Access Point User Guide
Table Of Contents
- Introduction
- Installation and Initialization
- System Status
- Advanced Configuration
- System
- Network
- Interfaces
- Management
- Filtering
- Alarms
- Bridge
- QoS
- Radius Profiles
- SSID/VLAN/Security
- Monitoring
- Commands
- Troubleshooting
- Command Line Interface (CLI)
- General Notes
- Command Line Interface (CLI) Variations
- CLI Command Types
- Using Tables and Strings
- Configuring the AP using CLI commands
- Set Basic Configuration Parameters using CLI Commands
- Set System Name, Location and Contact Information
- Set Static IP Address for the AP
- Change Passwords
- Set Network Names for the Wireless Interface
- Enable 802.11d Support and Set the Country Code
- Enable and Configure TX Power Control for the Wireless Interface(s)
- Configure SSIDs (Network Names), VLANs, and Profiles
- Download an AP Configuration File from your TFTP Server
- Backup your AP Configuration File
- Set up Auto Configuration
- Other Network Settings
- Configure the AP as a DHCP Server
- Configure the DNS Client
- Configure DHCP Relay
- Configure DHCP Relay Servers
- Maintain Client Connections using Link Integrity
- Change your Wireless Interface Settings
- Set Ethernet Speed and Transmission Mode
- Set Interface Management Services
- Configure Syslog
- Configure Intra BSS
- Configure Wireless Distribution System
- Configure MAC Access Control
- Set RADIUS Parameters
- Set Rogue Scan Parameters
- Set Hardware Configuration Reset Parameters
- Set VLAN/SSID Parameters
- Set Security Profile Parameters
- CLI Monitoring Parameters
- Parameter Tables
- CLI Batch File
- ASCII Character Chart
- Specifications
- Technical Support
- Statement of Warranty
- Regulatory Compliance
Advanced Configuration AP-4000 Series User Guide
System
44
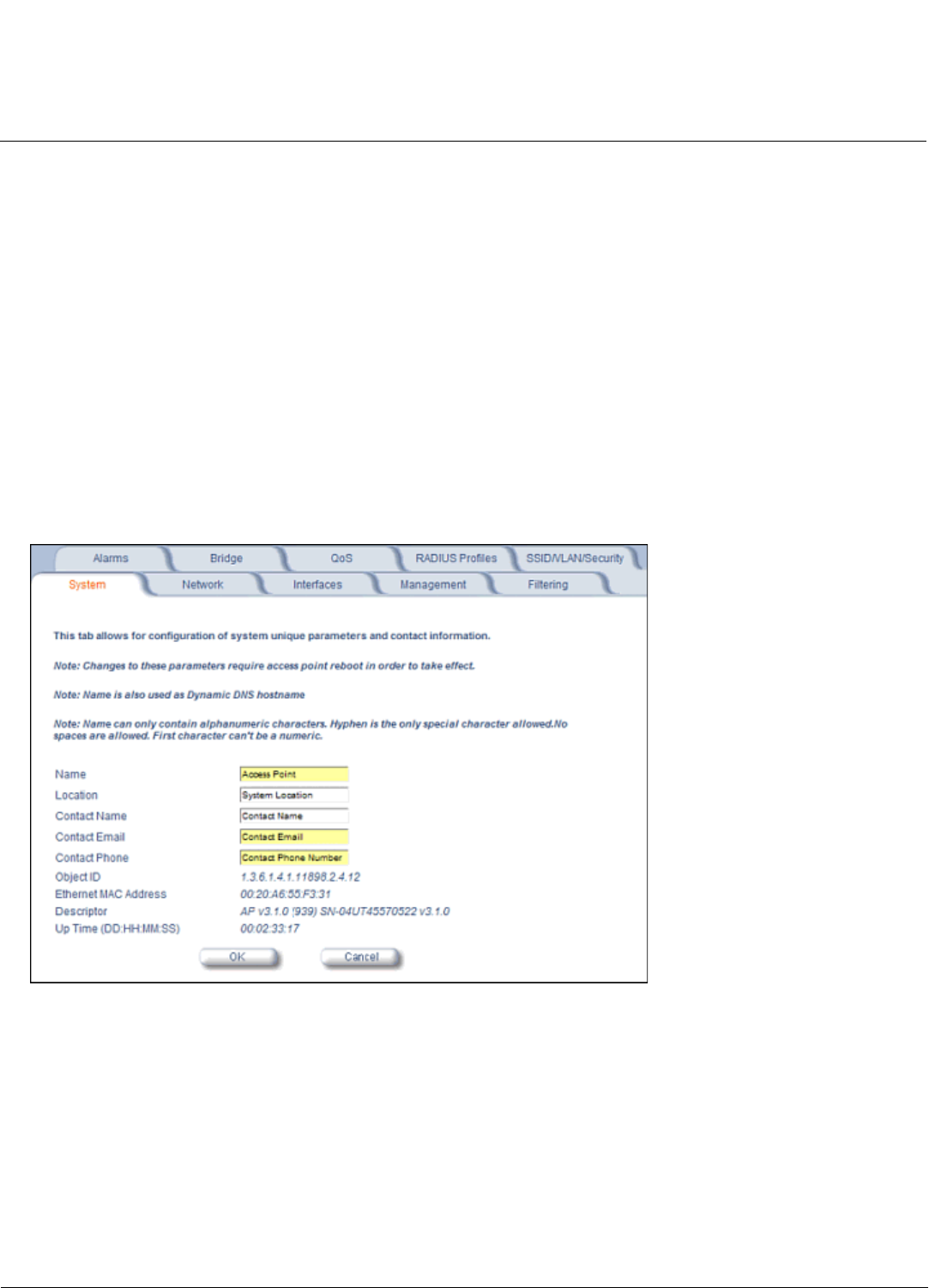
System
You can configure and view the following parameters within the System Configuration screen:
• Name: The name assigned to the AP. See the Dynamic DNS Support and Access Point System Naming Convention
sections for rules on naming the AP.
• Location: The location where the AP is installed.
• Contact Name: The name of the person responsible for the AP.
• Contact Email: The email address of the person responsible for the AP.
• Contact Phone: The telephone number of the person responsible for the AP.
• Object ID: This is a read-only field that displays the Access Point’s system object identification number; this
information is useful if you are managing the AP using SNMP.
• Ethernet MAC Address: This is a read-only field that displays the unique MAC (Media Access Control) address for
the Access Point’s Ethernet interface. The MAC address is assigned at the factory.
• Descriptor: This is a read-only field that reports the Access Point’s name, serial number, current image software
version, and current bootloader software version.
• Up Time: This is a read-only field that displays how long the Access Point has been running since its last reboot.
Figure 4-2 System Tab
Dynamic DNS Support
DNS is a distributed database mapping the user readable names and IP addresses (and more) of every registered
system on the Internet. Dynamic DNS is a lightweight mechanism which allows for modification of the DNS data of host
systems whose IP addresses change dynamically. Dynamic DNS is usually used in conjunction with DHCP for assigning
meaningful names to host systems whose IP addresses change dynamically.
Access Points provide DDNS support by adding the host name (option 12) in DHCP Client messages, which is used by
the DHCP server to dynamically update the DNS server.










