User's Manual
044-05156 Rev C 23
4.5.1.2 Main Amplifier
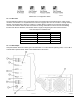
The main amplifier employs class AB amplification for maximum efficiency. The error amplifier and feed forward
loops are employed to correct signal nonlinearities introduced by the class AB main amplifier. The error amplifier
operates in class AB mode. The RF input signals are amplified by a preamp and coupled to an attenuator and
phase shifter in the first feed-forward loop. The main signal is phase shifted by 180 degrees and amplified in the
premain amplifier. The output from the premain amplifier is fed to the class AB main amplifier. The output from the
main amplifier is typically 180 watts. The signal is output to several couplers and a delay line.
The signal output from the main amplifier is sampled using a coupler, and the sample signal is combined with the
main input signal and input to the second feed-forward loop. The error signal is attenuated, phase shifted 180
degrees, then fed to the error amplifier where it is amplified to a level identical to the sampled output from the main
amplifier. The output from the error amplifier is then coupled back and added to the output from the main amplifier.
The control loops continuously make adjustments to cancel out any distortion in the final output signals.
Pre
Amp
Pre
Main
Main
Amp
Error
Amp
Delay
Feed Forward Loop control
2nd Loop
Phase & Gain
1st Loop
Phase & Gain
Delay
Alarms & Display
+15 +5 -5
Power Supply
RF Out
RFL
PWR
FWD
PWR
Front Panel
Smart Rack
+27VDC
Pre
Dist
Phase
& Gain
G3S-1900-125 Power Amplifier Module Functional Block Diagram
The 2nd loop control section obtains a sample of the distortion added to the output signals by the main amplifiers,
phase shifts the signals by 180 degrees, then feeds it to the error amplifier. There it is amplified to the same power
level as the input sample and coupled on to the main output signal. The final output is monitored by the 2nd loop
and adjusted to ensure that the signal distortion and IMD on the final output is canceled out.
The input and output of the amplifier employ two-stage, class AB amplifiers, which provide approximately 25 dB of
gain in the 60 MHz frequency band from 1930 to 1990 MHz. The amplifier operates on +27 Vdc, and is mounted
directly on a heat sink, which is temperature monitored by a thermal sensor. If the heat sink temperature exceeds
85°C, a high temperature fault occurs. The alarm logic controls the transistor bias voltage, which shuts down the
amplifier.
4.5.1.3 Error Amplifier
The main function of the error amplifier is to sample and amplify the signal distortion level generated by the main
amplifier, to a level that cancels out the distortion and IMD when the error signal is coupled onto the main signal at
the amplifier output. The error amplifier is a balanced multistage, class AB amplifier, has 75 dB of gain, and
produces over 100-watts peak output. The amplifier operates on +27 Vdc and is mounted directly on a heat sink.
4.5.1.4 Amplifier Monitoring
In the main and error amplifier modules, all normal variations are automatically compensated for by the feedforward
loop control. However, when large variations occur beyond the adjustment range of the loop control, a loop fault
will occur. The alarms are displayed on the front panel indicators and output via a 21-pin connector on the rear of
the module to the subrack summary board for subsequent remote monitoring via the ALARMS connector.
4.5.2 Amplifier Module Cooling