11.3
Table Of Contents
- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Overview
- Audio and MIDI Basics
- Using Reason Rack Plugin as an Instrument
- Using Reason Rack Plugin as an Effect
- Working in the Rack
- Routing Audio and CV
- Sounds, Patches and the Browser
- The I/O device
- Kong Drum Designer
- Introduction
- Overview
- About file formats
- Using patches
- Pad Settings
- The Drum and FX section
- The Drum modules
- The Support Generator modules
- The FX modules
- Connections
- Using Kong as an effect device
- Using external effects with Kong
- Redrum Drum Computer
- Introduction
- About file formats
- Using patches
- Programming patterns
- Redrum parameters
- Using Redrum as a sound module
- Connections
- Dr. Octo Rex Loop Player
- Introduction
- About REX file formats
- Loading and saving Dr. Octo Rex patches
- Playing Loops
- Adding Loops
- Playing individual Loop Slices
- Slice handling
- Dr. Octo Rex panel parameters
- Dr. Octo Rex synth parameters
- Connections
- Europa Shapeshifting Synthesizer
- Introduction
- Panel overview
- Signal flow
- Playing and using Europa
- Panel reference
- Sound Engines On/Off and Edit Focus section
- The Oscillator section
- The Modifiers section
- The Spectral Filter
- The Harmonics section
- The Unison section
- The User Wave and Mixer section
- The Filter section
- The Amplifier section
- The Envelopes section
- Envelope 1, 2, 3 and 4
- Preset
- Adding a Sustain stage
- Adding and removing envelope points
- Changing the envelope curve shape
- Looping the envelope
- Editing levels only
- Creating “free form” envelope curves
- Using the Envelope 3 and Envelope 4 curves as Sound Engine waveforms
- Using the Envelope 4 curve as a Spectral Filter curve
- The LFO section
- The Effects section
- The Modulation Bus section
- Connections
- Tips and Tricks
- Grain Sample Manipulator
- Thor Polysonic Synthesizer
- Subtractor Synthesizer
- Malström Synthesizer
- Monotone Bass Synthesizer
- ID8 Instrument Device
- Rytmik Drum Machine
- Radical Piano
- Klang Tuned Percussion
- Pangea World Instruments
- Humana Vocal Ensemble
- NN-XT Sampler
- Introduction
- Panel overview
- Loading complete Patches and REX files
- Using the main panel
- Overview of the Remote Editor panel
- About Samples and Zones
- Selections and Edit Focus
- Adjusting parameters
- Managing Zones and Samples
- Working with Grouping
- Working with Key Ranges
- Setting Root Notes and Tuning
- Using Automap
- Layered, crossfaded and velocity switched sounds
- Using Alternate
- Sample parameters
- Group parameters
- Synth parameters
- Connections
- NN-19 Sampler
- Introduction
- General sampling principles
- About audio file formats
- About Key Zones and samples
- Loading a Sample into an empty NN-19
- Loading SoundFont samples
- Loading REX slices as samples
- Creating Key Zones
- Selecting Key Zones
- Setting the Key Zone Range
- Deleting a Key Zone
- About Key zones, assigned and unassigned samples
- Adding sample(s) to a Key Map
- Setting the Root Key
- Removing sample(s) from a Key Map
- Removing all unassigned samples
- Rearranging samples in a Key Map
- Setting Sample Level
- Tuning samples
- Looping Samples
- About the Solo Sample function
- Automap Samples
- NN-19 synth parameters
- Play Parameters
- Connections
- MIDI Out Device
- Quartet Chorus Ensemble
- Sweeper Modulation Effect
- Alligator Triple Filtered Gate
- Pulveriser
- The Echo
- Scream 4 Sound Destruction Unit
- BV512 Vocoder
- Introduction
- Setting up for vocoding
- Using the BV512 as an equalizer
- BV512 parameters
- Connections
- Tips and tricks
- RV7000 Mk II Advanced Reverb
- Neptune Pitch Adjuster and Voice Synth
- Introduction
- Overview and basic concepts
- Setting up for pitch processing
- Using pitch correction
- Using pitch shifting (Transpose)
- Using Formant control
- Using the Voice Synth
- Panel parameters
- Connections
- Softube Amps
- Audiomatic Retro Transformer
- Channel Dynamics Compressor & Gate
- Channel EQ Equalizer
- Master Bus Compressor
- Synchronous Timed Effect Modulator
- The MClass Effects
- Half-Rack Effects
- The Combinator
- Pulsar Dual LFO
- RPG-8 Arpeggiator
- Matrix Pattern Sequencer
- Mixer 14:2
- The Line Mixer 6:2
- Working with Players
- Settings
- The Reason Rack Plugin Settings dialog
- Index
THE MCLASS EFFECTS674
Lo/Hi Shelf parameters
A shelving equalizer will boost or cut frequencies below or above the selected frequency.
The following parameters are available for the Lo/Hi Shelf bands:
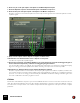
About the graphic display
The graphic display to the left in the device panel shows the frequency response curve as set by the EQ parameters.
This gives a visual feedback and helps you tailor the EQ settings.
The MClass Stereo Imager
The MClass Stereo Imager splits the signal into two frequency bands; “Hi” and “Lo” and allows you to widen or narrow
the stereo image of each band. A typical application of the Stereo Imager is to widen the higher frequencies and nar-
row the lower frequencies. This will make the bass end “tight” whilst “opening up” the higher frequencies.
This is most often used as an insert effect in stereo.
! The MClass Stereo Imager does not create stereo from mono input! For the device to work properly it must
connected with stereo in/out, and the input signal must contain a stereo audio signal.
Parameters
The following parameters are available:
|
Parameter
|
Description
Frequency Frequencies below (Lo Shelf) or above (Hi Shelf) the selected frequency will be boosted or cut.
• The Lo Shelf range is 30 Hz to 600 Hz.
• The Hi Shelf range is 3 kHz to 12 kHz.
Gain Specifies how much the level should be boosted or cut. The gain range is ±18 dB.
Q This governs the slope of the shelving curve. The higher the value, the steeper the curve slope. High
Q settings will also produce a “bump” in the opposite cut/boost direction at the set frequency.
|
Parameter
|
Description
X-Over
Frequency
This determines the crossover frequency between the Hi and Lo band. Range is 100 Hz - 6 kHz. Frequen-
cies below this will be affected by the Lo Width setting; frequencies above will be affected by the Hi Width
setting.
Lo Width This adjusts the stereo width for the Lo band. Turn anti-clockwise to narrow the stereo width (i.e. to make
it more “mono”), and clockwise to widen the stereo image. Center position means no change from original
signal. The “Active” LED indicates whether Low Width is activated or not. Note that for the Lo band, it is
more common to narrow the stereo image, as the low frequency content in a mix is usually mixed center
and can become less defined if widened.
Hi Width This adjusts the stereo width for the Hi band. Turn anti-clockwise to narrow the stereo width (i.e. to make
it more “mono”), and clockwise to widen the stereo image. Center position means no change from original
signal. The “Active” LED indicates whether Hi Width is activated or not.
Solo switch This allows you to listen to the Lo and Hi bands separately, for reference purposes. “Normal” is the stan-
dard operating mode.