Gigabit Ethernet Switch User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Chapter 1. Introduction
- Chapter 2. Installing the Switch
- Chapter 3. Switch Management
- Chapter 4. Console Interface
- 4.1 Login Screen
- 4.2 Main Menu
- 4.3 System Information Menu
- 4.4 Management Setup Menu
- 4.5 Device Control Menu
- 4.5.1 Setting the System Operation Mode
- 4.5.2 Layer 2 Menu
- 4.5.3 Using the Bridge Menu
- 4.5.4 Configuring Virtual LANs
- 4.5.5 Configuring IGMP Snooping
- 4.5.6 Configuring IP Settings
- 4.5.7 Security Menu
- 4.5.8 Jumbo Packet Configuration
- 4.6 Monitoring the Switch
- 4.6.1 Displaying Port Statistics
- 4.6.2 Layer 2 Address Tables
- 4.6.3 Displaying Bridge Information
- 4.6.4 Displaying VLAN Information
- 4.6.5 IP Multicast Registration Table
- 4.6.6 IP Address Table
- 4.7 Resetting the System
- 4.8 Logging Off the System
- Chapter 5. Web Interface
- 5.1 Web-Based Configuration and Monitoring
- 5.2 Navigating the Web Browser Interface
- 5.3 Panel Display
- 5.4 Main Menu
- 5.5 System Information Menu
- 5.6 Management Setup Menu
- 5.7 Device Control Menu
- 5.7.1 Layer 2 Menu
- 5.7.2 Using the Bridge Menu
- 5.7.3 Configuring Virtual LANs
- 5.7.4 Configuring IGMP Snooping
- 5.7.5 Configuring IP Settings
- 5.7.6 Configuring Security Filters
- 5.7.7 Jumbo Packet Configuration
- 5.8 Monitoring the Switch
- 5.9 Resetting the System
- Chapter 6.Advanced Topics
- Appendix A Troubleshooting
- Appendix B Pin Assignments
- GLOSSARY
WGS3 Layer 3 Switch User’s Manual
- 190 -
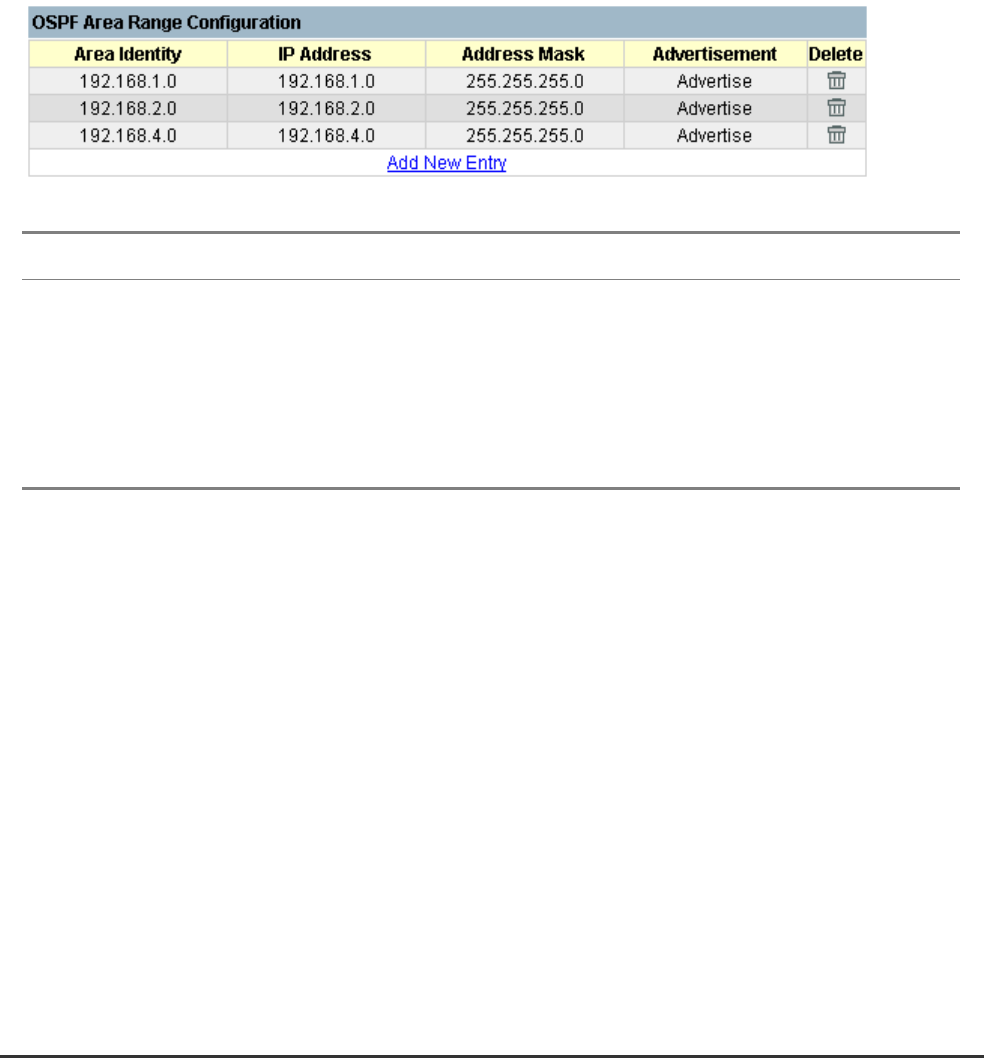
5.7.5.2.3.2 OSPF Area Range Configuration
After you configure an area identifier, you can specify a subnetwork address range that covers all the
individual networks in this area. This technique limits the amount of traffic exchanged between Area
Border Routers (ABRs) by allowing them to advertise a single summary range. By summarizing routes,
the routing changes within an area do not have to be updated in the backbone ABRs or in other areas.
To optimize the route summary, first configure all the OSPF routers in an area so that they fall within a
contiguous address range. The route summary consists of an address and mask, where the mask can be
a Variable Length Subnet Mask (VLSM). Using VLSMs allows you to configure each subnetwork within a
larger network with its own subnet mask. This provides a longer subnet mask that covers fewer host IP
addresses, thereby reducing the size of the routing tables that have to be exchanged. (For more
information on VSLMs, see RFCs 1219 and 1878.)
Parameter Description
Area Identity An OSPF area that includes all the OSPF routers within the assigned address
range
IP Address The IP address used to calculate the area range.
Address Mask The subnet mask used to calculate the area range.
Advertisement Enables or disables advertising for this range.










