User Manual
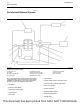
Illustration 10 g02720984
Typical example
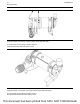
The NOx Reduction System (NRS) operates with the
transfer of the hot exhaust gas from the exhaust
manifold to the assembly of the exhaust gas valve.
The assembly of the exhaust gas valve consists of an
exhaust gas valve and an electronically controlled
actuator.
As the electronically controlled actuator (7) starts to
open the flow of exhaust gas from the exhaust gas
valve mixes with the air flow from the charge air
aftercooler. The mixing of the exhaust gas and the air
flow from the charge air aftercooler reduces the
oxygen content of the gas mixture. This results in a
lower combustion temperature, so decreases the
production of NOx.
As the demand for more exhaust gas increases the
electronically controlled actuator opens further. The
further opening of the actuator increases the flow of
exhaust gas from the exhaust gas valve. As the
demand for exhaust gas decreases, the electronically
controlled actuator closes. This decreases the flow of
exhaust gas from the exhaust gas valve.
The hot exhaust gas is then cooled in the exhaust
cooler (6). The cooled gas then travels from the
exhaust cooler (6) to the inlet manifold.
Exhaust gases from the exhaust manifold enter the
inlet of the turbocharger in order to turn the
turbocharger turbine wheel. The turbine wheel is
connected to a shaft that rotates. The exhaust gases
pass from the turbocharger through the following
components: exhaust outlet, Diesel Oxidation
Catalyst (DOC), Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) and
exhaust pipe.
14 UENR0623-02
Engine Operation
This document has been printed from SPI2. NOT FOR RESALE