Operating instructions
Choosing a Ham Radio 9
heard, as when accessing a repeater. This keeps you from hearing other users on the same
frequency, just like “privacy codes” on the popular handheld radios that use the FRS and
GMRS channels. (You still have to listen to the channel before transmitting.)
• Digital Coded Squelch (DCS) – a continuous sequency of sub-audible tones must be
received during a transmission to keep the output audio turned on. DCS is used by groups
sharing a frequency so that they only hear audio from other group members. (Like tone-
receive squelch, listen before transmitting.)
• Call sign squelch – digital systems, such as D-STAR, send the call sign of the receiv-
ing station along with the transmitted signal. The station called will then be alerted to the
incoming call.
• Attenuation – some radios attenuate the received signal when the squelch threshold is
set to high levels. This reduces interference from overload interference where strong pag-
ing and commercial signals are present.
• Monitor – an FM radio’s monitor button or key temporarily defeats or “opens” the
squelch so that you can hear any station using the channel. This is used to listen for weak
signals or for other stations before transmitting.
All new radios can generate sub-audible repeater access tones. (These are also called
PL or CTCSS tones.) Some have a feature called tone scan that enables the radio to
determine what access tones a repeater requires by listening to the stations using it. This is
very useful when traveling or accessing an unfamiliar repeater.
• DTMF or Touch Tone
dual-frequency tones are used to dial phone numbers through a
repeater’s auto-patch or to enter IRLP and Echolink access codes. A radio’s ability to store
and play back sequences of DTMF tones saves a lot of time when using either service.
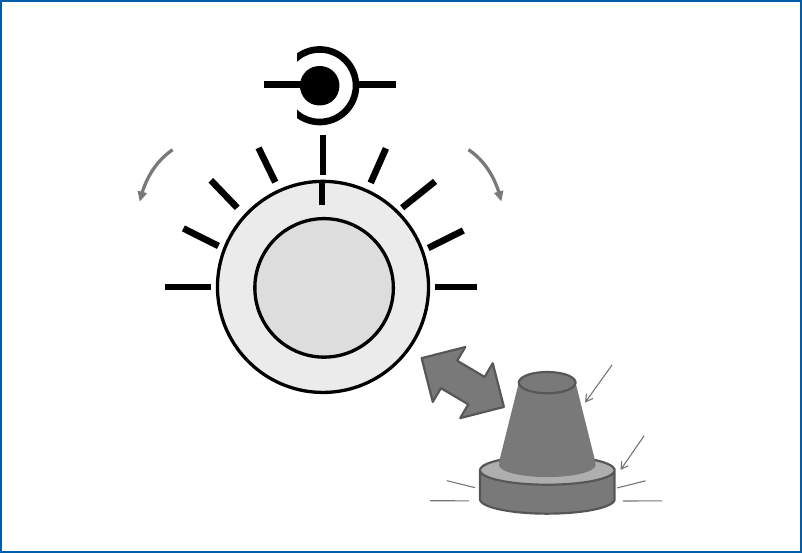
Figure3
SquelchVolume
Tighter
Closed
Looser
Open
Volumeknob
Squelchring
Figure3—SquelchisthecircuitryinFMradiosthatpreventstheuserfromhavingtolisten
tonoiseorunwantedsignalsbymutingtheradio’saudiooutputunlessthepropertypeof
signalisreceived.
TopDownView
SideView










