- Pep Smart I/O User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Preface.pdf
- Introduction.pdf
- Table of Contents
- General Information
- Weights & Measures
- 1.1 Product Overview
- 1.2 Ordering Information
- 1.3 Product Information
- 1.4 Installation
- 1.4.1 Overview
- 1.4.2 SMART I/O Module Installation
- 1.4.3 RJ45 Telephone Connector Installation
- 1.4.4 Screw Terminal Block Installation
- 1.4.5 Battery Installation
- 1.5 ISaGRAF-Installation
- 1.5.1 Before Installing
- 1.5.2 Installation of the ISaGRAF for Windows Workbench
- 1.5.3 Installation of PEP Library Functions
- 1.5.4 Demo Application
- Table of Contents
- SM-BASE.pdf
- Table of Contents
- 2. SMART-BASE
- 2.1 Specifications
- 2.2 Board Overview
- 2.3 Functional Description
- 2.4 Configuration
- 2.4.1 Jumper J1: Boot Selection (Pin Connector)
- 2.4.2 Jumper J6: LED Function (Pin Connector)
- 2.5 Pinouts
- 2.5.1 SMART Module Piggyback Connectors
- 2.5.2 Screw Terminal Pinouts
- 2.5.3 Timer I/O Screw Terminal (SCR1)
- 2.5.4 Supply Screw Terminals (SCR2)
- 2.5.5 RS232 Telephone Connector (BU1)
- 2.5.6 RS485 D-Sub Connector for Half-Duplex Operation (Profibus)
- 2.5.7 SPI Connector (ST7)
- 2.6 ‘C’ Programming
- 2.6.1 SMART-BASE Library
- 2.6.2 SMTselIn
- 2.6.3 SMTsettout
- 2.6.4 SMTpre
- 2.6.5 SMTstasto
- 2.6.6 SMTrd
- 2.6.7 SMTtin
- 2.6.8 SMTstat
- 2.6.9 SMTout
- 2.6.10 SMLed
- 2.6.11 SMwdon
- 2.6.12 SMwdtrig
- 2.6.13 SMwdoff
- 2.7 ISaGRAF Programming
- 2.7.1 The ISaGRAF Board Parameters
- 2.7.2 The ISaGRAF Operate Calls
- 2.8 Flash Utility
- Table of Contents
- SM-EXT.pdf
- Digital.pdf
- Table of Contents
- 4. Digital Modules
- 4.1 SM-DIN1
- 4.1.1 Introduction
- 4.1.2 Specifications
- 4.1.3 Front Panel Layout
- 4.1.4 Board Overview
- 4.1.5 Functional Description
- 4.1.6 Configuration
- 4.1.7 Pinouts
- 4.1.8 ‘C’ Programming
- 4.1.8.1 SM-DIN1 Library
- 4.1.8.2 SMDIN1Init
- 4.1.8.3 SMDIN1DeInit
- 4.1.8.4 SMDIN1Get
- 4.1.9 ISaGRAF Programming
- 4.1.9.1 The ISaGRAF Board Parameters
- 4.1.9.2 The ISaGRAF Operate Calls
- 4.2 SM-DOUT1
- 4.2.1 Introduction
- 4.2.2 Specifications
- 4.2.3 Front Panel Layout
- 4.2.4 Board Overview
- 4.2.5 Functional Description
- 4.2.6 Configuration
- 4.2.7 Pinouts
- 4.2.8 ‘C’ Programming
- 4.2.8.1 SM-DOUT1 Library
- 4.2.8.2 SMDOUT1Init
- 4.2.8.3 SMDOUT1DeInit
- 4.2.8.4 SMDOUT1Get
- 4.2.8.5 SMDOUT1Set
- 4.2.9 ISaGRAF Programming
- 4.2.9.1 The ISaGRAF Board Parameters
- 4.2.9.2 The ISaGRAF Operate Calls
- 4.3 SM-REL1
- 4.3.1 Introduction
- 4.3.2 Specifications
- 4.3.3 Front Panel Layout
- 4.3.4 Board Overview
- 4.3.5 Functional Description
- 4.3.6 Configuration
- 4.3.7 Pinouts
- 4.3.8 ‘C’ Programming
- 4.3.8.1 SM-REL1 Library
- 4.3.8.2 SMREL1Init
- 4.3.8.3 SMREL1DeInit
- 4.3.8.4 SMREL1Reset
- 4.3.8.5 SMREL1GetRly
- 4.3.8.6 SMREL1SetRly
- 4.3.8.7 SMREL1GetLed
- 4.3.8.8 SMREL1SetLed
- 4.3.8.9 SMREL1GetExtVcc
- 4.3.9 ISaGRAF Programming
- 4.3.9.1 The ISaGRAF Board Parameters
- 4.3.9.2 The ISaGRAF Operate Calls
- Table of Contents
- Analog.pdf
- Table of Contents
- 5. Analog Modules
- 5.1 SM-DAD1
- 5.1.1 Introduction
- 5.1.2 Specifications
- 5.1.3 Front Panel Layout
- 5.1.4 Board Overview
- 5.1.5 Functional Description
- 5.1.5.1 Input Circuitry
- 5.1.5.2 Output Circuitry
- 5.1.6 Configuration
- 5.1.7 Pinouts
- 5.1.8 ‘C’ Programming
- 5.1.8.1 SM-DAD1 Library
- 5.1.8.2 SMDAD1Init
- 5.1.8.3 SMDAD1DeInit
- 5.1.8.4 SMDAD1GetVRaw
- 5.1.8.5 SMDAD1GetV
- 5.1.8.6 SMDAD1PutVRaw
- 5.1.8.7 SMDAD1PutV
- 5.1.8.8 SMDAD1SetLed
- 5.1.8.9 SMDAD1ClrLed
- 5.1.9 ISaGRAF Programming
- 5.1.9.1 The ISaGRAF Board Parameters
- 5.1.9.2 The ISaGRAF Operate Calls
- 5.2 SM-PT100
- 5.2.1 Introduction
- 5.2.2 Specifications
- 5.2.3 Front Panel Layout
- 5.2.4 Board Overview
- 5.2.5 Functional Description
- 5.2.6 Configuration
- 5.2.7 Pinouts
- 5.2.8 ‘C’ Programming
- 5.2.8.1 SM-PT100 Library
- 5.2.8.2 SMADCInit
- 5.2.8.3 SMADCCalibrate
- 5.2.8.4 SMADCSetCyclicCalib
- 5.2.8.5 SMADCSetSensorType
- 5.2.8.6 SMADCGetSensorType
- 5.2.8.7 SMADCSetPrecision
- 5.2.8.8 SMADCGetPrecision
- 5.2.8.9 SMADCSetMode
- 5.2.8.10 SMADCGetMode 5-47
- 5.2.8.11 SMADCSetSignal
- 5.2.8.12 SMADCSetGain
- 5.2.8.13 SMADCGetGain
- 5.2.8.14 SMADCEnableRead
- 5.2.8.15 SMADCEnableConversion
- 5.2.8.16 SMADCReadRaw
- 5.2.8.17 SMADCReadConverted
- 5.2.8.18 SMADCDeinit
- 5.2.9 ISaGRAF Programming
- 5.2.9.1 The ISaGRAF Board Parameters
- 5.2.9.2 The ISaGRAF Operate Calls
- 5.3 SM-THERM
- 5.3.1 Introduction
- 5.3.2 Specifications
- 5.3.3 Front Panel Layout
- 5.3.4 Board Overview
- 5.3.5 Functional Description
- 5.3.6 Configuration
- 5.3.7 Pinouts
- 5.3.8 ‘C’ Programming
- 5.3.8.1 SM-THERM Library
- 5.3.8.2 SMADCInit
- 5.3.8.3 SMADCCalibrate
- 5.3.8.4 SMADCSetCyclicCalib
- 5.3.8.5 SMADCSetSensorType
- 5.3.8.6 SMADCGetSensorType
- 5.3.8.7 SMADCSetPrecision
- 5.3.8.8 SMADCGetPrecision
- 5.3.8.9 SMADCSetMode 5-75
- 5.3.8.10 SMADCGetMode
- 5.3.8.11 SMADCSetSignal
- 5.3.8.12 SMADCSetGain
- 5.3.8.13 SMADCGetGain
- 5.3.8.14 SMADCEnableRead
- 5.3.8.15 SMADCEnableConversion
- 5.3.8.16 SMADCReadRaw
- 5.3.8.17 SMADCReadConverted
- 5.3.8.18 SMADCDeinit
- 5.3.9 ISaGRAF Programming
- 5.3.9.1 The ISaGRAF Board Parameters
- 5.3.9.2 The ISaGRAF Operate Calls
- 5.4 SM-ADC1
- 5.4.1 Introduction
- 5.4.2 Specifications
- 5.4.3 Front Panel Layout
- 5.4.4 Board Overview
- 5.4.5 Functional Description
- 5.4.5.1 Input Circuitry
- 5.4.6 Configuration
- 5.4.7 Pinouts
- 5.4.8 ‘C’ Programming
- 5.4.8.1 SM-ADC1 Library
- 5.4.8.2 SMADC1Init
- 5.4.8.3 SMADC1GetVRaw
- 5.4.8.4 SMADC1GetV
- 5.4.8.5 SMADC1SetLed
- 5.4.8.6 SMADC1ClrLed
- 5.4.8.7 SMADC1DeInit
- 5.4.9 ISaGRAF Programming
- 5.4.9.1 The ISaGRAF Board Parameters
- 5.4.9.2 The ISaGRAF Operate Calls
- 5.5 SM-DAC1
- 5.5.1 Introduction
- 5.5.2 Specifications
- 5.5.3 Front Panel Layout
- 5.5.4 Board Overview
- 5.5.5 Functional Description
- 5.5.5.1 Output Circuitry
- 5.5.6 Configuration
- 5.5.7 Pinouts
- 5.5.8 ‘C’ Programming
- 5.5.8.1 SM-DAC1 Library
- 5.5.8.2 SMDAC1Init
- 5.5.8.3 SMDAC1OpenLoop
- 5.5.8.4 SMADAC1Operate
- 5.5.8.5 SMDAC1StandBy
- 5.5.8.6 SMDAC1PutVRaw
- 5.5.8.7 SMDAC1PutV
- 5.5.8.8 SMDAC1SetLed
- 5.5.8.9 SMDAC1ClrLed
- 5.5.8.10 SMDAC1DeInit
- 5.5.9 ISaGRAF Programming
- 5.5.9.1 The ISaGRAF Board Parameters
- 5.5.9.2 The ISaGRAF Operate Calls
- Table of Contents
- Comms.pdf
- Table of Contents
- 6. Communications Modules
- 6.1 SM-RS232 6
- 6.1.1 Introduction
- 6.1.2 Specifications
- 6.1.3 Front Panel Layout
- 6.1.4 Board Overview
- 6.1.5 Functional Description
- 6.1.6 Configuration
- 6.1.7 Pinouts
- 6.1.8 ISaGRAF Programming
- 6.1.8.1 The ISaGRAF Board Parameters
- 6.1.8.2 The ISaGRAF Operate Calls
- 6.1.9 OS-9 Programming
- 6.2 SM-SSI
- 6.2.1 Introduction
- 6.2.2 Specifications
- 6.2.3 Front Panel Layout
- 6.2.4 Board Overview
- 6.2.5 Functional Description
- 6.2.6 SSI Operation
- 6.2.7 Register Description
- 6.2.7.1 Control Register
- 6.2.7.2 CTRL1 Register
- 6.2.7.3 CTRL2 Register
- 6.2.7.4 CTRL3 Register
- 6.2.7.5 Compare Register
- 6.2.7.6 Identification Register
- 6.2.7.7 Status Register
- 6.2.7.8 STAT1 Register
- 6.2.7.9 STAT2 Register
- 6.2.7.10 Data Register
- 6.2.8 MATCH Function
- 6.2.9 Tested Sensors
- 6.2.10 Configuration
- 6.2.11 Pinouts
- 6.2.12 ‘C’ Programming
- 6.2.12.1 SM-SSI Library
- 6.2.12.2 SMSSIInit
- 6.2.12.3 SMSSIDeInit
- 6.2.12.4 SMSSISetSetPoint
- 6.2.12.5 SMSSISetCtrlReg
- 6.2.12.6 SMSSIGetStatus
- 6.2.12.7 SMSSIGetData
- 6.2.13 ISaGRAF Programming
- 6.2.13.1 The ISaGRAF Board Parameters
- Table of Contents
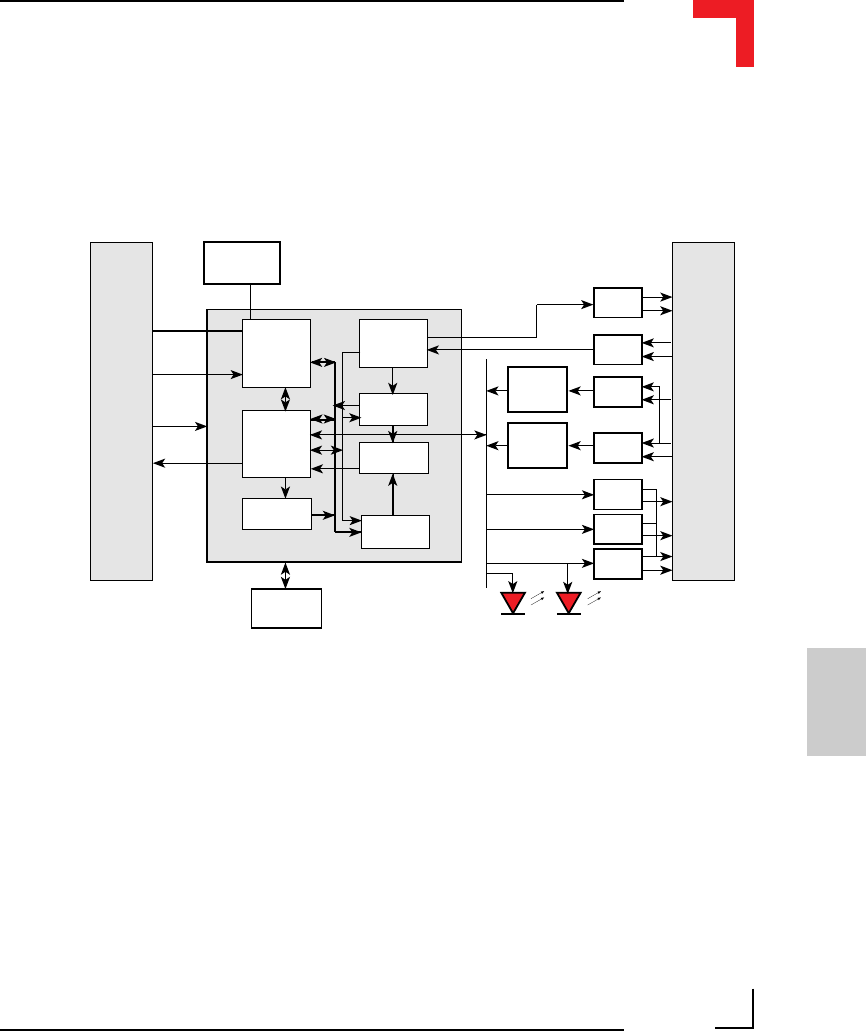
SMART I/O User’s Manual
©1996 PEP Modular Computers GmbHOctober 01, 1996 Page 6 - 19
6
Chapter 6 Communications Modules
6.2.5 Functional Description
Figure 6.2.5.1: SM-SSI Schematic Diagram
The Synchronous Serial Interface working together with a photographically
etched encoder disk allows absolute codes (positions) of rotating axis to be
continuously monitored. The greatest advantage of the SSI communication
process compared to that of standard serial/parallel procedures is that the
controller actually regulates the timing and speed of the data transmission
which further optimizes data security.
Simplicity in design with low conventional component count coupled with
the inherent safety offered through accurate axis position reading even after
power fail, enable this compact module to be utilized for equipment operat-
ing even in extreme environmental conditions.
SSI
Interface
Comparator
Comp. Value
(24-bit)
Configuration
Control
Logic
+
Status
Board ID
Last Value
(24-bit)
OPTO
OPTO
OPTO
OPTO
OPTO
OPTO
OPTO
RC +
Schmitt
RC +
Schmitt
SPROM
LED 1
Match
BU1
Analog
SSI
End of
range
switches
Encoder
Control
Match
FPGA
LED 0
Data Flow
Data
SPI Bus
P1-5
Clock +
Clock -
Data +
Data -
EOR1
EORCOM2
EOR2
Direction
Reset
Com+
BU1
SPI
I/O
Lines
Reset
Line
Int
Line
VCC
GND
STXD
SRXD
SCLK
SCS
NRESET
NINT
SPI
Interface
+
Selection
Decoder
EEPROM










