User Guide
Table Of Contents
- Intended Audience
- Revision History
- Introducing Fraud Management Filters
- Setting Up Fraud Management Filters
- Using Fraud Management Filters
- Customizing Websites to use Fraud Management Filters
- Fraud Management Filters Summary
- Fraud Management Filters Operating Principles
- Index
Fraud Management Filters June 23, 2009 7
1
Introducing Fraud Management
Filters
PayPal Fraud Management Filters enable you to identify potentially fraudulent transactions.
You must configure Fraud Management Filters to meet your needs; they are not active until
you configure them.
z Fraud Management Filters Overview
z Fraud Management Filters Examples
z Merchants With Third-Party Shopping Carts
Fraud Management Filters Overview
PayPal provides many Fraud Management Filters, which make it easier for you to detect and
respond to fraudulent transactions. You must configure the filters before they take effect.
Fraud management filters (FMF) provide you with tools, called filters, that can identify
potentially fraudulent transactions. The kinds of filters can be divided into the following
categories:
z Basic filters include filters that screen against the country of origin, the value of
transactions, and such. PayPal provides basic filters for business accounts and Website
Payments Pro accounts.
z Advanced filters include filters that screen credit card and addresses information, filters
that screen against lists of high-risk indicators, and filters that screen additional transaction
characteristics. Website Payments Pro merchants can upgrade to use advanced filters.
NOTE: Using advanced filters may incur additional charges.
Fraud Management Filters checks for payment characteristics that may indicate fraudulent
activity. You set up Fraud Management Filters to provide the tightest control possible over
payments so that you can deny payments that are likely to result in fraudulent transactions and
accept payments that are not typically a problem. Payments that may require further
investigation or intervention, such as comparing prior orders or contacting the customer for
more information, can be flagged or put on hold or pended for review.
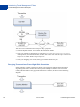
The following diagram, conceptually shows how Fraud Management Filters work in three
steps: