Installation guide
Table Of Contents
- Preface
- Introduction
- Management and Monitoring Capabilities
- Device Initialization
- Basic Configuration
- Device Configuration
- Device Management
- Device Monitoring
- Troubleshooting
- Frequency Domains and Channels
- Bootloader CLI and Scan Tool
- ASCII Character Chart
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Glossary
- Abbreviations
- Statement of Warranty
- Technical Services and Support
Device Configuration
ORiNOCO® 802.11n Access Points - Software Management Guide 37
5.4 Wireless Interface
The Wireless feature enables you to use Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) technology, that uses several antennas
to transfer multiple data streams thus enabling more data to be transferred in the same period of time. The wireless
architecture is based on the cellular architecture where the systems are divided into cells, and each cell is called Basic Service
Set (BSS). Each BSS is controlled by a Base Station called Access Point, which controls associated wireless clients. BSS is
identified by a Basic Service Set Identifier (BSSID), which corresponds to the Access Point’s MAC address.
The Wireless LAN (WLAN) can be formed of a single cell or of many cells. Each of the WLAN has an entry point which is called
Virtual Access Point (VAP). A VAP is a logical entity that exists within a physical WLAN access device. Each VAP is assigned a
unique BSSID and other relevant protocols that make these VAPs an independent entity. Each of the VAP can be configured
independently so that the user can provide unique authentication and security features. (Refer Virtual Access Point (VAP))
5.4.1 Interface 1
The Interface (Radio) of the AP device enables Wi-Fi Coverage. By default, Radio 1 is enabled in AP mode (See AP Mode)
5.4.1.1 Properties
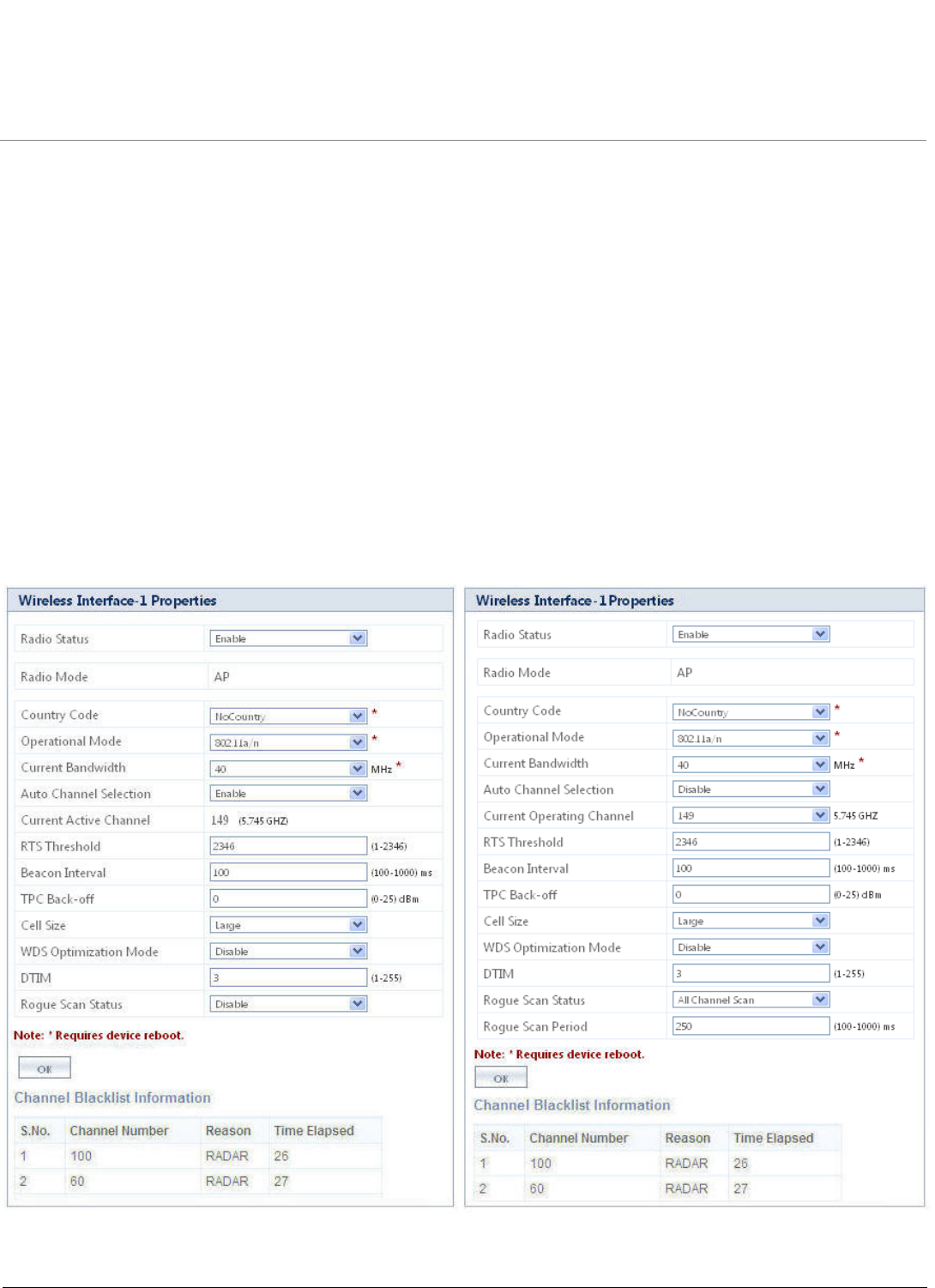
Navigate to CONFIGURATION > Wireless > Interface 1 > Properties. The Wireless Interface - 1 Properties screen
appears.
Figure 5-9 Wireless Interface-1 Properties










