and Device ID Read
- 15. Command Tables
- 16. Power-on/Reset State
- 17. System Considerations
- 18. Electrical Specifications
- 19. Input Test Waveforms and Measurement Levels
- 20. Output Test Load
- 21. AC Waveforms
- 21.1 Waveform 1 – SPI Mode 0 Compatible (for Frequencies up to 66MHz)
- 21.2 Waveform 2 – SPI Mode 3 Compatible (for Frequencies up to 66MHz)
- 21.3 Waveform 3 – RapidS Mode 0 (FMAX = 66MHz)
- 21.4 Waveform 4 – RapidS Mode 3 (FMAX = 66MHz)
- 21.5 Utilizing the RapidS Function
- 21.6 Reset Timing
- 21.7 Command Sequence for Read/Write Operations for Page Size 256-Bytes (Except Status Register Read, Manufacturer and Device ID Read)
- 21.8 Command Sequence for Read/Write Operations for Page Size 264-Bytes (Except Status Register Read, Manufacturer and Device ID Read)
- 22. Write Operations
- 23. Read Operations
- 24. Detailed Bit-level Read Waveform – RapidS Serial Interface Mode 0/Mode 3
- 24.1 Continuous Array Read (Legacy Opcode E8H)
- 24.2 Continuous Array Read (Opcode 0BH)
- 24.3 Continuous Array Read (Low Frequency: Opcode 03H)
- 24.4 Main Memory Page Read (Opcode: D2H)
- 24.5 Buffer Read (Opcode D4H or D6H)
- 24.6 Buffer Read (Low Frequency: Opcode D1H or D3H)
- 24.7 Read Sector Protection Register (Opcode 32H)
- 24.8 Read Sector Lockdown Register (Opcode 35H)
- 24.9 Read Security Register (Opcode 77H)
- 24.10 Status Register Read (Opcode D7H)
- 24.11 Manufacturer and Device Read (Opcode 9FH)
- 25. Auto Page Rewrite Flowchart
- 26. Ordering Information
- 27. Packaging Information
- 28. Revision History
- 29. Errata
4
3596N–DFLASH–11/2012
AT45DB081D
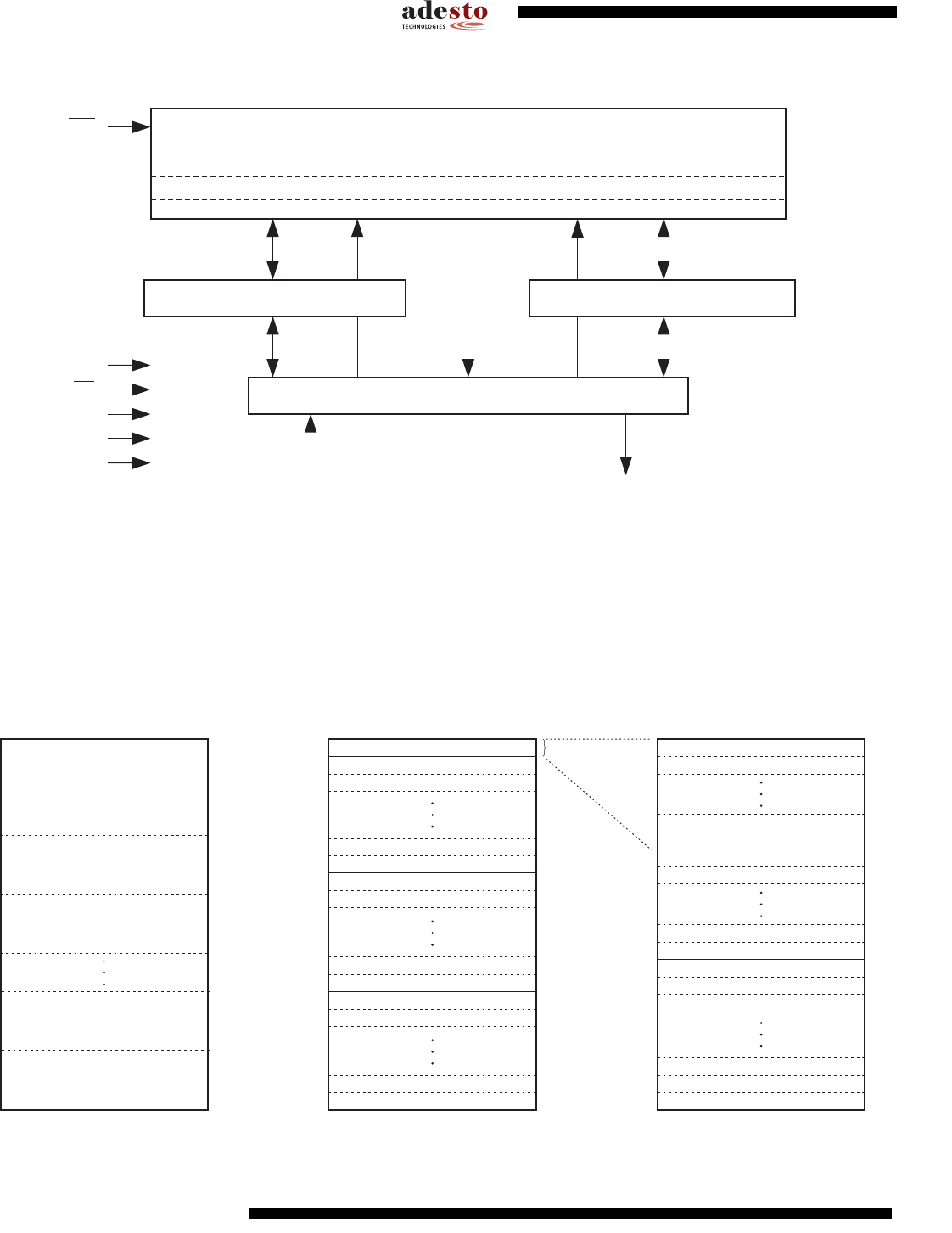
3. Block Diagram
4. Memory Array
To provide optimal flexibility, the memory array of the AT45DB081D is divided into three levels of granularity comprising of
sectors, blocks, and pages. The “Memory Architecture Diagram” illustrates the breakdown of each level and details the
number of pages per sector and block. All program operations to the DataFlash occur on a page by page basis. The erase
operations can be performed at the chip, sector, block or page level.
Figure 4-1. Memory Architecture Diagram
FLASH MEMORY ARRAY
PAGE (256-/264-BYTES)
BUFFER 2 (256-/264-BYTES)BUFFER 1 (256-/264-BYTES)
I/O INTERFACE
SCK
CS
RESET
VCC
GND
WP
SO SI
SECTOR 0a = 8 Pages
2,048-/2,112-bytes
SECTOR 0b = 248 Pages
63,488-/65,472-bytes
Block = 2,048-/2,112-bytes
8 Pages
SECTOR 0a
SECTOR 0b
Page = 256-/264-bytes
PAGE 0
PAGE 1
PAGE 6
PAGE 7
PAGE 8
PAGE 9
PAGE 4,094
PAGE 4,095
BLOCK 0
PAGE 14
PAGE 15
PAGE 16
PAGE 17
PAGE 18
BLOCK 1
SECTOR ARCHITECTURE BLOCK ARCHITECTURE PAGE ARCHITECTURE
BLOCK 0
BLOCK 1
BLOCK 30
BLOCK 31
BLOCK 32
BLOCK 33
BLOCK 510
BLOCK 511
BLOCK 62
BLOCK 63
BLOCK 64
BLOCK 65
SECTOR 1
SECTOR 15 = 256 Pages
65,536-/67,584-bytes
BLOCK 2
SECTOR 1 = 256 Pages
65,536-/67,584-bytes
SECTOR 14 = 256 Pages
65,536-/67,584-bytes
SECTOR 2 = 256 Pages
65,536-/67,584-bytes