Gigabit Ethernet Switch User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Chapter 1. Introduction
- Chapter 2. Installing the Switch
- Chapter 3. Switch Management
- Chapter 4. Console Interface
- 4.1 Login Screen
- 4.2 Main Menu
- 4.3 System Information Menu
- 4.4 Management Setup Menu
- 4.5 Device Control Menu
- 4.5.1 Setting the System Operation Mode
- 4.5.2 Layer 2 Menu
- 4.5.3 Using the Bridge Menu
- 4.5.4 Configuring Virtual LANs
- 4.5.5 Configuring IGMP Snooping
- 4.5.6 Configuring IP Settings
- 4.5.7 Security Menu
- 4.5.8 Jumbo Packet Configuration
- 4.6 Monitoring the Switch
- 4.6.1 Displaying Port Statistics
- 4.6.2 Layer 2 Address Tables
- 4.6.3 Displaying Bridge Information
- 4.6.4 Displaying VLAN Information
- 4.6.5 IP Multicast Registration Table
- 4.6.6 IP Address Table
- 4.7 Resetting the System
- 4.8 Logging Off the System
- Chapter 5. Web Interface
- 5.1 Web-Based Configuration and Monitoring
- 5.2 Navigating the Web Browser Interface
- 5.3 Panel Display
- 5.4 Main Menu
- 5.5 System Information Menu
- 5.6 Management Setup Menu
- 5.7 Device Control Menu
- 5.7.1 Layer 2 Menu
- 5.7.2 Using the Bridge Menu
- 5.7.3 Configuring Virtual LANs
- 5.7.4 Configuring IGMP Snooping
- 5.7.5 Configuring IP Settings
- 5.7.6 Configuring Security Filters
- 5.7.7 Jumbo Packet Configuration
- 5.8 Monitoring the Switch
- 5.9 Resetting the System
- Chapter 6.Advanced Topics
- Appendix A Troubleshooting
- Appendix B Pin Assignments
- GLOSSARY
WGS3 Layer 3 Switch User’s Manual
- 126 -
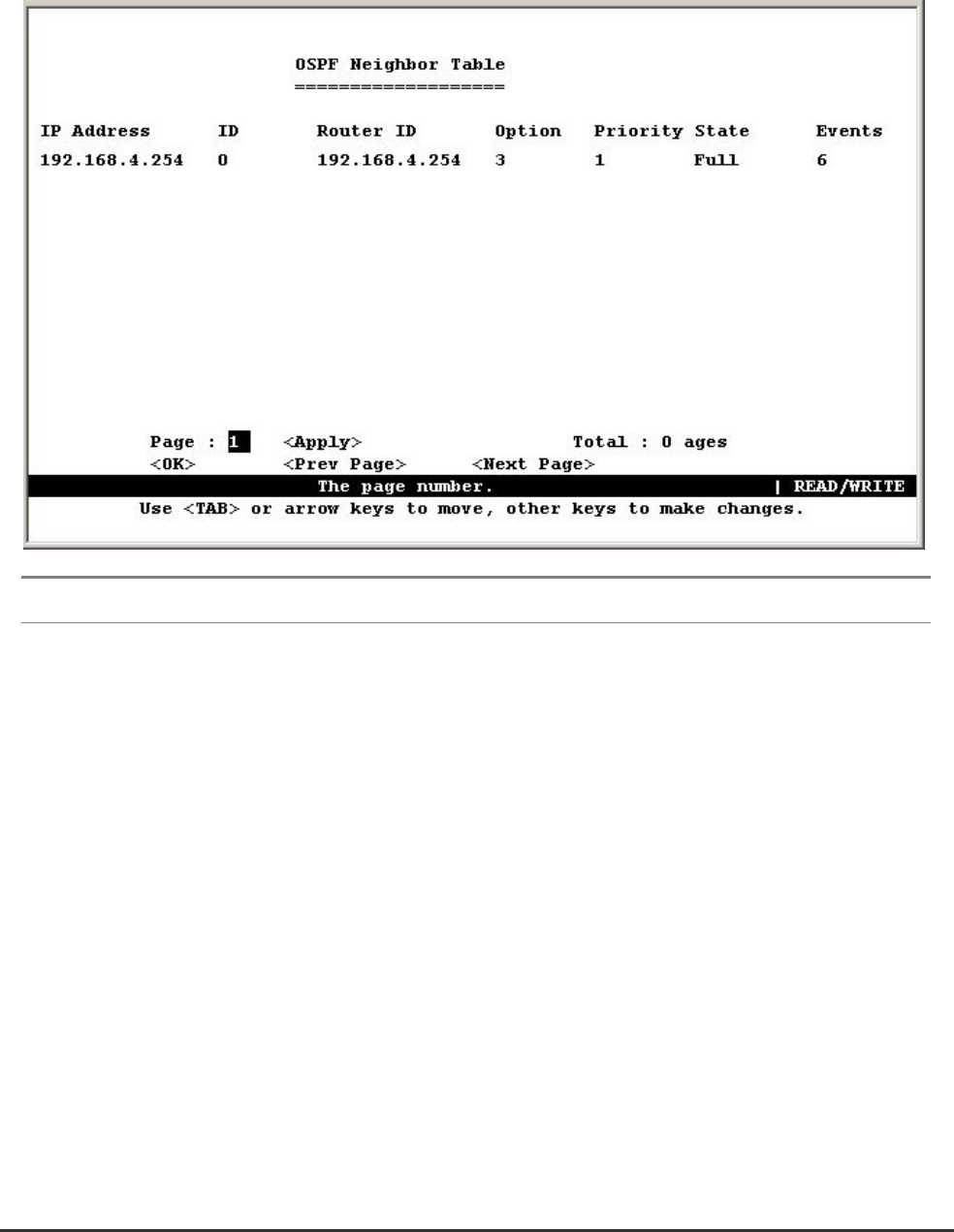
4.6.6.5.3 Displaying the Neighbor Table
Each router exchanges link state information with all neighbors physically attached to the same network
segment. This table displays a summary of the link state for all adjacent neighbors. (Note that
neighboring routers are discovered by this device via Hello messages.).
Parameter Description
IP Address IP address of the neighboring router
ID The index number of the router interface to which this neighbor is attached. For
IP protocol, this value will always be zero.
Router ID The OSPF identifier for the neighboring router.
Option The optional OSPF capabilities supported by the neighbor. The neighbor's
optional OSPF capabilities are also listed in its Hello packets. This enables
received Hellos to be rejected (i.e., neighbor relationships will not even start to
form) if there is a mismatch in certain crucial OSPF capabilities. The OSPF
optional capabilities currently accepted include external routing capability and
TOS capability.
You need to map the binary bits to the supported options. For example, “3”
indicates both routing capability and TOS capability.
Priority The neighbor’s router priority. This priority is used in electing the designated
router for the area in which it exists. This value will be set to zero if this router
cannot be elected.










