Gigabit Ethernet Switch User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Chapter 1. Introduction
- Chapter 2. Installing the Switch
- Chapter 3. Switch Management
- Chapter 4. Console Interface
- 4.1 Login Screen
- 4.2 Main Menu
- 4.3 System Information Menu
- 4.4 Management Setup Menu
- 4.5 Device Control Menu
- 4.5.1 Setting the System Operation Mode
- 4.5.2 Layer 2 Menu
- 4.5.3 Using the Bridge Menu
- 4.5.4 Configuring Virtual LANs
- 4.5.5 Configuring IGMP Snooping
- 4.5.6 Configuring IP Settings
- 4.5.7 Security Menu
- 4.5.8 Jumbo Packet Configuration
- 4.6 Monitoring the Switch
- 4.6.1 Displaying Port Statistics
- 4.6.2 Layer 2 Address Tables
- 4.6.3 Displaying Bridge Information
- 4.6.4 Displaying VLAN Information
- 4.6.5 IP Multicast Registration Table
- 4.6.6 IP Address Table
- 4.7 Resetting the System
- 4.8 Logging Off the System
- Chapter 5. Web Interface
- 5.1 Web-Based Configuration and Monitoring
- 5.2 Navigating the Web Browser Interface
- 5.3 Panel Display
- 5.4 Main Menu
- 5.5 System Information Menu
- 5.6 Management Setup Menu
- 5.7 Device Control Menu
- 5.7.1 Layer 2 Menu
- 5.7.2 Using the Bridge Menu
- 5.7.3 Configuring Virtual LANs
- 5.7.4 Configuring IGMP Snooping
- 5.7.5 Configuring IP Settings
- 5.7.6 Configuring Security Filters
- 5.7.7 Jumbo Packet Configuration
- 5.8 Monitoring the Switch
- 5.9 Resetting the System
- Chapter 6.Advanced Topics
- Appendix A Troubleshooting
- Appendix B Pin Assignments
- GLOSSARY
WGS3 Layer 3 Switch User’s Manual
- 189 -
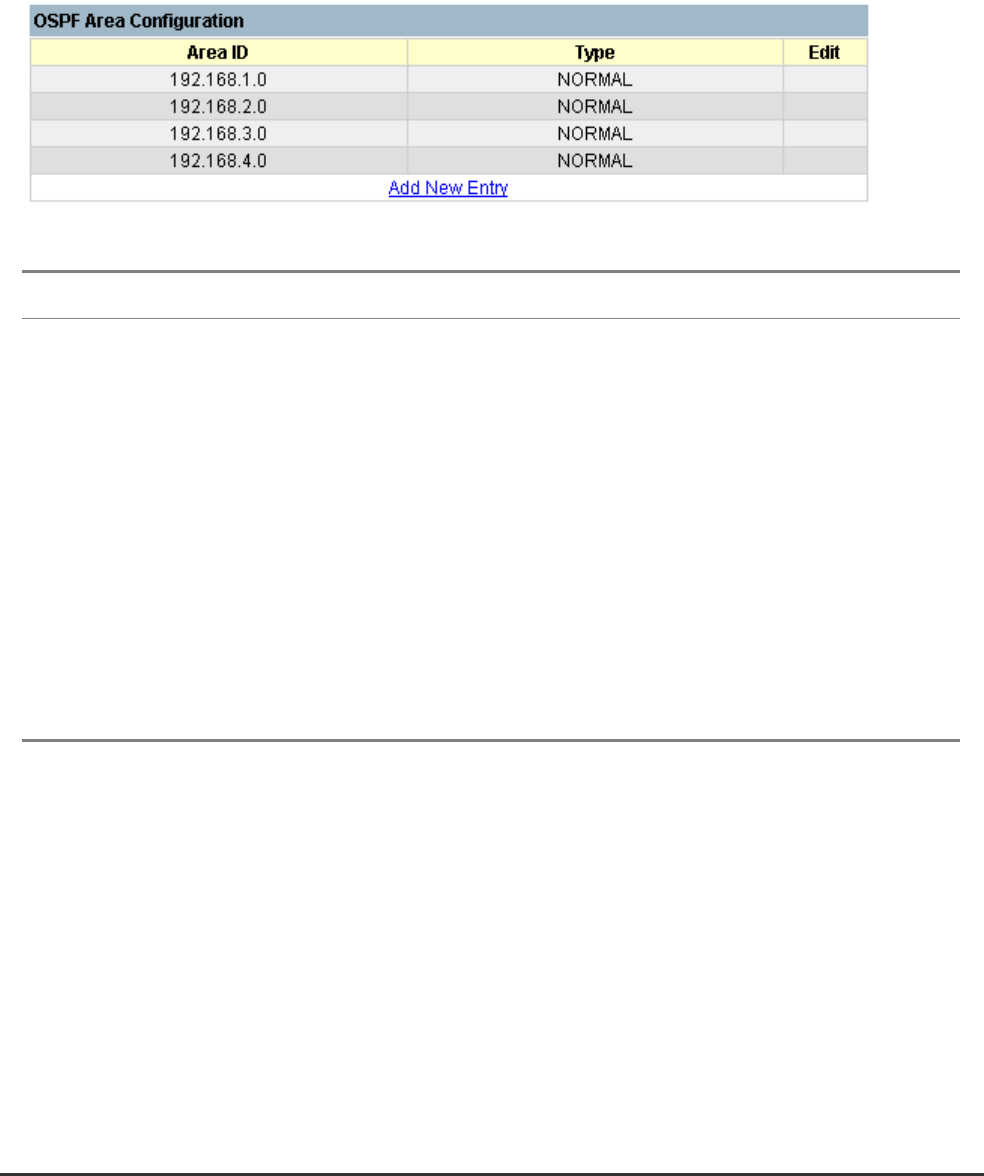
5.7.5.2.3.1 OSPF Area Configuration
OSPF protocol broadcast messages (i.e., Link State Advertisements) are restricted by area to limit their
impact on network performance. Before assigning an Area ID to a specific OSPF interface, you must first
specify the Area ID in this table. Each entry in this table identifies a logical group of OSPF routers that
actively exchange Link State Advertisements (LSAs) to ensure that they share an identical view of the
network topology. You can configure the area as a normal one which can send and receive external Link
State Advertisements (LSAs), a stubby area that cannot send or receive external LSAs, or a
not-so-stubby area (NSSA) that can import external route information into its area.
Parameter Description
Area ID An OSPF area identifier configured for a group of OSPF routers. (For information
on how to assign this identifier to a specific interface, see4.5.6.1.5 Configuring
OSPF.)
Type Indicates area type:
Normal – An area which can send or receive external route information.
Stub – An area which cannot send or receive external route information. It relies
on a single default route provided by its Area Border Router (ABR) to access
destinations outside of the stub. A stub can be used to reduce the amount of
topology data that has to be exchanged over the network.
NSSA – A not so stubby area cannot send but can receive external route
information. The ABR imports external routes and floods this information to all
routers within the NSSA.
An Autonomous System Boundary Router (ASBR) can import external routes and flood this information
to the entire Autonomous System.










